Abstract
Background
Behavioral disorders, such as supragastric belching (SGB) and rumination syndrome (RS), which may be treated by cognitive behavioral therapy, are common in patients with reflux symptoms refractory to proton pump inhibitors (PPI). Vonoprazan (VPZ) has been used as a new type of acid inhibitor in Japan since 2015. We herein investigated the prevalence of behavioral disorders in patients with VPZ-refractory reflux symptoms and attempted to identify predictive factors.
Methods
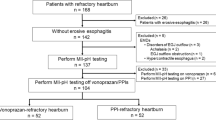
We retrospectively analyzed esophagogastroduodenograms, high-resolution manometry, and 24-h multiluminal impedance pH-metry (MIIpH) in patients with VPZ-refractory reflux symptoms (heartburn or regurgitation) receiving 20 mg VPZ who underwent these tests at our hospital between January 2015 and April 2020. Patients were divided as follows: non-erosive reflux disease with pathological esophageal acid exposure (NERD), functional heartburn (FH), reflux hypersensitivity (RH), excessive (> 13 per day) SGB, and possible RS based on MIIpH parameters.
Results
Among 49 patients, 6 (12.2%) had SGB, 4 (8.2%) possible RS, 29 (59.2%) FH, 9 (18.4%) RH, and 1 (2%) NERD. Possible RS patients had more postprandial non-acid reflux events than FH patients (p < 0.05). The multivariate logistic regression analysis did not identify any predictive factors with statistical significance.
Conclusion
More than 20% patients with VPZ-refractory reflux symptoms had behavioral disorders. The use of HRM and MIIpH may be clinically relevant for a better diagnosis and more specific treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gyawali CP, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E, et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: the Lyon Consensus. Gut. 2018;67:1351–62.
Cicala M, Emerenziani S, Guarino MPL, et al. Proton pump inhibitor resistance, the real challenge in gastro-esophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:6529–35.
Delshad SD, Almario CV, Chey WD, et al. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and proton pump inhibitor-refractory symptoms. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(1250–1261):e2.
Aziz Q, Fass R, Gyawali CP, et al. Esophageal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1368–79.
Herregods TVK, Troelstra M, Weijenborg PW, et al. Patients with refractory reflux symptoms often do not have GERD. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27:1267–73.
Ribolsi M, Cicala M, Zentilin P, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of refractoriness to optimal proton pump inhibitor therapy in non-erosive reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;48:1074–81.
Scarpellini E, Ang D, Pauwels A, et al. Management of refractory typical GERD symptoms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:281–94.
Yadlapati R, Tye M, Roman S, et al. Postprandial high-resolution impedance manometry identifies mechanisms of nonresponse to proton pump inhibitors. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(211–218):e1.
Sawada A, Guzman M, Nikaki K, et al. Identification of different phenotypes of esophageal reflux hypersensitivity and implications for treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.063.
Sawada A, Itami H, Nakagawa K, et al. Supragastric belching in Japan: lower prevalence and relevance for management of gastroesophageal reflux disease compared to United Kingdom. J Gastroenterol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-020-01720-9.
Glasinovic E, Wynter E, Arguero J, et al. Treatment of supragastric belching with cognitive behavioral therapy improves quality of life and reduces acid gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:539–47.
Barba E, Burri E, Accarino A, et al. Biofeedback-guided control of abdominothoracic muscular activity reduces regurgitation episodes in patients with rumination. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:100-106.e1.
Halland M, Parthasarathy G, Bharucha AE, et al. Diaphragmatic breathing for rumination syndrome: efficacy and mechanisms of action. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016;28:384–91.
Jenkins H, Sakurai Y, Nishimura A, et al. Randomised clinical trial: safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repeated doses of TAK-438 (vonoprazan), a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, in healthy male subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:636–48.
Sakurai Y, Mori Y, Okamoto H, et al. Acid-inhibitory effects of vonoprazan 20 mg compared with esomeprazole 20 mg or rabeprazole 10 mg in healthy adult male subjects—a randomised open-label cross-over study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42:719–30.
Ashida K, Sakurai Y, Nishimura A, et al. Randomised clinical trial: a dose-ranging study of vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vs. lansoprazole for the treatment of erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42:685–95.
Ashida K, Sakurai Y, Hori T, et al. Randomised clinical trial: Vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vslansoprazole for the healing of erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:240–51.
Hoshino S, Kawami N, Takenouchi N, et al. Efficacy of vonoprazan for proton pump inhibitor-resistant reflux esophagitis. Digestion. 2017;95:156–61.
Kinoshita Y, Sakurai Y, Shiino M, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of vonoprazan in patients with nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2016;81–82:1–7.
Kusano M, Shimoyama Y, Sugimoto S, et al. Development and evaluation of FSSG: frequency scale for the symptoms of GERD. J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:888–91.
Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, et al. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27:160–74.
Hanada Y, Hoshino S, Hoshikawa Y, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis of hiatus hernia under deep inspiration is not consistent with esophageal manometric diagnosis. J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:712–7.
Kuribayashi S, Iwakiri K, Shinozaki T, et al. Clinical impact of different cut-off values in high-resolution manometry systems on diagnosing esophageal motility disorders. J Gastroenterol. 2019;54:1078–82.
Sifrim D, Castell D, Dent J, et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux monitoring: review and consensus report on detection and definitions of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut. 2004;53:1024–31.
Nakagawa K, Sawada A, Hoshikawa Y, et al. Persistent postprandial regurgitation vs rumination in patients with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: identification of a distinct rumination pattern using ambulatory impedance-pH monitoring. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114:1248–55.
de Bortoli N, Martinucci I, Savarino E, et al. Proton pump inhibitor responders who are not confirmed as GERD patients with impedance and pH monitoring: who are they? Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014;26:28–35.
Vakil N, Van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, et al. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–20.
Bredenoord AJ, Weusten BLAM, Sifrim D, et al. Aerophagia, gastric, and supragastric belching: a study using intraluminal electrical impedance monitoring. Gut. 2004;53:1561–5.
Koukias N, Woodland P, Yazaki E, et al. Supragastric belching: Prevalence and association with gastroesophageal reflux disease and esophageal hypomotility. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;21:398–403.
Kessing BF, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJPM. Objective manometric criteria for the rumination syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:52–9.
Kanda Y. Statistical analysis using freely-available “EZR (Easy R)” software. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2015;56:2258–66.
Fletcher J, Wirz A, Young J, et al. Unbuffered highly acidic gastric juice exists at the gastroesophageal junction after a meal. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:775–83.
Frazzoni L, Frazzoni M, De Bortoli N, et al. Critical appraisal of Rome IV criteria: hypersensitive esophagus does belong to gastroesophageal reflux disease spectrum. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018;31:1–7.
Frazzoni M, de Bortoli N, Frazzoni L, et al. Impairment of chemical clearance and mucosal integrity distinguishes hypersensitive esophagus from functional heartburn. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52:444–51.
Stanghellini V, Hasler WL, Malagelada JR, et al. Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1380–92.
Ooi JLS, Vardar R, Sifrim D. Supragastric belching. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2016;32:302–9.
Halland M, Pandolfino J, Barba E. Diagnosis and treatment of rumination syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16:1549–55.
Thumshirn M, Camilleri M, Hanson RB, et al. Gastric mechanosensory and lower esophageal sphincter function in rumination syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1998;275:G314–21.
Hoshikawa Y, Fitzke H, Sweis R, et al. Rumination syndrome: assessment of vagal tone during and after meals and during diaphragmatic breathing. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13873.
Barba E, Accarino A, Soldevilla A, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of biofeedback for the treatment of rumination. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:1007–13.
Takahashi N, Take Y. Tegoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker to control gastric acid secretion and motility. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018;364:275–86.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. Satoko Nishimura for her administrative assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YH contributed to the study conception and design, analyzed clinical tests, performed statistical analyses, and wrote the draft. SH and NK performed and analyzed the clinical tests. KI contributed to the study conception and design and wrote the draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Katsuhiko Iwakiri has received lecture fees from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoshikawa, Y., Hoshino, S., Kawami, N. et al. Prevalence of behavioral disorders in patients with vonoprazan-refractory reflux symptoms. J Gastroenterol 56, 117–124 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-020-01751-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-020-01751-2