Abstract
Background/purpose
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a prominent side effect of the treatment of cancer. Despite this frequent complication, there has been no comprehensive review and quality appraisal of CIPN assessments. The purpose of this study is to provide a definitive quality appraisal of CIPN assessment strategies for clinical use.
Methods
Relevant studies were identified through database searches of Medline, Embase, CINAHL, and Cochrane. CIPN assessment strategies from included articles were extracted and initially rated by an oncologist and neurophysiologist according to criteria related to assessment depth, comprehensiveness, appropriateness, and reliability. The six highest scoring assessment strategies were the focus of a two-round Delphi survey of a working party of 32 physicians, nurses, and consumers to achieve consensus on the highest rated assessments for each criterion.
Results
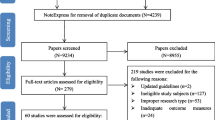
The database search yielded 117 distinct CIPN assessments that were extracted from 2373 articles. Three patient-reported outcome surveys and three clinician-based assessments were included in the Delphi survey. No consensus was generated regarding the best overall CIPN assessment, although good (≥70%) consensus was achieved regarding the best assessment within each criterion. The Participant Neurotoxicity Questionnaire (PNQ) was rated the highest overall and patient-reported outcome (PRO) assessment, while the Total Neuropathy Score clinical version (TNSc) was the highest rated clinician-based assessment.
Conclusions
A diverse range of CIPN assessments currently exists. While several assessments assess CIPN symptoms with adequate comprehensiveness, depth, language, and feasibility, the consensus ‘gold standard’ clinical assessment remains to be established.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kolb NA, Smith AG, Singleton JR, Beck SL, Stoddard GJ, Brown S, Mooney K (2016) The association of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy symptoms and the risk of falling. JAMA Neurol 73(7):860–866
Wolf S, Barton D, Kottschade L, Grothey A, Loprinzi C (2008) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: prevention and treatment strategies. Eur J Cancer 44(11):1507–1515
Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, Smith EML, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, Chauhan C, Gavin P, Lavino A, Lustberg MB (2014) Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol 32:1941–1967
Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F, Mattavelli L, Susani E, Alberti P, Cortinovis D, Bidoli P (2010) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity assessment: a critical revision of the currently available tools. Eur J Cancer 46(3):479–494
Hausheer FH, Schilsky RL, Bain S, Berghorn EJ, Lieberman F (2006) Diagnosis, management, and evaluation of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Semin Oncol 33(1):15–49
Postma T, Heimans J (2000) Grading of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Ann Oncol 11(5):509–513
Park SB, Goldstein D, Krishnan AV, Lin CSY, Friedlander ML, Cassidy J, Koltzenburg M, Kiernan MC (2013) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: a critical analysis. CA Cancer J Clin 63(6):419–437
National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services (2010) Common terminology criteria for adverse events v4.03
Cornblath D, Chaudhry V, Carter K, Lee D, Seysedadr M, Miernicki M, Joh T (1999) Total neuropathy score validation and reliability study. Neurology 53(8):1660–1660
Calhoun E, Welshman E, Chang CH, Lurain J, Fishman D, Hunt T, Cella D (2003) Psychometric evaluation of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynecologic Oncology Group—Neurotoxicity (Fact/GOG-Ntx) questionnaire for patients receiving systemic chemotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer 13(6):741–748
Postma T, Aaronson N, Heimans J, Muller M, Hildebrand J, Delattre J-Y, Hoang-Xuan K, Lanteri-Minet M, Grant R, Huddart R (2005) The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: the QLQ-CIPN20. Eur J Cancer 41(8):1135–1139
Cavaletti G, Cornblath D, Merkies I, Postma T, Rossi E, Frigeni B, Alberti P, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou A (2012) The chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy outcome measures standardization study: from consensus to the first validity and reliability findings. Ann Oncol 24(2):454–462
Hershman DL, Weimer LH, Wang A, Kranwinkel G, Brafman L, Fuentes D, Awad D, Crew KD (2011) Association between patient reported outcomes and quantitative sensory tests for measuring long-term neurotoxicity in breast cancer survivors treated with adjuvant paclitaxel chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 125(3):767–774
Smith EML, Barton DL, Qin R, Steen PD, Aaronson NK, Loprinzi CL (2013) Assessing patient-reported peripheral neuropathy: the reliability and validity of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-CIPN20 Questionnaire. Qual Life Res 22(10):2787–2799
Monfort SM, Pan X, Patrick R, Ramaswamy B, Wesolowski R, Naughton MJ, Loprinzi CL, Chaudhari AM, Lustberg MB 2017 Gait, balance, and patient-reported outcomes during taxane-based chemotherapy in early-stage breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat
England J, Gronseth G, Franklin G, Miller R, Asbury A, Carter G, Cohen J, Fisher M, Howard JF, Kinsella L (2005) Distal symmetric polyneuropathy: a definition for clinical research; report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology 64(2):199–207
Krøigård T, Schrøder H, Qvortrup C, Eckhoff L, Pfeiffer P, Gaist D, Sindrup S (2014) Characterization and diagnostic evaluation of chronic polyneuropathies induced by oxaliplatin and docetaxel comparing skin biopsy to quantitative sensory testing and nerve conduction studies. Eur J Neurol 21(4):623–629
Gewandter JS, Burke L, Cavaletti G, Dworkin RH, Gibbons C, Gover TD, Herrmann DN, McArthur M, Justin C, McDermott MP (2016) Content validity of symptom-based measures for diabetic, chemotherapy, and HIV peripheral neuropathy. Muscle Nerve
Griffith KA, Merkies IS, Hill EE, Cornblath DR (2010) Measures of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review of psychometric properties. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15(4):314–325
Victorian Home and Community Care Program (2004) The review and identification of an existing, validated, comprehensive assessment tool—final report. Department of Health and Human Services, Victoria
Tofthagen CS, McMillan SC, Kip KE (2011) Development and psychometric evaluation of the chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy assessment tool. Cancer Nurs 34(4):E10–E20
Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Aranishi T, Morita S, Kuroi K, Ohsumi S, Makino H, Mukai H, Katsumata N (2009) Feasibility and validity of the Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire during taxane chemotherapy in a phase III randomized trial in patients with breast cancer: N-SAS BC 02. Support Care Cancer 17(12):1483–1491
Almadrones L, McGuire DB, Walczak JR, Florio CM, Tian C (2004) Psychometric evaluation of two scales assessing functional status and peripheral neuropathy associated with chemotherapy for ovarian cancer: a gynecologic oncology group study. Oncol Nurs Forum 31(3):615–623
Cavaletti G, Jann S, Pace A, Plasmati R, Siciliano G, Briani C, Cocito D, Padua L, Ghiglione E, Manicone M (2006) Multi-center assessment of the Total Neuropathy Score for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. J Peripher Nerv Syst 11(2):135–141
McKenna HP (1994) The Delphi technique: a worthwhile research approach for nursing? J Adv Nurs 19(6):1221–1225
Boonen A, van Berkel M, Kirchberger I, Cieza A, Stucki G, van der Heijde D (2009) Aspects relevant for functioning in patients with ankylosing spondylitis according to the health professionals: a Delphi study with the ICF as reference. Rheumatology 48(8):997–1002
Hasson F, Keeney S, McKenna H (2000) Research guidelines for the Delphi survey technique. J Adv Nurs 32(4):1008–1015
Van Hecke O, Kamerman PR, Attal N, Baron R, Bjornsdottir G, Bennett DL, Bennett MI, Bouhassira D, Diatchenko L, Freeman R (2015) Neuropathic pain phenotyping by international consensus (NeuroPPIC) for genetic studies: a NeuPSIG systematic review, Delphi survey, and expert panel recommendations. Pain 156(11):2337–2353
Tofthagen CS (2008) Development and psychometric evaluation of the chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy assessment tool. University of South Florida, Tampa
GOG toxicity criteria [https://www.pathology.med.umich.edu/gynonc/bluebook/appendix/appen1.html]
Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F, Piatti M, Rota S, Briani C, Zara G, Plasmati R, Pastorelli F, Caraceni A (2007) The Total Neuropathy Score as an assessment tool for grading the course of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: comparison with the National Cancer Institute-Common Toxicity Scale. J Peripher Nerv Syst 12(3):210–215
Cavaletti G, Bogliun G, Marzorati L, Zincone A, Piatti M, Colombo N, Parma G, Lissoni A, Fei F, Cundari S (2003) Grading of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity using the Total Neuropathy Scale. Neurology 61(9):1297–1300
Smith EML, Cohen JA, Pett MA, Beck SL (2011) The validity of neuropathy and neuropathic pain measures in patients with cancer receiving taxanes and platinums. Oncol Nurs Forum 38(2):133–142
Smith EML, Beck SL, Cohen J (2008) The total neuropathy score: a tool for measuring chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncol Nurs Forum 35(1):96–102
Alberti P, Rossi E, Cornblath D, Merkies I, Postma T, Frigeni B, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou A, Kalofonos H (2014) Physician-assessed and patient-reported outcome measures in chemotherapy-induced sensory peripheral neurotoxicity: two sides of the same coin. Ann Oncol 25(1):257–264
Di Maio M, Gallo C, Leighl NB, Piccirillo MC, Daniele G, Nuzzo F, Gridelli C, Gebbia V, Ciardiello F, De Placido S (2015) Symptomatic toxicities experienced during anticancer treatment: agreement between patient and physician reporting in three randomized trials. J Clin Oncol 33(8):910–915
Légaré F, Ratté S, Gravel K, Graham ID (2008) Barriers and facilitators to implementing shared decision-making in clinical practice: update of a systematic review of health professionals’ perceptions. Patient Educ Couns 73(3):526–535
PRO-CTCAE [https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/pro-ctcae/english.pdf]
Chiang M-C, Lin Y-H, Pan C-L, Tseng T-J, Lin W-M, Hsieh S-T (2002) Cutaneous innervation in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 59(7):1094–1098
Hovaguimian A, Gibbons CH (2011) Diagnosis and treatment of pain in small-fiber neuropathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep 15(3):193–200
Griffith KA, Couture DJ, Zhu S, Pandya N, Johantgen ME, Cavaletti G, Davenport JM, Tanguay LJ, Choflet A, Milliron T (2014) Evaluation of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy using current perception threshold and clinical evaluations. Support Care Cancer 22(5):1161–1169
Lauria G, Hsieh ST, Johansson O, Kennedy WR, Leger JM, Mellgren SI, Nolano M, Merkies IS, Polydefkis M, Smith AG (2010) European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. Eur J Neurol 17(7):903–912
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Cancer Institute NSW Translational Program Grant (14/TPG/1-05), National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) project grant (#1080521), and NHMRC Program Grant (#1037746).
Special thanks to Monica O’Brien, medical librarian at UNSW Australia, for her assistance with the creation of the database search strategy and members of the IN FOCUS Delphi working party (Dr. Sally Baron-Hay, Hayley Beer, Dr. Stephen Begbie, Dr. Barbara Bennett, Dr. Adam Boyce, Professor Frances Boyle, Dr. Karen Briscoe, Dr. Carol Cheung, Keith Cox, Dr. Emma Devenney, Jo Gardiner, Dr. Nidhi Garg, Dr. Matthew George, Professor David Goldstein, Associate Professor Peter Grimison, Dr. William Huynh, Associate Professor Chris Karapetis, Professor Matthew Kiernan, Tracy King, Professor Arun Krishnan, Professor Craig Lewis, Associate Professor Cindy Lin, Dr. Rob Lindeman, Sue McCullough, Phil Mendoza-Jones, Dr. Susanna Park, Dr. Jenny Shannon, Professor Steve Vucic, Dr. Kate Webber, Carmel Woodrow, Dr. Craig Underhill, Professor Desmond Yip).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
(DOCX 102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCrary, J...M., Goldstein, D., Boyle, F. et al. Optimal clinical assessment strategies for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a systematic review and Delphi survey. Support Care Cancer 25, 3485–3493 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-017-3772-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-017-3772-y