Abstract
Background
The Glasgow prognostic score (GPS) is a preoperatively determined inflammation-based score. Reports suggest a significant correlation between the GPS and prognosis in several cancer types. We aimed to clarify the prognostic significance of the modified GPS (mGPS) in patients undergoing gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Methods
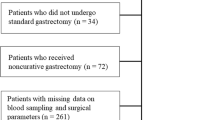
Two hundred and ninety-four patients with gastric cancer, 195 aged < 75 years (group NE) and 99 aged > 75 years (group E), who underwent gastrectomy from March 2005 to March 2011 were enrolled. Patients with an elevated C-reactive protein level (> 0.5 mg/dL) and hypoalbuminemia (< 3.8 g/dL) were assigned a mGPS of 2, those with either 1 abnormality were assigned a mGPS of 1, and those with neither abnormality were assigned a mGPS of 0. Cox proportional hazard models and Kaplan–Meier analysis were used to evaluate the usefulness of mGPS as a prognostic indicator.
Results
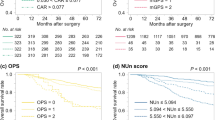
In the NE group, the prognosis of the 3 groups stratified by mGPS did not differ significantly. In multivariate Cox regression analysis, the type of gastrectomy, peritoneal metastasis, and stage were independently associated with poor prognosis. However, group E patients with a mGPS of 2 had significantly poorer prognosis than those with a mGPS of 0 or 1. In this age group, stage and mGPS were independently associated with poor prognosis.
Conclusions
In patients aged > 75 years undergoing potentially curative gastrectomy, the preoperative mGPS was an independent predictor of survival. Therefore, mGPS can be a useful prognostic indicator in elderly patients with gastric cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roder DM. The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2002;5:5–11.
Saito H, Osaki T, Murakami D, Sakamoto T, Kanaji S, Tatebe S, et al. Effect of age on prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. ANZ J Surg. 2006;76:458–61.
Saif MW, Makrilia N, Zalonis A, Merikas M, Syrigos K. Gastric cancer in the elderly: an overview. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010;36:709–17.
Watanabe M, Iwatsuki M, Iwagami S, Ishimoto T, Baba Y, Baba H. Prognostic nutritional index predicts outcomes of gastrectomy in the elderly. World J Surg. 2012;36:1632–9.
Watanabe M, Miyata H, Gotoh M, Baba H, Kimura W, Tomita N, et al. Total gastrectomy risk model: data from 20,011 Japanese patients in a nationwide internet-based database. Ann Surg. 2013; in press.
Mahmoud FA, Rivera NI. The role of C-reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in advanced cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2002;4:250–5.
Crumley AB, McMillan DC, McKernan M, McDonald AC, Stuart RC. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score in patients with inoperable gastro-oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:637–41.
Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:448–54.
Hwang JE, Kim HN, Kim DE, Choi HJ, Jung SH, Shim HJ, et al. Prognostic significance of a systemic inflammatory response in patients receiving first-line palliative chemotherapy for recurred or metastatic gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:489.
Lamb GW, Aitchison M, Ramsey S, Housley SL, McMillan DC. Clinical utility of the Glasgow Prognostic Score in patients undergoing curative nephrectomy for renal clear cell cancer: basis of new prognostic scoring systems. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:279–83.
Tartour E, Dorval T, Mosseri V, Deneux L, Mathiot C, Brailly H, et al. Serum interleukin 6 and C-reactive protein levels correlate with resistance to IL-2 therapy and poor survival in melanoma patients. Br J Cancer. 1994;69:911–3.
Ishizuka M, Nagata H, Takagi K, Horie T, Kubota K. Inflammation-based prognostic score is a novel predictor of postoperative outcome in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2007;246:1047–51.
Sharma R, Zucknick M, London R, Kacevska M, Liddle C, Clarke SJ. Systemic inflammatory response predicts prognosis in patients with advanced-stage colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2008;7:331–7.
Moyes LH, Leitch EF, McKee RF, Anderson JH, Horgan PG, McMillan DC. Preoperative systemic inflammation predicts postoperative infectious complications in patients undergoing curative resection for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:1236–9.
Kobayashi T, Teruya M, Kishiki T, Endo D, Takenaka Y, Tanaka H, et al. Inflammation-based prognostic score, prior to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, predicts postoperative outcome in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 2008;144:729–35.
Glen P, Jamieson NB, McMillan DC, Carter R, Imrie CW, McKay CJ. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score in patients with inoperable pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2006;6:450–3.
Nozoe T, Iguchi T, Egashira A, Adachi E, Matsukuma A, Ezaki T. Significance of modified Glasgow prognostic score as a useful indicator for prognosis of patients with gastric carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2011;201:186–91.
Dutta S, Al-Mrabt NM, Fullarton GM, Horgan PG, McMillan DC. A comparison of POSSUM and GPS models in the prediction of post-operative outcome in patients undergoing oesophago-gastric cancer resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:2808–17.
Japanese Gastric Cancer A. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edition. Gastric Cancer. 2011;14:101–12.
Japanese Gastric Cancer A. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2010 (ver. 3). Gastric Cancer. 2011;14:113–23.
Roxburgh CS, McMillan DC. Role of systemic inflammatory response in predicting survival in patients with primary operable cancer. Future Oncol. 2010;6:149–63.
La Torre M, Nigri G, Cavallini M, Mercantini P, Ziparo V, Ramacciato G. The Glasgow prognostic score as a predictor of survival in patients with potentially resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:2917–23.
Du Clos TW. Function of C-reactive protein. Ann Med. 2000;32:274–8.
Legouffe E, Rodriguez C, Picot MC, Richard B, Klein B, Rossi JF, et al. C-reactive protein serum level is a valuable and simple prognostic marker in non Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 1998;31:351–7.
Crumley AB, Stuart RC, McKernan M, McDonald AC, McMillan DC. Comparison of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) with performance status (ECOG-ps) in patients receiving palliative chemotherapy for gastroesophageal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:e325–9.
Forrest LM, McMillan DC, McArdle CS, Angerson WJ, Dagg K, Scott HR. A prospective longitudinal study of performance status, an inflammation-based score (GPS) and survival in patients with inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:1834–6.
McMillan DC, Elahi MM, Sattar N, Angerson WJ, Johnstone J, McArdle CS. Measurement of the systemic inflammatory response predicts cancer-specific and non-cancer survival in patients with cancer. Nutr Cancer. 2001;41:64–9.
Al-Shaiba R, McMillan DC, Angerson WJ, Leen E, McArdle CS, Horgan P. The relationship between hypoalbuminaemia, tumour volume and the systemic inflammatory response in patients with colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:205–7.
Lien YC, Hsieh CC, Wu YC, Hsu HS, Hsu WH, Wang LS, et al. Preoperative serum albumin level is a prognostic indicator for adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia. J Gastrointest Surg. 2004;8:1041–8.
Lee J, Lim T, Uhm JE, Park KW, Park SH, Lee SC, et al. Prognostic model to predict survival following first-line chemotherapy in patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:886–91.
Crumley AB, Stuart RC, McKernan M, McMillan DC. Is hypoalbuminemia an independent prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer? World J Surg. 2010;34:2393–8.
Andreyev HJ, Norman AR, Oates J, Cunningham D. Why do patients with weight loss have a worse outcome when undergoing chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies? Eur J Cancer. 1998;34:503–9.
Yoshida S, Saito K, Koga F, Yokoyama M, Kageyama Y, Masuda H, et al. C-reactive protein level predicts prognosis in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. BJU Int. 2008;101:978–81.
Guillem P, Triboulet JP. Elevated serum levels of C-reactive protein are indicative of a poor prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2005;18:146–50.
Shimada H, Kitabayashi H, Nabeya Y, Okazumi S, Matsubara H, Funami Y, et al. Treatment response and prognosis of patients after recurrence of esophageal cancer. Surgery. 2003;133:24–31.
Shiraishi N, Inomata M, Osawa N, Yasuda K, Adachi Y, Kitano S. Early and late recurrence after gastrectomy for gastric carcinoma. Univariate and multivariate analyses. Cancer. 2000;89:255–61.
Adachi Y, Oshiro T, Mori M, Maehara Y, Sugimachi K. Prediction of early and late recurrence after curative resection for gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1996;77:2445–8.
Acknowledgments
The contents of this manuscript are the sole responsibility of the authors. Those who funded the study had no role in the study design, data collection, and analysis; decision to publish; or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirashima, K., Watanabe, M., Shigaki, H. et al. Prognostic significance of the modified Glasgow prognostic score in elderly patients with gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 49, 1040–1046 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0855-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0855-5