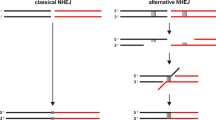
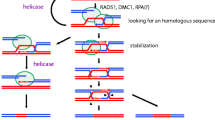
Abstract
Homologous recombination during meiosis is crucial for the DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair that promotes the balanced segregation of homologous chromosomes and enhances genetic variation. In most eukaryotes, two recombinases RAD51 and DMC1 form nucleoprotein filaments on single-stranded DNA generated at DSB sites and play a central role in the meiotic DSB repair and genome stability. These nucleoprotein filaments perform homology search and DNA strand exchange to initiate repair using homologous template-directed sequences located elsewhere in the genome. Multiple factors can regulate the assembly, stability, and disassembly of RAD51 and DMC1 nucleoprotein filaments. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of the meiotic functions of RAD51 and DMC1 and the role of their positive and negative modulators. We discuss the current models and regulators of homology searches and strand exchange conserved during plant meiosis. Manipulation of these repair factors during plant meiosis also holds a great potential to accelerate plant breeding for crop improvements and productivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboussekhra A, Chanet R, Zgaga Z, Cassier-Chauvat C, Heude M, Fabre F (1989) RADH, a gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encoding a putative DNA helicase involved in DNA repair. Characteristics of radH mutants and sequence of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7211–7219. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/17.18.7211
Aboussekhra A, Chanet R, Adjiri A, Fabre F (1992) Semidominant suppressors of Srs2 helicase mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae map in the RAD51 gene, whose sequence predicts a protein with similarities to procaryotic RecA proteins. Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.12.7.3224
Abreu CM, Prakash R, Romanienko PJ, Roig I, Keeney S, Jasin M (2018) Shu complex SWS1-SWSAP1 promotes early steps in mouse meiotic recombination. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06384-x
Arbel A, Zenvirth D, Simchen G (1999) Sister chromatid-based DNA repair is mediated by RAD54, not by DMC1 or TID1. EMBO J 18:2648–2658. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.9.2648
Azumi Y, Liu D, Zhao D, Li W, Wang G, Hu Y et al (2002) Homolog interaction during meiotic prophase I in Arabidopsis requires the SOLO DANCERS gene encoding a novel cyclin-like protein. EMBO J 21(12):3081–3095
Bachrati CZ, Borts RH, Hickson ID (2006) Mobile D-loops are a preferred substrate for the Bloom’s syndrome helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl258
Barakate A, Arrieta M, Macaulay M, Vivera S, Davidson D, Stephens J et al (2021) Downregulation of barley regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1 alters the distribution of meiotic crossovers. Front Plant Sci 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.745070
Barber LJ, Youds JL, Ward JD, McIlwraith MJ, O’Neil NJ, Petalcorin MIR et al (2008) RTEL1 Maintains genomic stability by suppressing homologous recombination. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.016
Bennett RJ, Sharp JA, Wang JC (1998) Purification and characterization of the Sgs1 DNA helicase activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.16.9644
Benson FE, Stasiak A, West SC (1994) Purification and characterization of the human Rad51 protein, an analogue of E. coli RecA. EMBO J 13:5764–5771. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06914.x
Bernstein KA, Reid RJD, Sunjevaric I, Demuth K, Burgess RC, Rothstein R (2011) The Shu complex, which contains Rad51 paralogues, promotes DNA repair through inhibition of the Srs2 anti-recombinase. Mol Biol Cell 22:1599–1607. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E10-08-0691
Bianco PR, Bradfield JJ, Castanza LR, Donnelly AN (2007) Rad54 oligomers translocate and cross-bridge double-stranded DNA to stimulate synapsis. J Mol Biol 374:618–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.052
Bishop DK (1994) RecA homologs Dmc1 and Rad51 interact to form multiple nuclear complexes prior to meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell 79:1081–1092. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(94)90038-8
Bishop DK, Park D, Xu L, Kleckner N (1992) DMC1: A meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression. Cell 69:439–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90446-J
Bishop DK, Nikolski Y, Oshiro J, Chon J, Shinohara M, Chen X (1999) High copy number suppression of the meiotic arrest caused by a dmc1 mutation: REC114 imposes an early recombination block and RAD54 promotes a DMC1-independent DSB repair pathway. Genes Cells 4:425–443. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00273.x
Bizard AH, Hickson ID (2014) The dissolution of double holliday junctions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016477
Blackwell AR, Dluzewska J, Szymanska-Lejman M, Desjardins S, Tock AJ, Kbiri N et al (2020) MSH 2 shapes the meiotic crossover landscape in relation to interhomolog polymorphism in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2020104858
Blanck S, Kobbe D, Hartung F, Fengler K, Focke M, Puchta H (2009) A SRS2 homolog from Arabidopsis thaliana disrupts recombinogenic DNA intermediates and facilitates single strand annealing. Nucleic Acids Res 37:7163–7176. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp753
Blanton HL, Radford SJ, McMahan S, Kearney HM, Ibrahim JG, Sekelsky J (2005) REC, drosophila MCM8, drives formation of meiotic crossovers. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/jourral.pgen.0010040
Blary A, Jenczewski E (2019) Manipulation of crossover frequency and distribution for plant breeding. Theor Appl Genet 132:575–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3240-1
Blary A, Gonzalo A, Eber F, Bérard A, Bergès H, Bessoltane N et al (2018) FANCM limits meiotic crossovers in Brassica crops. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00368
Bleuyard JY, White CI (2004) The Arabidopsis homologue of Xrcc3 plays an essential role in meiosis. EMBO J 23:439–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600055
Bleuyard JY, Gallego ME, White CI (2006) Recent advances in understanding of the DNA double-strand break repair machinery of plants. DNA Repair (Amst) 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.08.017
Bonilla B, Hengel SR, Grundy MK, Bernstein KA (2020) RAD51 gene family structure and function. Annu Rev Genet 54:25–46. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-021920-092410
Brown MS, Bishop DK (2015) DNA strand exchange and RecA homologs in meiosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a016659. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016659
Brown MS, Grubb J, Zhang A, Rust MJ, Bishop DK (2015) Small Rad51 and Dmc1 complexes often co-occupy both ends of a meiotic DNA double strand break. PLoS Genet 11:e1005653. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005653
Bugreev DV, Mazina OM, Mazin AV (2009) Bloom syndrome helicase stimulates RAD51 DNA strand exchange activity through a novel mechanism. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.029371
Bugreev DV, Pezza RJ, Mazina OM, Voloshin ON, Camerini-Otero RD, Mazin AV (2011) The resistance of DMC1 D-loops to dissociation may account for the DMC1 requirement in meiosis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1946
Busygina V, Sehorn MG, Shi IY, Tsubouchi H, Roeder GS, Sung P (2008) Hed1 regulates Rad51-mediated recombination via a novel mechanism. Genes Dev 22:786–795. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1638708
Busygina V, Saro D, Williams G, Leung WK, Say AF, Sehorn MG et al (2012) Novel attributes of hed1 affect dynamics and activity of the rad51 presynaptic filament during meiotic recombination. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.297309
Byun MY, Kim WT (2014) Suppression of OsRAD51D results in defects in reproductive development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J 79:256–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12558
Callender TL, Laureau R, Wan L, Chen X, Sandhu R, Laljee S et al (2016) Mek1 down regulates Rad51 activity during yeast meiosis by phosphorylation of Hed1. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006226
Candelli A, Holthausen JT, Depken M, Brouwer I, Franker MAM, Marchetti M et al (2014) Visualization and quantification of nascent RAD51 filament formation at single-monomer resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:15090–15095. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307824111
Carreira A, Hilario J, Amitani I, Baskin RJ, Shivji MKK, Venkitaraman AR et al (2009) The BRC repeats of BRCA2 modulate the DNA-binding selectivity of RAD51. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.019
Ceballos SJ, Heyer W-D (2011) Functions of the Snf2/Swi2 family Rad54 motor protein in homologous recombination. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1809:509–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.06.006
Chakraborty U, Alani E (2016) Understanding how mismatch repair proteins participate in the repair/anti-recombination decision. FEMS Yeast Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fow071
Chan Y-L, Brown MS, Qin D, Handa N, Bishop DK (2014) The third exon of the budding yeast meiotic recombination gene HOP2 is required for calcium-dependent and recombinase Dmc1-specific stimulation of homologous strand assimilation. J Biol Chem 289:18076–18086. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.558601
Chang HY, Liao CY, Su GC, Lin SW, Wang HW, Chi P (2015) Functional relationship of ATP hydrolysis, presynaptic filament stability, and homologous DNA pairing activity of the human meiotic recombinase DMC1. J Biol Chem 290:19863–19873. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.666289
Charlot F, Chelysheva L, Kamisugi Y, Vrielynck N, Guyon A, Epert A et al (2014) RAD51B plays an essential role during somatic and meiotic recombination in Physcomitrella. Nucleic Acids Res 42:11965–11978. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku890
Chen XJ, Guan MX, Clark-Walker GD (1993) MGM101, a nuclear gene involved in maintenance of the mitochondrial genome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/21.15.3473
Chen Z, Yang H, Pavletich NP (2008) Mechanism of homologous recombination from the RecA-ssDNA/dsDNA structures. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06971
Chintapalli SV, Bhardwaj G, Babu J, Hadjiyianni L, Hong Y, Todd GK et al (2013) Reevaluation of the evolutionary events within recA/RAD51 phylogeny. BMC Genom 14:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-240
Cho NW, Dilley RL, Lampson MA, Greenberg RA (2014) Interchromosomal homology searches drive directional ALT telomere movement and synapsis. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.030
Cloud V, Chan Y-L, Grubb J, Budke B, Bishop DK (2012) Rad51 is an accessory factor for Dmc1-mediated joint molecule formation during meiosis. Science 337:1222–1225. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1219379
Cooper TJ, Crawford MR, Hunt LJ, Marsolier-Kergoat M-C, Llorente B, Neale MJ (2021) Mismatch repair disturbs meiotic class I crossover control. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/480418
Couteau F, Belzile F, Horlow C, Grandjean O, Vezon D, Doutriaux M-P (1999) Random chromosome segregation without meiotic arrest in both male and female meiocytes of a dmc1 mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 11:1623–1634. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.11.9.1623
Crickard JB (2021) Discrete roles for Rad54 and Rdh54 during homologous recombination. Curr Opin Genet Dev 71:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2021.06.013
Crickard JBB, Greene EC (2018) Biochemical attributes of mitotic and meiotic presynaptic complexes. DNA Repair (Amst) 71:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.08.018
Crickard JB, Kaniecki K, Kwon Y, Sung P, Greene EC (2018) Meiosis-specific recombinase Dmc1 is a potent inhibitor of the Srs2 antirecombinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115:E10041–E10048. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810457115
Crickard JB, Kwon Y, Sung P, Greene EC (2019a) Dynamic interactions of the homologous pairing 2 (Hop2)–meiotic nuclear divisions 1 (Mnd1) protein complex with meiotic presynaptic filaments in budding yeast. J Biol Chem 294:490–501. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.006146
Crickard JB, Xue C, Wang W, Kwon Y, Sung P, Greene EC (2019b) The RecQ helicase Sgs1 drives ATP-dependent disruption of Rad51 filaments. Nucleic Acids Res 47:4694–4706. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz186
Crickard JB, Moevus CJ, Kwon Y, Sung P, Greene EC (2020) Rad54 drives ATP hydrolysis-dependent DNA sequence alignment during homologous recombination. Cell 181:1380-1394.e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.056
Crismani W, Girard C, Froger N, Pradillo M, Santos JL, Chelysheva L et al (2012) FANCM limits meiotic crossovers. Science 336:1588–1590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1220381
Crismani W, Portemer V, Froger N, Chelysheva L, Horlow C, Vrielynck N et al (2013) MCM8 is required for a pathway of meiotic double-strand break repair independent of DMC1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003165
Da Ines O, Degroote F, Amiard S, Goubely C, Gallego ME, White CI (2013a) Effects of XRCC2 and RAD51B mutations on somatic and meiotic recombination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 74:959–970. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12182
Da Ines O, Degroote F, Goubely C, Amiard S, Gallego ME, White CI (2013b) Meiotic recombination in Arabidopsis is catalysed by DMC1, with RAD51 playing a supporting role. PLoS Genet 9:e1003787. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003787
Dai J, Voloshin O, Potapova S, Camerini-Otero RD (2017) Meiotic knockdown and complementation reveals essential role of RAD51 in mouse spermatogenesis. Cell Rep 18:1383–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.024
Danilowicz C, Yang D, Kelley C, Prévost C, Prentiss M (2015) The poor homology stringency in the heteroduplex allows strand exchange to incorporate desirable mismatches without sacrificing recognition in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv610
De Muyt A, Pereira L, Vezon D, Chelysheva L, Gendrot G, Chambon A et al (2009) A high throughput genetic screen identifies new early meiotic recombination functions in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000654
De Muyt A, Jessop L, Kolar E, Sourirajan A, Chen J, Dayani Y et al (2012) BLM helicase ortholog Sgs1 is a central regulator of meiotic recombination intermediate metabolism. Mol Cell 46:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.02.020
Dernburg AF, McDonald K, Moulder G, Barstead R, Dresser M, Villeneuve AM (1998) Meiotic recombination in C. elegans initiates by a conserved mechanism and is dispensable for homologous chromosome synapsis. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81481-6
Di Capua E, Engel A, Stasiak A, Koller T (1982) Characterization of complexes between recA protein and duplex DNA by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol 157:87–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(82)90514-9
Ding H, Schertzer M, Wu X, Gertsenstein M, Selig S, Kammori M et al (2004) Regulation of murine telomere length by Rtel: an essential gene encoding a helicase-like protein. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.05.026
Dirks R, Van Dun K, De Snoo CB, Van Den Berg M, Lelivelt CLC, Voermans W et al (2009) Reverse breeding: a novel breeding approach based on engineered meiosis. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2009.00450.x
Domenichini S, Raynaud C, Ni DA, Henry Y, Bergounioux C (2006) Atmnd1-Δ1 is sensitive to gamma-irradiation and defective in meiotic DNA repair. DNA Repair (Amst). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.12.007
Dorn A, Puchta H (2019) DNA helicases as safekeepers of genome stability in plants. Genes (Basel) 10:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121028
Draeger T, Martin AC, Alabdullah AK, Pendle A, Rey MD, Shaw P et al (2020) Dmc1 is a candidate for temperature tolerance during wheat meiosis. Theor Appl Genet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03508-9
Dray E, Siaud N, Dubois E, Doutriaux M-P (2006) Interaction between Arabidopsis Brca2 and its partners Rad51, Dmc1, and Dss1. Plant Physiol 140:1059–1069. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.075838
Emmanuel E, Yehuda E, Melamed-Bessudo C, Avivi-Ragolsky N, Levy AA (2006) The role of AtMSH2 in homologous recombination in Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400577
Essers J, Hendriks RW, Swagemakers SMA, Troelstra C, de Wit J, Bootsma D et al (1997) Disruption of mouse RAD54 reduces ionizing radiation resistance and homologous recombination. Cell 89:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80199-3
Fasching CL, Cejka P, Kowalczykowski SC, Heyer WD (2015) Top3-Rmi1 dissolve Rad51-mediated D loops by a topoisomerase-based mechanism. Mol Cell 57:595–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.022
Fayos I, Mieulet D, Petit J, Meunier AC, Périn C, Nicolas A et al (2019) Engineering meiotic recombination pathways in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 17:2062–2077. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13189
Fernandes JB, Duhamel M, Seguéla-Arnaud M, Froger N, Girard C, Choinard S et al (2018) FIGL1 and its novel partner FLIP form a conserved complex that regulates homologous recombination. PLOS Genet 14:e1007317. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007317
Fu R, Wang C, Shen H, Zhang J, Higgins JD, Liang W (2020) Rice OsBRCA2 is required for DNA double-strand break repair in meiotic cells. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.600820
Game JC, Mortimer RK (1974) A genetic study of X-ray sensitive mutants in yeast. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen. https://doi.org/10.1016/0027-5107(74)90176-6
Game JC, Zamb TJ, Braun RJ (1980) The role of radiation (rad) genes in meiotic recombination in yeast. Genetics 94:51–68
Gari K, Décaillet C, Delannoy M, Wu L, Constantinou A (2008) Remodeling of DNA replication structures by the branch point translocase FANCM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804777105
Gasior SL, Olivares H, Ear U, Hari DM, Weichselbaum R, Bishop DK (2001) Assembly of RecA-like recombinases: distinct roles for mediator proteins in mitosis and meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.121046198
Gerton JL, DeRisi JL (2002) Mnd1p: an evolutionarily conserved protein required for meiotic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:6895–6900. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.102167899
Girard C, Crismani W, Froger N, Mazel J, Lemhemdi A, Horlow C et al (2014) FANCM-associated proteins MHF1 and MHF2, but not the other Fanconi anemia factors, limit meiotic crossovers. Nucleic Acids Res 42:9087–9095. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku614
Girard CCCC, Chelysheva L, Choinard S, Froger N, Macaisne N, Lehmemdi A et al (2015) AAA-ATPase FIDGETIN-LIKE 1 and helicase FANCM antagonize meiotic crossovers by distinct mechanisms. PLoS Genet 11:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005369
Godin SK, Meslin C, Kabbinavar F, Bratton-Palmer DS, Hornack C, Mihalevic MJ et al (2015) Evolutionary and functional analysis of the invariant SWIM domain in the conserved Shu2/SWS1 protein family from Saccharomyces cerevisiae to Homo sapiens. Genetics 199:1023–1033. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.114.173518
Grell RF (1984) Time of recombination in the Drosophila melanogaster oocyte. III. Selection and characterization of temperature-sensitive and-insensitive, recombination-deficient alleles in Drosophila. Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/108.2.425
Hartmann M, Kohl KP, Sekelsky J, Hatkevich T (2019) Meiotic MCM proteins promote and inhibit crossovers during meiotic recombination. Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.119.302221
Hartung F, Plchová H, Puchta H (2000) Molecular characterisation of RecQ homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.21.4275
Hartung F, Suer S, Puchta H (2007) Two closely related RecQ helicases have antagonistic roles in homologous recombination and DNA repair in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18836–18841. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705998104
Hernandez Sanchez-Rebato M, Bouatta AM, Gallego ME, White CI, Da Ines O (2021) RAD54 is essential for RAD51-mediated repair of meiotic DSB in Arabidopsis. PLOS Genet 17:e1008919. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008919
Hinch AG, Becker PW, Li T, Moralli D, Zhang G, Bycroft C et al (2020) The configuration of RPA, RAD51, and DMC1 binding in meiosis reveals the nature of critical recombination intermediates. Mol Cell 79:689-701.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.015
Hirakawa T, Matsunaga S (2019) Characterization of DNA repair foci in root cells of Arabidopsis in response to DNA damage. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00990
Holloway JK, Morelli MA, Borst PL, Cohen PE (2010) Mammalian BLM helicase is critical for integrating multiple pathways of meiotic recombination. J Cell Biol 188:779–789. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200909048
Holzen TM, Shah PP, Olivares HA, Bishop DK (2006) Tid1/Rdh54 promotes dissociation of Dmc1 from nonrecombinogenic sites on meiotic chromatin. Genes Dev 20:2593–2604. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1447106
Hong S, Sung Y, Yu M, Lee M, Kleckner N, Kim KP (2013) The logic and mechanism of homologous recombination partner choice. Mol Cell 51:440–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.008
Hu Q, Li Y, Wang H, Shen Y, Zhang C, Du G et al (2017) MEICA 1 (meiotic chromosome association 1) interacts with TOP3α and regulates meiotic recombination in rice. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00241
Huang J, Smith AR, Zhang T, Zhao D (2016) Creating completely both male and female sterile plants by specifically ablating microspore and megaspore mother cells. Front Plant Sci 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00030
Hunter N (2015) Meiotic recombination: the essence of heredity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016618
Ira G, Malkova A, Liberi G, Foiani M, Haber JE (2003) Srs2 and Sgs1-Top3 suppress crossovers during double-strand break repair in yeast. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00886-9
Ito K, Murayama Y, Kurokawa Y, Kanamaru S, Kokabu Y, Maki T et al (2020) Real-time tracking reveals catalytic roles for the two DNA binding sites of Rad51. Nat Commun 11:2950. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16750-3
Janicka S, Kühn K, Le Ret M, Bonnard G, Imbault P, Augustyniak H et al (2012) A RAD52-like single-stranded DNA binding protein affects mitochondrial DNA repair by recombination. Plant J 72:423–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05097.x
Jensen RB, Carreira A, Kowalczykowski SC (2010) Purified human BRCA2 stimulates RAD51-mediated recombination. Nature 467:678–683. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09399
Jing J, Zhang T, Wang Y, Cui Z, He Y (2019) ZmRAD51C is essential for double-strand break repair and homologous recombination in maize meiosis. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215513
Joanna W, Sheba A, Stefan S, Wendy B, Stephen VK, Jian Q et al (2006) Differential contributions of mammalian Rad54 paralogs to recombination, DNA damage repair, and meiosis. Mol Cell Biol 26:976–989. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.26.3.976-989.2006
Kang H, Shin H, Kalantzi A, Toseland CP, Kim H, Gruber S et al (2015) Crystal structure of Hop2–Mnd1 and mechanistic insights into its role in meiotic recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 43:3841–3856. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv172
Karow JK, Chakraverty RK, Hickson ID (1997) The Bloom’s syndrome gene product is a 3’-5’ DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.49.30611
Kaur H, DeMuyt A, Lichten M (2015) Top3-Rmi1 DNA single-strand decatenase is integral to the formation and resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates. Mol Cell 57:583–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.020
Kerzendorfer C (2006) The Arabidopsis thaliana MND1 homologue plays a key role in meiotic homologous pairing, synapsis and recombination. J Cell Sci 119:2486–2496. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02967
Kerzendorfer C, Vignard J, Pedrosa-Harand A, Siwiec T, Akimcheva S, Jolivet S et al (2006) The Arabidopsis thaliana MND1 homologue plays a key role in meiotic homologous pairing, synapsis and recombination. J Cell Sci 119:2486–2496. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02967
Klein HL (1997) RDH54, a RAD54 homologue in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is required for mitotic diploid-specific recombination and repair and for meiosis. Genetics 147:1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/147.4.1533
Klovstad M, Abdu U, Schüpbach T (2008) Drosophila brca2 is required for mitotic and meiotic DNA repair and efficient activation of the meiotic recombination checkpoint. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0040031
Knoll A, Puchta H (2011) The role of DNA helicases and their interaction partners in genome stability and meiotic recombination in plants. J Exp Bot 62:1565–1579. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq357
Knoll A, Higgins JD, Seeliger K, Reha SJ, Dangel NJ, Bauknecht M et al (2012) The Fanconi anemia ortholog FANCM ensures ordered homologous recombination in both somatic and meiotic cells in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:1448–1464. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.096644
Kobayashi W, Liu E, Ishii H, Matsunaga S, Schlögelhofer P, Kurumizaka H (2019) Homologous pairing activities of Arabidopsis thaliana RAD51 and DMC1. J Biochem 165:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvy105
Kohl KP, Jones CD, Sekelsky J (2012) Evolution of an MCM complex in flies that promotes meiotic crossovers by blocking BLM helicase. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1228190
Kooistra R, Vreeken K, Zonneveld JB, de Jong AN, Eeken JC, Osgood CJ et al (1997) The Drosophila melanogaster RAD54 homolog, DmRAD54, is involved in the repair of radiation damage and recombination. Mol Cell Biol 17:6097–6104. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.17.10.6097
Kou Y, Chang Y, Li X, Xiao J, Wang S (2012) The rice RAD51C gene is required for the meiosis of both female and male gametocytes and the DNA repair of somatic cells. J Exp Bot 63:5323–5335. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers190
Krejci L, Van Komen S, Li Y, Villemain J, Reddy MS, Klein H et al (2003) DNA helicase Srs2 disrupts the Rad51 presynaptic filament. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01577
Kristensen CN, Bystol KM, Li B, Serrano L, Brenneman MA (2010) Depletion of DSS1 protein disables homologous recombinational repair in human cells. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.08.007
Kumar R, Duhamel M, Coutant E, Ben-Nahia E, Mercier R (2019) Antagonism between BRCA2 and FIGL1 regulates homologous recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz225
Kunkel TA, Erie DA (2005) Dna mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem 74:681–710. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133243
Kurzbauer M-T, Uanschou C, Chen D, Schlögelhofer P (2012) The recombinases DMC1 and RAD51 Are functionally and spatially separated during meiosis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:2058–2070. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.098459
L’Hôte D, Vatin M, Auer J, Castille J, Passet B, Montagutelli X et al (2011) Fidgetin-like1 is a strong candidate for a dynamic impairment of male meiosis leading to reduced testis weight in mice. PLoS ONE 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027582
Lan WH, Lin SY, Kao CY, Chang WH, Yeh HY, Chang HY et al (2020) Rad51 facilitates filament assembly of meiosis-specific Dmc1 recombinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1920368117
Lao JP, Oh SD, Shinohara M, Shinohara A, Hunter N (2008) Rad52 promotes postinvasion steps of meiotic double-strand-break repair. Mol Cell 29:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.014
Lao JP, Cloud V, Huang CC, Grubb J, Thacker D, Lee CY et al (2013) Meiotic crossover control by concerted action of Rad51-Dmc1 in homolog template bias and robust homeostatic regulation. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003978
Lario LD, Botta P, Casati P, Spampinato CP (2015) Role of AtMSH7 in UV-B-induced DNA damage recognition and recombination. J Exp Bot 66:3019–3026. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru464
Lee JY, Terakawa T, Qi Z, Steinfeld JB, Redding S, Kwon Y et al (2015) Base triplet stepping by the Rad51/RecA family of recombinases. Science 349:977–981. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aab2666
Lee JY, Steinfeld JB, Qi Z, Kwon Y, Sung P, Greene EC (2017) Sequence imperfections and base triplet recognition by the Rad51/RecA family of recombinases. J Biol Chem 292:11125–11135. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.787614
Lee M, Shorthouse D, Mahen R, Hall BA, Venkitaraman AR (2021) Cancer-causing BRCA2 missense mutations disrupt an intracellular protein assembly mechanism to disable genome maintenance. Nucleic Acids Res 49:5588–5604. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab308
Leu JY, Chua PR, Roeder GS (1998) The meiosis-specific Hop2 protein of S. cerevisiae ensures synapsis between homologous chromosomes. Cell 94:375–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81480-4
Li W, Chen C, Markmann-Mulisch U, Timofejeva L, Schmelzer E, Ma H et al (2004) The Arabidopsis AtRAD51 gene is dispensable for vegetative development but required for meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:10596–10601. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0404110101
Li L, Jean M, Belzile F (2006) The impact of sequence divergence and DNA mismatch repair on homeologous recombination in Arabidopsis. Plant J. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02657.x
Li X, Yu M, Bolaños-Villegas P, Zhang J, Ni D, Ma H et al (2021) Fanconi anemia ortholog FANCM regulates meiotic crossover distribution in plants. Plant Physiol 186:344–360. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab061
Lin Z, Kong H, Nei M, Ma H (2006) Origins and evolution of the recA/RAD51 gene family: evidence for ancient gene duplication and endosymbiotic gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:10328–10333. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604232103
Liu Y, Richards TA, Aves SJ (2009) Ancient diversification of eukaryotic MCM DNA replication proteins. BMC Evol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-9-60
Liu J, Doty T, Gibson B, Heyer WD (2010) Human BRCA2 protein promotes RAD51 filament formation on RPA-covered single-stranded DNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1904
Liu J, Renault L, Veaute X, Fabre F, Stahlberg H, Heyer WD (2011) Rad51 paralogues Rad55-Rad57 balance the antirecombinase Srs2 in Rad51 filament formation. Nature 479:245–248. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10522
Liu Y, Gaines WA, Callender T, Busygina V, Oke A, Sung P et al (2014) Down-regulation of Rad51 activity during meiosis in yeast prevents competition with Dmc1 for repair of double-strand breaks. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004005
Lo T, Pellegrini L, Venkitaraman AR, Blundell TL (2003) Sequence fingerprints in BRCA2 and RAD51: implications for DNA repair and cancer. DNA Repair (Amst) 2:1015–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1568-7864(03)00097-1
Lok BH, Carley AC, Tchang B, Powell SN (2013) RAD52 inactivation is synthetically lethal with deficiencies in BRCA1 and PALB2 in addition to BRCA2 through RAD51-mediated homologous recombination. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.391
Lorenz A, Osman F, Sun W, Nandi S, Steinacher R, Whitby MC (2012) The fission yeast FANCM ortholog directs non-crossover recombination during meiosis. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1220111
Lorenz A, Mehats A, Osman F, Whitby MC (2014) Rad51/Dmc1 paralogs and mediators oppose DNA helicases to limit hybrid DNA formation and promote crossovers during meiotic recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 42:13723–13735. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1219
Lovett ST, Mortimer RK (1987) Characterization of null mutants of the RAD55 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects of temperature, osmotic strength and mating type. Genetics 116:547–553. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/116.4.547
Luo S, Yeh H, Lan W, Wu Y-M, Yang C, Chang H et al (2021) Identification of fidelity-governing factors in human recombinases DMC1 and RAD51 from cryo-EM structures. Nat Commun 12:115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20258-1
Lutzmann M, Grey C, Traver S, Ganier O, Maya-Mendoza A, Ranisavljevic N et al (2012) MCM8- and MCM9-deficient mice reveal gametogenesis defects and genome instability due to impaired homologous recombination. Mol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.048
Marini V, Krejci L (2010) Srs2: The “odd-job man” in DNA repair. DNA Repair (Amst). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.01.007
Marsolier-Kergoat M-C, Khan MM, Schott J, Zhu X, Llorente B (2018) Mechanistic view and genetic control of DNA recombination during meiosis. Mol Cell 70:9-20.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.02.032
Martinez JS, von Nicolai C, Kim T, Ehlén Å, Mazin AV, Kowalczykowski SC et al (2016) BRCA2 regulates DMC1-mediated recombination through the BRC repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:3515–3520. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1601691113
Martini E, Borde V, Legendre M, Audic S, Regnault B, Soubigou G et al (2011) Genome-wide analysis of heteroduplex DNA in mismatch repair-deficient yeast cells reveals novel properties of meiotic recombination pathways. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002305
Martino J, Bernstein KA (2016) The Shu complex is a conserved regulator of homologous recombination. FEMS Yeast Res 16:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fow073
Mason JM, Dusad K, Wright WD, Grubb J, Budke B, Heyer WD et al (2015) RAD54 family translocases counter genotoxic effects of RAD51 in human tumor cells. Nucleic Acids Res 43:3180–3196. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv175
Masson JY, West SC (2001) The Rad51 and Dmc1 recombinases: a non-identical twin relationship. Trends Biochem Sci 26:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01742-4
Masson JY, Tarsounas MC, Stasiak AZ, Stasiak A, Shah R, McIlwraith MJ et al (2001) Identification and purification of two distinct complexes containing the five RAD51 paralogs. Genes Dev. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.947001
Matsuzaki K, Kondo S, Ishikawa T, Shinohara A (2019) Human RAD51 paralogue SWSAP1 fosters RAD51 filament by regulating the anti-recombinase FIGNL1 AAA+ ATPase. Nat Commun 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09190-1
Mbantenkhu M, Wang X, Nardozzi JD, Wilkens S, Hoffman E, Patel A et al (2011) Mgm101 is a Rad52-related protein required for mitochondrial DNA recombination. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.307512
McIlwraith MJ, West SC (2008) DNA repair synthesis facilitates RAD52-mediated second-end capture during DSB repair. Mol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.11.037
McKim KS, Hayashi-Hagihara A (1998) mei-W68 in Drosophila melanogaster encodes a Spo11 homolog: evidence that the mechanism for initiating meiotic recombination is conserved. Genes Dev 12:2932–2942. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.12.18.2932
Meeusen S, Tieu Q, Wong E, Weiss E, Schieltz D, Yates JR et al (1999) Mgm101p is a novel component of the mitochondrial nucleoid that binds DNA and is required for the repair of oxidatively damaged mitochondrial DNA. J Cell Biol 145:291–304. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.145.2.291
Mercier R, Mézard C, Jenczewski E, Macaisne N, Grelon M (2015) The molecular biology of meiosis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66:297–327. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-035923
Messiaen S, Le Bras A, Duquenne C, Barroca V, Moison D, Déchamps N et al (2013) Rad54 is required for the normal development of male and female germ cells and contributes to the maintainance of their genome integrity after genotoxic stress. Cell Death Dis 4:e774–e774. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.281
Mets DG, Meyer BJ (2009) Condensins regulate meiotic DNA break distribution, thus crossover frequency, by controlling chromosome structure. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.035
Mhaskar AN, Koornneef L, Zelensky AN, Houtsmuller AB, Baarends WM (2021) High resolution view on the regulation of recombinase accumulation in mammalian meiosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.672191
Mieulet D, Aubert G, Bres C, Klein A, Droc G, Vieille E et al (2018) Unleashing meiotic crossovers in crops. Nat Plants. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-018-0311-x
Myung K, Datta A, Chen C, Kolodner RD (2001) SGS1, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae homologue of BLM and WRN, suppresses genome instability and homeologous recombination. Nat Genet 27:113–116. https://doi.org/10.1038/83673
Nimonkar AV, Amitani I, Baskin RJ, Kowalczykowski SC (2007) Single molecule imaging of Tid1/Rdh54, a Rad54 homolog that translocates on duplex DNA and can disrupt joint molecules*. J Biol Chem 282:30776–30784. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M704767200
Nimonkar AV, Dombrowski CC, Siino JS, Stasiak AZ, Stasiak A, Kowalczykowski SC (2012) Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dmc1 and Rad51 proteins preferentially function with Tid1 and Rad54 proteins, respectively, to promote DNA strand invasion during genetic recombination*. J Biol Chem 287:28727–28737. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.373290
Niu H, Klein HL (2017) Multifunctional roles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Srs2 protein in replication, recombination and repair. FEMS Yeast Res 17:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fow111
Odahara M, Inouye T, Nishimura Y, Sekine Y (2015) RECA plays a dual role in the maintenance of chloroplast genome stability in Physcomitrella patens. Plant J 84:516–526. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13017
Oh SD, Lao JP, Hwang PY-H, Taylor AF, Smith GR, Hunter N (2007) BLM ortholog, Sgs1, prevents aberrant crossing-over by suppressing formation of multichromatid joint molecules. Cell 130:259–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.035
Oh SD, Lao JP, Taylor AF, Smith GR, Hunter N (2008) RecQ helicase, Sgs1, and XPF family endonuclease, Mus81-Mms4, resolve aberrant joint molecules during meiotic recombination. Mol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.07.006
Osakabe K, Yoshioka T, Ichikawa H, Toki S (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of RAD51-like genes from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 50:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016047231597
Osakabe K, Abe K, Yoshioka T, Osakabe Y, Todoriki S, Ichikawa H et al (2006) Isolation and characterization of the RAD54 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 48:827–842. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02927.x
Panoli AP, Ravi M, Sebastian J, Nishal B, Reddy TV, Marimuthu MPA et al (2006) AtMNDI is required for homologous pairing during meiosis in Arabidopsis. BMC Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-7-24
Pâques F, Haber JE (1999) Multiple pathways of recombination induced by double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:349–404. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.63.2.349-404.1999
Park JY, Singh TR, Nassar N, Zhang F, Freund M, Hanenberg H et al (2014) Breast cancer-associated missense mutants of the PALB2 WD40 domain, which directly binds RAD51C, RAD51 and BRCA2, disrupt DNA repair. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.421
Paul MW, Sidhu A, Liang Y, van Rossum-Fikkert SE, Odijk H, Zelensky AN et al (2021) Role of brca2 dna-binding and c-terminal domain in its mobility and conformation in dna repair. Elife 10:1–23. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.67926
Payne M, Hickson ID (2009) Genomic instability and cancer: lessons from analysis of Bloom’s syndrome. Biochem Soc Trans 37:553–559. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0370553
Pećina-Šlaus N, Kafka A, Salamon I, Bukovac A (2020) Mismatch repair pathway, genome stability and cancer. Front Mol Biosci 7:122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00122
Pellegrini L, Yu DS, Lo T, Anand S, Lee M, Blundell TL et al (2002) Insights into DNA recombination from the structure of a RAD51–BRCA2 complex. Nature 420:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01230
Peterson SE, Keeney S, Jasin M (2020) Mechanistic insight into crossing over during mouse meiosis. Mol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.009
Petukhova GV, Romanienko PJ, Camerini-Otero RD (2003) The Hop2 protein has a direct role in promoting interhomolog interactions during mouse meiosis. Dev Cell 5:927–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00369-1
Petukhova GV, Pezza RJ, Vanevski F, Ploquin M, Masson JY, Camerini-Otero RD (2005) The Hop2 and Mnd1 proteins act in concert with Rad51 and Dmc1 in meiotic recombination. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:449–453. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb923
Pezza RJ, Petukhova GV, Ghirlando R, Camerini-Otero RD (2006) Molecular activities of meiosis-specific proteins Hop2, Mnd1, and the Hop2-Mnd1 complex. J Biol Chem 281:18426–18434. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M601073200
Pezza RJ, Voloshin ON, Volodin AA, Boateng KA, Bellani MA, Mazin AV et al (2014) The dual role of HOP2 in mammalian meiotic homologous recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1234
Pittman DL, Cobb J, Schimenti KJ, Wilson LA, Cooper DM, Brignull E et al (1998) Meiotic prophase arrest with failure of chromosome synapsis in mice deficient for Dmc1, a germline-specific RecA homolog. Mol Cell 1:697–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80069-6
Prakash R, Satory D, Dray E, Papusha A, Scheller J, Kramer W et al (2009) Yeast Mphl helicase dissociates Rad51-made D-loops: implications for crossover control in mitotic recombination. Genes Dev. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1737809
Prakash R, Freyer L, Saiz N, Gavrilov S, Wang RQ, Romanienko PJ et al (2021) XRCC3 loss leads to midgestational embryonic lethality in mice. DNA Repair (Amst). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103227
Qi Z, Redding S, Lee JY, Gibb B, Kwon Y, Niu H et al (2015) DNA sequence alignment by microhomology sampling during homologous recombination. Cell 160:856–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.029
Qiu Y, Antony E, Doganay S, RanKoh H, Lohman TM, Myong S (2013) Srs2 prevents Rad51 filament formation by repetitive motion on DNA. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3281
Rabitsch KP, Tóth A, Gálová M, Schleiffer A, Schaffner G, Aigner E et al (2001) A screen for genes required for meiosis and spore formation based on whole-genome expression. Curr Biol 11:1001–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00274-3
Rajendra E, Venkitaraman AR (2009) Two modules in the BRC repeats of BRCA2 mediate structural and functional interactions with the RAD51 recombinase. Nucleic Acids Res 38:82–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp873
Ramesh MA, Malik SB, Logsdon JM (2005) A phylogenomic inventory of meiotic genes: evidence for sex in Giardia and an early eukaryotic origin of meiosis. Curr Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.003
Rampler E, Stranzl T, Orban-Nemeth Z, Hollenstein DM, Hudecz O, Schlögelhofer P et al (2015) Comprehensive cross-linking mass spectrometry reveals parallel orientation and flexible conformations of plant HOP2–MND1. J Proteome Res 14:5048–5062. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00903
Recker J, Knoll A, Puchta H (2014) The Arabidopsis thaliana homolog of the helicase RTEL1 plays multiple roles in preserving genome stability. Plant Cell Online 26:4889–4902. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.132472
Reitz D, Chan YL, Bishop DK (2021) How strand exchange protein function benefits from ATP hydrolysis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 71:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2021.06.016
Reuter M, Zelensky A, Smal I, Meijering E, van Cappellen WA, de Gruiter HM et al (2014) BRCA2 diffuses as oligomeric clusters with RAD51 and changes mobility after DNA damage in live cells. J Cell Biol 207:599–613. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201405014
Rijkers T, Van Den Ouweland J, Morolli B, Rolink AG, Baarends WM, Van Sloun PPH et al (1998) Targeted inactivation of mouse RAD52Reduces homologous recombination but not resistance to ionizing radiation. Mol Cell Biol 18:6423–6429. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.18.11.6423
Robert T, Dervins D, Fabre F, Gangloff S (2006) Mrc1 and Srs2 are major actors in the regulation of spontaneous crossover. EMBO J. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601158
Rong L, Palladino F, Aguilera A, Klein HL (1991) The hyper-gene conversion hpr5-1 mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an allele of the SRS2/RADH gene. Genetics 127:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/127.1.75
Roy U, Kwon Y, Marie L, Symington L, Sung P, Lisby M et al (2021) The Rad51 paralog complex Rad55-Rad57 acts as a molecular chaperone during homologous recombination. Mol Cell 81:1043-1057.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.12.019
Samach A, Melamed-Bessudo C, Avivi-Ragolski N, Pietrokovski S, Levy AA (2011) Identification of plant RAD52 homologs and characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana RAD52 -like genes. Plant Cell 23:4266–4279. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.091744
Sandhu R, Monge Neria F, Monge Neria J, Chen X, Hollingsworth NM, Börner GV (2020) DNA helicase Mph1FANCM ensures meiotic recombination between parental chromosomes by dissociating precocious displacement loops. Dev Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2020.04.010
Santa Maria SR, Kwon Y, Sung P, Klein HL (2013) Characterization of the interaction between the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51 recombinase and the DNA translocase Rdh54*. J Biol Chem 288:21999–22005. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.480475
Saponaro M, Callahan D, Zheng X, Krejci L, Haber JE, Klein HL et al (2010) Cdk1 targets Srs2 to complete synthesis-dependent strand annealing and to promote recombinational repair. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000858
Sasaki M, Lange J, Keeney S (2010) Genome destabilization by homologous recombination in the germ line. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:182–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2849
Sasanuma H, Tawaramoto MS, Lao JP, Hosaka H, Sanda E, Suzuki M et al (2013) A new protein complex promoting the assembly of Rad51 filaments. Nat Commun 4:1676. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2678
Sasanuma H, Sakurai HSM, Furihata Y, Challa K, Palmer L, Gasser SM et al (2019) Srs2 helicase prevents the formation of toxic DNA damage during late prophase I of yeast meiosis. Chromosoma. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-019-00709-5
Schaefer DGG, Delacote F, Charlot F, Vrielynck N, Guyon-Debast A, Le Guin S et al (2010) RAD51 loss of function abolishes gene targeting and de-represses illegitimate integration in the moss Physcomitrella patens. DNA Repair (Amst) 9:526–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.02.001
Schröpfer S, Kobbe D, Hartung F, Knoll A, Puchta H (2014) Defining the roles of the N-terminal region and the helicase activity of RECQ4A in DNA repair and homologous recombination in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 42:1684–1697. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1004
Schwacha A, Kleckner N (1997) Interhomolog bias during meiotic recombination: meiotic functions promote a highly differentiated interhomolog-only pathway. Cell 90:1123–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80378-5
Seeliger K, Dukowic-Schulze S, Wurz-Wildersinn R, Pacher M, Puchta H (2012) BRCA2 is a mediator of RAD51- and DMC1-facilitated homologous recombination in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 193:364–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03947.x
Séguéla-Arnaud M, Crismani W, Larchevêque C, Mazel J, Froger N, Choinard S et al (2015) Multiple mechanisms limit meiotic crossovers: TOP3α and two BLM homologs antagonize crossovers in parallel to FANCM. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:4713–4718. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1423107112
Sehorn MG, Sigurdsson S, Bussen W, Unger VM, Sung P (2004) Human meiotic recombinase Dmc1 promotes ATP-dependent homologous DNA strand exchange. Nature 429:433–437. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02563
Serra H, Da Ines O, Degroote F, Gallego ME, White CI (2013) Roles of XRCC2, RAD51B and RAD51D in RAD51-independent SSA recombination. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003971
Serra H, Svačina R, Baumann U, Whitford R, Sutton T, Bartoš J et al (2021) Ph2 encodes the mismatch repair protein MSH7-3D that inhibits wheat homoeologous recombination. Nat Commun 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21127-1
Shah PP, Zheng X, Epshtein A, Carey JN, Bishop DK, Klein HL (2010) Swi2/Snf2-related translocases prevent accumulation of toxic Rad51 complexes during mitotic growth. Mol Cell 39:862–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.028
Shaked H, Melamed-Bessudo C, Levy AA (2005) High-frequency gene targeting in Arabidopsis plants expressing the yeast RAD54 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12265–12269. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0502601102
Sharan SK, Pyle A, Coppola V, Babus J, Swaminathan S, Benedict J et al (2004) BRCA2 deficiency in mice leads to meiotic impairment and infertility. Development. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.00888
Sheridan SD, Yu X, Roth R, Heuser JE, Sehorn MG, Sung P et al (2008) A comparative analysis of Dmc1 and Rad51 nucleoprotein filaments. Nucleic Acids Res 36:4057–4066. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn352
Shi W, Tang D, Shen Y, Xue Z, Zhang F, Zhang C et al (2019) OsHOP2 regulates the maturation of crossovers by promoting homologous pairing and synapsis in rice meiosis. New Phytol. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15664
Shinohara A, Ogawa H, Ogawa T (1992) Rad51 protein involved in repair and recombination in S. cerevisiae is a RecA-like protein. Cell 69:457–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90447-K
Shinohara A, Gasior S, Ogawa T, Kleckner N, Bishop DK (1997a) Saccharomyces cerevisiae recA homologues RAD51 and DMC1 have both distinct and overlapping roles in meiotic recombination. Genes Cells 2:615–629. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2443.1997.1480347.x
Shinohara M, Shita-Yamaguchi E, Buerstedde J-M, Shinagawa H, Ogawa H, Shinohara A (1997b) Characterization of the roles of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD54 gene and a homologue of RAD54, RDH54/TID1, in mitosis and meiosis. Genetics 147:1545–1556. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/147.4.1545
Shinohara M, Gasior SL, Bishop DK, Shinohara A (2000) Tid1/Rdh54 promotes colocalization of rad51 and dmc1 during meiotic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:10814–10819. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.20.10814
Shor E, Weinstein J, Rothstein R (2005) A genetic screen for top3 suppressors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identifies SHU1, SHU2, PSY3 and CSM2: four genes involved in error-free DNA repair. Genetics 169:1275–1289. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.036764
Siaud N, Dray E, Gy I, Gérard E, Takvorian N, Doutriaux M-P (2004) Brca2 is involved in meiosis in Arabidopsis thaliana as suggested by its interaction with Dmc1. EMBO J 23:1392–1401. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600146
Siaud N, Barbera MA, Egashira A, Lam I, Christ N, Schlacher K et al (2011) Plasticity of BRCA2 function in homologous recombination: genetic interactions of the PALB2 and DNA binding domains. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002409
Slotman JA, Paul MW, Carofiglio F, de Gruiter HM, Vergroesen T, Koornneef L et al (2020) Super-resolution imaging of RAD51 and DMC1 in DNA repair foci reveals dynamic distribution patterns in meiotic prophase. PLOS Genet 16:e1008595. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008595
Solinger JA, Kiianitsa K, Heyer W-D (2002) Rad54, a Swi2/Snf2-like recombinational repair protein, disassembles Rad51:dsDNA filaments. Mol Cell 10:1175–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00743-8
Spies M, Fishel R (2015) Mismatch repair during homologous and homeologous recombination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022657
Steinfeld JB, Beláň O, Kwon Y, Terakawa T, Al-Zain A, Smith MJ et al (2019) Defining the influence of Rad51 and Dmc1 lineage-specific amino acids on genetic recombination. Genes Dev 33:1191–1207. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.328062.119
Su H, Cheng Z, Huang J, Lin J, Copenhaver GP, Ma H et al (2017) Arabidopsis RAD51, RAD51C and XRCC3 proteins form a complex and facilitate RAD51 localization on chromosomes for meiotic recombination. PLoS Genet 13:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006827
Sugiyama T, Kantake N, Wu Y, Kowalczykowski SC (2006) Rad52-mediated DNA annealing after Rad51-mediated DNA strand exchange promotes second ssDNA capture. EMBO J. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601412
Sullivan MR, Bernstein KA (2018) RAD-ical new insights into RAD51 regulation. Genes (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9120629
Sun W, Nandi S, Osman F, Ahn JS, Jakovleska J, Lorenz A et al (2008) The FANCM ortholog Fml1 promotes recombination at stalled replication forks and limits crossing over during DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cell 32:118–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.024
Sung P (1994) Catalysis of ATP-dependent homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange by yeast RAD51 protein. Science 265:1241–1243. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8066464
Sung P, Klein H (2006) Mechanism of homologous recombination: mediators and helicases take on regulatory functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:739–750. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2008
Symington LS (2002) Role of RAD52 epistasis group genes in homologous recombination and double-strand break repair. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:630–670. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.66.4.630-670.2002
Taagen E, Bogdanove AJ, Sorrells ME (2020) Counting on crossovers: controlled recombination for plant breeding. Trends Plant Sci 25:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2019.12.017
Takata M, Sasaki MS, Tachiiri S, Fukushima T, Sonoda E, Schild D et al (2001) Chromosome instability and defective recombinational repair in knockout mutants of the five Rad51 paralogs. Mol Cell Biol 21:2858–2866. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.21.8.2858-2866.2001
Tang D, Miao C, Li Y, Wang H, Liu X, Yu H et al (2014) OsRAD51C is essential for double-strand break repair in rice meiosis. Front Plant Sci 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00167
Tang S, Wu MKY, Zhang R, Hunter N (2015) Pervasive and essential roles of the top3-rmi1 decatenase orchestrate recombination and facilitate chromosome segregation in meiosis. Mol Cell 57:607–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.021
Tavares EM, Wright WD, Heyer WD, Le Cam E, Dupaigne P (2019) In vitro role of Rad54 in Rad51-ssDNA filament-dependent homology search and synaptic complexes formation. Nat Commun 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12082-z
Taylor MRG, Špírek M, Chaurasiya KR, Ward JD, Carzaniga R, Yu X et al (2015) Rad51 paralogs remodel pre-synaptic Rad51 filaments to stimulate homologous recombination. Cell 162:271–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.015
Tham KC, Kanaar R, Lebbink JHG (2016) Mismatch repair and homeologous recombination. DNA Repair (Amst) 38:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.11.010
Thorslund T, Esashi F, West SC (2007) Interactions between human BRCA2 protein and the meiosis-specific recombinase DMC1. EMBO J 26:2915–2922. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601739
Thorslund T, McIlwraith MJ, Compton SA, Lekomtsev S, Petronczki M, Griffith JD et al (2010) The breast cancer tumor suppressor BRCA2 promotes the specific targeting of RAD51 to single-stranded DNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1905
Trouiller B, Schaefer DG, Charlot F, Nogué F (2006) MSH2 is essential for the preservation of genome integrity and prevents homeologous recombination in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj423
Tsubouchi H, Roeder GS (2002) The Mnd1 protein forms a complex with Hop2 to promote homologous chromosome pairing and meiotic double-strand break repair. Mol Cell Biol 22:3078–3088. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.22.9.3078-3088.2002
Tsubouchi H, Roeder GS (2006) Budding yeast Hed1 down-regulates the mitotic recombination machinery when meiotic recombination is impaired. Genes Dev. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1422506
Uanschou C, Ronceret A, Von Harder M, De Muyt A, Vezon D, Pereira L et al (2014) Sufficient amounts of functional HOP2/MND1 complex promote interhomolog DNA repair but are dispensable for intersister DNA repair during meiosis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:4924–4940. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.118521
Uringa EJ, Youds JL, Lisaingo K, Lansdorp PM, Boulton SJ (2011) RTEL1: an essential helicase for telomere maintenance and the regulation of homologous recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq1045
Veaute X, Jeusset J, Soustelle C, Kowalczykowski SC, Le Cam E, Fahre F (2003) The Srs2 helicase prevents recombination by disrupting Rad51 nucleoprotein filaments. Nature 423:309–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01585
Venkitaraman AR (2002) Cancer susceptibility and the functions of BRCA1 and BRCA2. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00615-3
Vignard J, Siwiec T, Chelysheva L, Vrielynck N, Gonord F, Armstrong SJ et al (2007) The interplay of RecA-related proteins and the MND1–HOP2 complex during meiosis in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet 3:e176. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0030176
Villeneuve AM, Hillers KJ (2001) Whence meiosis? Cell 106:647–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00500-1
Wang G (2004) Genome-wide analysis of the cyclin family in Arabidopsis and comparative phylogenetic analysis of plant cyclin-like proteins. Plant Physiol 135:1084–1099. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.040436
Wang Y, Copenhaver GP (2018) Meiotic recombination: mixing it up in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69:577–609. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040431
Wang Y, Xiao R, Wang H, Cheng Z, Li W, Zhu G et al (2014) The Arabidopsis RAD51 paralogs RAD51B, RAD51D and XRCC2 play partially redundant roles in somatic DNA repair and gene regulation. New Phytol 201:292–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12498
Ward JD, Muzzini DM, Petalcorin MIR, Martinez-Perez E, Martin JS, Plevani P et al (2010) Overlapping mechanisms promote postsynaptic RAD-51 filament disassembly during meiotic double-strand break repair. Mol Cell 37:259–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.026
Whitbread AL, Dorn A, Röhrig S, Puchta H (2021) Different functional roles of RTR complex factors in DNA repair and meiosis in Arabidopsis and tomato. Plant J 106:965–977. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15211
Wicky C, Alpi A, Passannante M, Rose A, Gartner A, Müller F (2004) Multiple genetic pathways involving the Caenorhabditis elegans Bloom’s syndrome genes him-6, rad-51, and top-3 are needed to maintain genome stability in the germ line. Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.24.11.5016-5027.2004
Wijnker E, van Dun K, de Snoo CB, Lelivelt CLC, Keurentjes JJB, Naharudin NS et al (2012) Reverse breeding in Arabidopsis thaliana generates homozygous parental lines from a heterozygous plant. Nat Genet 44:467–470. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2203
Wooster R, Bignell G, Lancaster J, Swift S, Seal S, Mangion J et al (1995) Identification of the breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA2. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/378789a0
Wu L, Davies SL, Levitt NC, Hickson ID (2001) Potential role for the BLM helicase in recombinational repair via a conserved interaction with RAD51. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M009471200
Wu Z, Ji J, Tang D, Wang H, Shen Y, Shi W et al (2015) OsSDS is essential for DSB formation in rice meiosis. Front Plant Sci 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00021
Xu J, Zhao L, Xu Y, Zhao W, Sung P, Wang H-WW (2017) Cryo-EM structures of human RAD51 recombinase filaments during catalysis of DNA-strand exchange. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3336
Xu Z, Zhang J, Xu M, Ji W, Yu M, Tao Y et al (2018) Rice RAD51 paralogs play essential roles in somatic homologous recombination for DNA repair. Plant J 95:282–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13949
Xue X, Sung P, Zhao X (2015) Functions and regulation of the multitasking FANCM family of DNA motor proteins. Genes Dev 29:1777–1788. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.266593.115
Yang H, Jeffrey PD, Miller J, Kinnucan E, Sun Y, Thoma NH et al (2002) BRCA2 function in DNA binding and recombination from a BRCA2-DSS1-ssDNA structure. Science 297:1837–1849
Yoshida K, Kondoh G, Matsuda Y, Habu T, Nishimune Y, Morita T (1998) The mouse RecA-like gene Dmc1 is required for homologous chromosome synapsis during meiosis. Mol Cell 1:707–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80070-2
Youds JL, Mets DG, McIlwraith MJ, Martin JS, Ward JD, Oneil NJ et al (2010) RTEL-1 enforces meiotic crossover interference and homeostasis. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183112
Yuan J, Chen J (2013) FIGNL1-containing protein complex is required for efficient homologous recombination repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:10640–10645. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1220662110
Yuan S-SS, Lee SY, Chen G, Song M, Tomlinson GE, Lee EY (1999) BRCA2 is required for ionizing radiation-induced assembly of Rad51 complex in vivo. Cancer Res 59:3547–3551
Zhang T, Wang X, Lu Y, Cai X, Ye Z, Zhang J (2013) Genome-wide analysis of the cyclin gene family in tomato. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010120
Zhang B, Wang M, Tang D, Li Y, Xu M, Gu M et al (2015) XRCC3 is essential for proper double-strand break repair and homologous recombination in rice meiosis. J Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv253
Zhang P, Zhang Y, Sun L, Sinumporn S, Yang Z, Sun B et al (2017) The rice AAA-ATPase OsFIGNL1 is essential for male meiosis. Front Plant Sci 8:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01639
Zhang F, Shen Y, Miao C, Cao Y, Shi W, Du G et al (2020) OsRAD51D promotes homologous pairing and recombination by preventing nonhomologous interactions in rice meiosis. New Phytol 227:824–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16595
Zickler D, Kleckner N (2015) Recombination, pairing, and synapsis of homologs during meiosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a016626. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016626
Zierhut C, Berlinger M, Rupp C, Shinohara A, Klein F (2004) Mnd1 is required for meiotic interhomolog repair. Curr Biol 14:752–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2004.04.030
Ziolkowski PA, Berchowitz LE, Lambing C, Yelina NE, Zhao X, Kelly KA et al (2015) Juxtaposition of heterozygous and homozygous regions causes reciprocal crossover remodelling via interference during Arabidopsis meiosis. Elife 4:1–29. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03708
Acknowledgements
We apologize that every significant finding could not be discussed in this review due to space and/or scope limitations. We would like to thank Frédéric Baudat, Eric Jenczewski, and Mathilde Grelon for the fruitful discussions, valuable suggestions, and critical reading of the manuscript. RK is funded by ANR-FIRE ANR-17-426 CE12-0015. The IJPB benefits from the support of the LabEx Saclay Plant Sciences-SPS (ANR-17-EUR-0007). This work has benefited from the support of IJPB's Plant Observatory technological platforms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Frederic Berger.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emmenecker, C., Mézard, C. & Kumar, R. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in plant meiosis: role of eukaryotic RecA recombinases and their modulators. Plant Reprod 36, 17–41 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-022-00443-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-022-00443-6