Abstract
Background
Tight junctions play a critical role in the maintenance of intestinal barrier function. Partitioning-defective protein 3 (Par-3) can regulate intestinal barrier function through the modulation of tight junction assembly and cell polarity. However, the mechanisms are still not fully understood.
Methods
Adult C57BL/6 mice were treated with dextran sulfate sodium for 7 days, and segments of colon were harvested for immunofluorescent staining of Par-3. Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells were treated with tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) for 24 h, and Par-3 expression was detected by Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence. Additionally, Caco-2 cells were treated with Par-3 small interfering RNA, and altered expression and subcellular localization of tight junction proteins were studied by Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence. Furthermore, the interaction between Par-3 and myosin light chain (MLC) was detected by immunoprecipitation.
Results
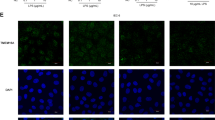
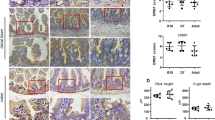
Par-3 was downregulated in murine dextran sulfate sodium induced acute inflammation and TNF-α-treated Caco-2 cells. Depletion of Par-3 expression by small interfering RNA delayed intestinal epithelial barrier development in Caco-2 cells. This regulation was due to the redistribution of the tight junction protein occludin rather than the altered total levels of tight junction proteins. Par-3 silencing blocked the trafficking of occludin from or through the Golgi complex to the cell surface, and dramatically induced occludin accumulated at the Golgi complex. Importantly, Par-3 can interact with MLC, and loss of Par-3 upregulated MLC kinase expression and MLC phosphorylation, which contributed to intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction.
Conclusions
These results indicate that Par-3 plays an important role in the modulation of intestinal barrier function by regulating delivery of occludin as well as suppression of MLC phosphorylation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham KE, Turner JR. Myosin light chain kinase: pulling the strings of epithelial tight junction function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1258:34–42.
Nusrat A, Turner JR, Madara JL. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. IV. Regulation of tight junctions by extracellular stimuli: nutrients, cytokines, and immune cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G851–7.
Turner JR. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application. Am J Pathol. 2006;169:1901–9.
Visser J, Rozing J, Sapone A, et al. Tight junctions, intestinal permeability, and autoimmunity: celiac disease and type 1 diabetes paradigms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1165:195–205.
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, et al. Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003;81:1–44.
Paris L, Tonutti L, Vannini C, et al. Structural organization of the tight junctions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778:646–59.
Shin K, Fogg VC, Margolis B. Tight junctions and cell polarity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:207–35.
Mankertz J, Schulzke JD. Altered permeability in inflammatory bowel disease: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007;23:379–83.
Stallmach A, Giese T, Schmidt C, et al. Cytokine/chemokine transcript profiles reflect mucosal inflammation in Crohn’s disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004;19:308–15.
Andoh A, Yagi Y, Shioya M, et al. Mucosal cytokine network in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:5154–61.
Bruewer M, Luegering A, Kucharzik T, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines disrupt epithelial barrier function by apoptosis-independent mechanisms. J Immunol. 2003;171:6164–72.
Koch S, Nusrat A. Dynamic regulation of epithelial cell fate and barrier function by intercellular junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1165:220–7.
Marano CW, Lewis SA, Garulacan LA, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases sodium and chloride conductance across the tight junction of CACO-2 BBE, a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Membr Biol. 1998;161:263–74.
Youakim A, Ahdieh M. Interferon-γ decreases barrier function in T84 cells by reducing ZO-1 levels and disrupting apical actin. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:G1279–88.
Bruewer M, Utech M, Ivanov AI, et al. Interferon-gamma induces internalization of epithelial tight junction proteins via a macropinocytosis-like process. FASEB J. 2005;19:923–33.
Yang S, Yu M, Sun L, et al. Interferon-γ-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014;34:195–203.
Schumann M, Gunzel D, Buergel N, et al. Cell polarity-determining proteins Par-3 and PP-1 are involved in epithelial tight junction defects in coeliac disease. Gut. 2012;61:220–8.
Joberty G, Petersen C, Gao L, et al. The cell-polarity protein Par-6 links Par-3 and atypical protein kinase C to Cdc42. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:531–9.
Wapenaar MC, Monsuur AJ, van Bodegraven AA, et al. Associations with tight junction genes PARD3 and MAGI2 in Dutch patients point to a common barrier defect for coeliac disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2008;57:463–7.
Chen X, Macara IG. Par-3 controls tight junction assembly through the Rac exchange factor Tiam1. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:262–9.
Wells CL, van de Westerlo EM, Jechorek RP, et al. Cytochalasin-induced actin disruption of polarized enterocytes can augment internalization of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1998;66:2410–9.
Melgar S, Karlsson L, Rehnstrom E, et al. Validation of murine dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis using four therapeutic agents for human inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008;8:836–44.
Fries W, Muja C, Crisafulli C, et al. Dynamics of enterocyte tight junctions: effect of experimental colitis and two different anti-TNF strategies. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;294:G938–47.
Suenaert P, Bulteel V, Lemmens L, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment restores the gut barrier in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(8):2000–4.
Marchiando AM, Shen L, Graham WV, et al. Caveolin-1-dependent occludin endocytosis is required for TNF-induced tight junction regulation in vivo. J Cell Biol. 2010;189:111–26.
Al-Sadi R, Boivin M, Ma T. Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier. Front Biosci Landmark Ed. 2009;14:2765–78.
Shen L, Black ED, Witkowski ED, et al. Myosin light chain phosphorylation regulates barrier function by remodeling tight junction structure. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:2095–106.
Chen J, Zhang M. The Par-3/Par-6/aPKC complex and epithelial cell polarity. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319:1357–64.
Gopalakrishnan S, Hallett MA, Atkinson SJ, et al. aPKC-PAR complex dysfunction and tight junction disassembly in renal epithelial cells during ATP depletion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C1094–102.
McCaffrey LM, Montalbano J, Mihai C, et al. Loss of the Par-3 polarity protein promotes breast tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:601–14.
Nighot PK, Blikslager AT. Chloride channel ClC-2 modulates tight junction barrier function via intracellular trafficking of occludin. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012;302:C178–87.
Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, et al. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1996;134:1031–49.
Yu AS, McCarthy KM, Francis SA, et al. Knockdown of occludin expression leads to diverse phenotypic alterations in epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;288:C1231–41.
McCarthy KM, Skare IB, Stankewich MC, et al. Occludin is a functional component of the tight junction. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:2287–98.
Wong V, Gumbiner BM. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the extracellular domain of occludin perturbs the tight junction permeability barrier. J Cell Biol. 1997;136:399–409.
Saitou M, Furuse M, Sasaki H, et al. Complex phenotype of mice lacking occludin, a component of tight junction strands. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:4131–42.
Raleigh DR, Marchiando AM, Zhang Y, et al. Tight junction-associated MARVEL proteins marveld3, tricellulin, and occludin have distinct but overlapping functions. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:1200–13.
Ivanov AI, Nusrat A, Parkos CA. Endocytosis of epithelial apical junctional proteins by a clathrin-mediated pathway into a unique storage compartment. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:176–88.
Shen L, Turner JR. Actin depolymerization disrupts tight junctions via caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:3919–36.
Kienzle C, von Blume J. Secretory cargo sorting at the trans-Golgi network. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24:584–93.
Wakana Y, van Galen J, Meissner F, et al. A new class of carriers that transport selective cargo from the trans Golgi network to the cell surface. EMBO J. 2012;31:3976–90.
Jin Y, Atkinson SJ, Marrs JA, et al. Myosin II light chain phosphorylation regulates membrane localization and apoptotic signaling of tumor necrosis factor receptor-1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:30342–9.
Matsui T, Watanabe T, Matsuzawa K, et al. PAR-3 and aPKC regulate Golgi organization through CLASP2 phosphorylation to generate cell polarity. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26:751–61.
Odell AF, Hollstein M, Ponnambalam S, et al. A VE-cadherin–PAR-3–α-catenin complex regulates the Golgi localization and activity of cytosolic phospholipase A2α in endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23:1783–96.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81330013 and NSFC 81272078 to H.Y., NSFC 81200288 to W.S.W., NSFC 81270451 to W.DX.), and the Program of Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research (IRT 13050 to H.Y.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Yang, S., Qiu, Y. et al. Par-3 modulates intestinal epithelial barrier function through regulating intracellular trafficking of occludin and myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Gastroenterol 50, 1103–1113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-015-1066-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-015-1066-z