Abstract
Background
The optimal therapy for recurrent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection after liver transplantation has not yet been established. This study aimed to clarify the efficacy and safety of interferon-free therapy with sofosbuvir and ledipasvir without ribavirin for 12 weeks in Japanese patients with HCV genotype 1b infection after living donor liver transplantation.
Methods
A cohort study of living donor liver transplant recipients with recurrent HCV genotype 1b infection treated with sofosbuvir (400 mg/day) and ledipasvir (90 mg/day) was performed at six liver transplant centers in Japan.
Results
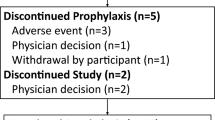
Fifty-four patients were treated with sofosbuvir and ledipasvir. Thirty-eight patients (70%) were treatment experienced, including 17 patients who had undergone prior direct-acting-antiviral-based triple therapy. Ten patients had resistance-associated substitutions at L31 or Y93 in the NS5A region of the HCV genome. Fifty-three patients completed the 12-week treatment protocol; treatment was discontinued in one patient who developed pneumonia at 4 weeks and died thereafter. All 53 patients who completed the treatment regimen achieved a sustained virological response 12 weeks after completion of treatment. Treatment was well tolerated in most patients, but seven patients developed serious adverse events, including hemorrhagic duodenal ulcers (n = 3), infection (n = 2), pleural effusion (n = 1), and alveolar hemorrhage (n = 1).
Conclusions
Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir treatment without ribavirin for 12 weeks was highly effective in achieving a sustained virological response in Japanese patients who developed recurrent HCV genotype 1b infection after living donor liver transplantation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAA:
-
Direct-acting antiviral
- ETR:
-
End-of treatment response
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- LDLT:
-
Living donor liver transplantation
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PPI:
-
Proton pump inhibitor
- RVR:
-
Rapid virological response
- SVR:
-
Sustained virological response
- SVR12:
-
Sustained virological response at 12 weeks
References
Berenguer M, Schuppan D. Progression of liver fibrosis in post-transplant hepatitis C: mechanisms, assessment and treatment. J Hepatol. 2013;58(5):1028–41.
Terrault N. Liver transplantation in the setting of chronic HCV. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26(4):531–48.
Ueda Y, Uemoto S. Interferon-free therapy for hepatitis C in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2016;100(1):54–60.
AASLD/IDSA HCV Guidance Panel. Hepatitis C guidance: AASLD-IDSA recommendations for testing, managing, and treating adults infected with hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2015;62(3):932–54.
Kumada H, Suzuki Y, Ikeda K, et al. Daclatasvir plus asunaprevir for chronic HCV genotype 1b infection. Hepatology. 2014;59(6):2083–91.
Ueda Y, Uemoto S. Decreased tacrolimus concentration following a temporal increase during interferon-free therapy with asunaprevir and daclatasvir in patients with recurrent hepatitis C after liver transplantation. Transpl Int. 2016;29(1):119–21.
Ohno O, Mizokami M, Wu RR, et al. New hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotyping system that allows for identification of HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4, 5a, and 6a. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35(1):201–7.
Charlton M, Everson GT, Flamm SL, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for treatment of HCV infection in patients with advanced liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(3):649–59.
Manns M, Samuel D, Gane EJ, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir plus ribavirin in patients with genotype 1 or 4 hepatitis C virus infection and advanced liver disease: a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(6):685–97.
Brown RS Jr, O’Leary JG, Reddy KR, et al. Interferon-free therapy for genotype 1 hepatitis C in liver transplant recipients: real-world experience from the hepatitis C therapeutic registry and research network. Liver Transplant. 2016;22(1):24–33.
Crittenden NE, Buchanan LA, Pinkston CM, et al. Simeprevir and sofosbuvir with or without ribavirin to treat recurrent genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2016;22(5):635–43.
Gutierrez JA, Carrion AF, Avalos D, et al. Sofosbuvir and simeprevir for treatment of hepatitis C virus infection in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplant. 2015;21(6):823–30.
Jackson WE, Hanouneh M, Apfel T, et al. Sofosbuvir and simeprevir without ribavirin effectively treat hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection after liver transplantation in a two-center experience. Clin Transplant. 2016;30(6):709–13.
Pungpapong S, Aqel B, Leise M, et al. Multicenter experience using simeprevir and sofosbuvir with or without ribavirin to treat hepatitis C genotype 1 after liver transplant. Hepatology. 2015;61(6):1880–6.
Saab S, Greenberg A, Li E, et al. Sofosbuvir and simeprevir is effective for recurrent hepatitis C in liver transplant recipients. Liver Int. 2015;35(11):2442–7.
Coilly A, Fougerou-Leurent C, de Ledinghen V, et al. Multicentre experience using daclatasvir and sofosbuvir to treat hepatitis C recurrence—the ANRS CUPILT study. J Hepatol. 2016;65(4):711–8.
Afdhal N, Reddy KR, Nelson DR, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for previously treated HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(16):1483–93.
Afdhal N, Zeuzem S, Kwo P, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(20):1889–98.
Kowdley KV, Gordon SC, Reddy KR, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for 8 or 12 weeks for chronic HCV without cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(20):1879–88.
Mizokami M, Yokosuka O, Takehara T, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination with and without ribavirin for 12 weeks in treatment-naive and previously treated Japanese patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C: an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(6):645–53.
Tapper EB, Bacon BR, Curry MP, et al. Evaluation of proton pump inhibitor use on treatment outcomes with ledipasvir and sofosbuvir in a real-world cohort study. Hepatology. 2016;64:1893–9.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Research Program on Hepatitis from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, Y., Ikegami, T., Akamatsu, N. et al. Treatment with sofosbuvir and ledipasvir without ribavirin for 12 weeks is highly effective for recurrent hepatitis C virus genotype 1b infection after living donor liver transplantation: a Japanese multicenter experience. J Gastroenterol 52, 986–991 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-017-1310-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-017-1310-9