Abstract
Key message
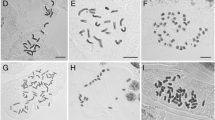
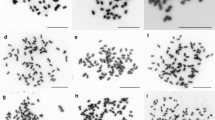
Polyploidy (diploid to octoploid) was evidenced from seven Psidium species, besides the outcomes of the whole-genome duplication about the nuclear DNA content, DNA sequence, and distribution.
Abstract
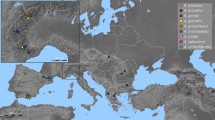
The previous studies have reported the occurrence of polyploid species in Psidium, all deriving from the basic chromosome number x = 11, which is conserved in Myrtaceae. Here, we aimed to assess the ploidy levels of seven Psidium species and to investigate the genomic outcomes of this karyotype change. Data on chromosome number, ploidy level, nuclear DNA content, and DNA sequence (SSR markers) were sought, quantified, and compared to geographical distribution of the studied Psidium species. A euploid series based on x = 11 was evidenced, with diploid, tetraploid, hexaploid, and octoploid species. These species also differed regarding at least one of the other analyzed traits, especially the hexaploids and the octoploid in relation to the others. Diploid species show restricted geographical distribution in the Atlantic Forest, differently from the polyploid species, which occur in several biomes in Brazil. Ploidy level of the Psidium species is related with the nuclear genome size and both seems to be related with species’ geographical distribution. Besides polyploidy, the genetic changes associated with numerical chromosome shift shown in this study, which increases the knowledge about the diversification and distribution of Psidium species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alix K, Gérard PR, Schwarzacher T et al (2017) Polyploidy and interspecific hybridization: partners for adaptation, speciation and evolution in plants. Ann Bot 120:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx079
Andrade FG, Forni-Martins ER (1998) Estudos cromossômicos em espécies de Myrtaceae. Genet Mol Biol 21(Suppl.):166
Aranguren Y, Valecillos C, Fermín G (2010)Variability of Venezuelan guava geographic landraces employing phenotypic markers. In: Proceedings of the second international guava symposium, Mexico, Acta horticulturae, vol 849, pp 87–95
Atchison E (1947) Chromosome numbers in the Myrtaceae. Am J Bot 34:159–164
Azmi A, Noin M, Landré P, Prouteau M, Boudet AM, Chriqui AM D (1997) High frequency plant regeneration from Eucalyptus globulus Labill. hypocotyls: ontogenesis and ploidy level of the regenerants. Plant Cell 51:9–16
Baker HG (1965) Characteristics and modes of origin of weeds. In: Baker HG, Stebbins GL (eds) The genetics of colonizing species. Academic Press, New York, pp 147–168
Barker MS, Husband BC, Pires JC (2016) Spreading winge and flying high: the evolutionary importance of polyploidy after a century of study. Am J Bot 103:1139–1145. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1600272
Beest MT, Roux JJL, Richardson DM, Brysting AK, Suda J, Magdalena Kubesová M, Pysek P (2012) The more the better? The role of polyploidy in facilitating plant invasions. Ann Bot 109:19–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr277
Bennetzen JL, Kellogg EA (1997) Do plants have a-oneway ticket to genomic obesity? Plant Cell 9:1509–1514
Berger BA, Kriebel R, Spalink D, Sytsma KJ (2016) Divergence times, historical biogeography, and shifts in speciation rates of Myrtales. Mol Phylogenet Evol 95:116–136
BFG (2015) Growing knowledge: an overview of seed plant diversity in Brazil. Rodriguésia 66:1085–1113. https://doi.org/10.1590/2175-7860201566411
Bolkhovskikh Z, Matvejeva VG, Zakharyeva O (1969) Chromosome numbers of flowering plants. Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Saint Petersburg
Bretagnolle F, Lumaret R (1995) Bilateral polyploidization in Dactylis glomerata L. subsp. lusitanica: occurrence, morphological and genetic characteristics of first polyploids. Euphytica 84:197–207
Brighton CA, Ferguson IK (1976) Chromosome counts in the genus Melaleuca (Myrtaceae). Kew Bull 31:27–33
Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR, Almeida PM (2007) Plant cytogenetics: still looking for the perfect mitotic chromosomes. Nucleus 50:453–462
Comai L (2005) The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nat Rev Genet 6:836–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1711
Coser SM, Ferreira MFS, Ferreira A, Mitre LK, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2012) Assessment of genetic diversity in Psidium guajava L. using different approaches. Sci Hortic 148:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.09.030
Costa IR, Forni-Martins ER (2006a) Chromosome studies in species of Eugenia, Myrciaria and Plinia (Myrtaceae) from southeastern Brazil. Aust J Bot 54:409–415. https://doi.org/10.1071/BT04199
Costa IR, Forni-Martins ER (2006b) Chromosome studies in Brazilian species of Campomanesia Ruiz & Pávon and Psidium. L. (Myrtaceae Juss.). Caryologia 59:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2006.10797891
Costa IR, Forni-Martins ER (2007) Karyotype analysis in South American species of Myrtaceae. Bot J Linn Soc 155:571–580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.2007.00704.x
Costa SR, Santos CAF (2013) Allelic database and divergence among Psidium accessions by using microsatellite markers. Genet Mol Res 12:6802–6812
Costa IR, Dornelas MC, Forni-Martins ER (2008) Nuclear genome size variation in fleshy-fruited neotropical Myrtaceae. Plant Syst Evol 276:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-008-0088-x
Dhooghe E, Van Laere K, Eeckhaut T, Leus L, Huylenbroeck JV (2011) Mitotic chromosome doubling of plant tissues in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:359–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9786-5
Edger PP, Pires JC (2009) Gene and genome duplications: the impact of dosage-sensitivity on the fate of nuclear genes. Chromosome Res 17:699–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-009-9055-9
Ehrendorfer F (1980) Polyploidy and distribution. In: Lewis WH (ed) Polyploidy: biological relevance. Plenum, New York, pp 45–60
Goldblatt P (1981) Index to plant chromosome numbers 1975–1978. Monographs in systematic botany from the Missouri Botanical Garden, Saint Louis
Goldblatt P, Johnson DE (1996) Index to plant chromosome numbers 1992–1993. Missouri Botanical Garden, Saint Louis
Grant V (1981) Plant speciation, 2nd edn. Columbia University Press, New York
Grattapaglia D, René E, Vaillancourt RE, Shepherd M, Thumma BR, Foley W, Külheim C, Potts BM, Myburg AA (2012) Progress in Myrtaceae genetics and genomics: Eucalyptus as the pivotal genus. Tree Genet Genomes 8:463–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-012-0491-x
Greilhuber J, Doleźel J, Lysák M, Bennett MD (2005) The origin, evolution and proposed stabilization of the terms ‘genome size’ and ‘C-value’ to describe nuclear DNA contents. Ann Bot 95:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci019
Hancock JF, Bringhurst RS (1981) Evolution in California populations of diploid and octoploid Fragaria (Rosaceae): a comparison. Am J Bot 68:1–5
Husband BC, Baldwin SJ, Suda J (2013) The incidence of polyploidy in natural plant populations: major patterns and evolutionary processes. In: Leitch IJ, Greilhuber J, Doležel J, Wendel JF (eds) Plant genome diversity 2: physical structure, behaviour and evolution of plant genomes. Springer, Wien, pp 255–276
Kay QON (1969) The origin and distribution of diploid and tetraploid Tripleurospermum inodorum (L.) Schultz Bip. Watsonia 7:130–141
Kron P, Suda J, Husband BC (2007) Applications of flow cytometry to evolutionary and population biology. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 38:847–876. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.38.091206.095504
Levin DA (2002) The role of chromosomal change in plant evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Lewis WH (1980) Polyploidy in angiosperms: dicotyledons. In: Lewis WH (ed) Polyploidy: biological relevance. Plenum Press, New York, pp 241–268
Lucas EJ, Harris SA, Mazine FF, Belsham SR, Nic Lughadha EM, Telford A, Peter E. Gasson PE, Chase MW (2007) Suprageneric phylogenetics of Myrteae, the generically richest tribe in Myrtaceae (Myrtales). Taxon 56:1105–1128. https://doi.org/10.2307/25065906
Madlung A (2013) Polyploidy and its effect on evolutionary success: old questions revisited with new tools. Heredity 110:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2012.79
Maherali H, Walden AE, Husband BC (2009) Genome duplication and the evolution of physiological responses to water stress. New Phytol 184:721–731. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02997.x
Marchant DB, Soltis DE, Soltis PS (2016) Patterns of abiotic niche shifts in allopolyploids relative to their progenitors. New Phytol 212:708–718. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14069
Marques AM, Tuler AC, Carvalho CR, Carrijo TT, Ferreira MFS, Clarindo WR (2016) Refinement of the karyological aspects of Psidium guineense (Swartz, 1788): a comparison with Psidium guajava (Linnaeus, 1753). Comp Cytogenet 10:117–128. https://doi.org/10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i1.6462
Moore RJ (1977) Index to plant chromosome numbers 1973–1974. Regnum Veg 96:1–257 p
Münzbergová Z (2007) No effect of ploidy level in plant response to competition in a common garden experiment. Biol J Linn Soc 92:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00820.x
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Murillo -AJ, Ruiz- PE, Landrum LR, Stuessy TF, Barfuss MHJ (2012) Phylogenetic relationships in Myrceugenia (Myrtaceae) based on plastid and nuclear DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 62:764–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2011.11.021
Oliveira SC, Nunes ACP, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2013) In vitro polyploidization from shoot tips of Jatropha curcas L.: a biodiesel plant. Plant Growth Regul 69:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-012-9749-4
Otto FJ (1990) DAPI staining of fixed cells for high-resolution flow 670 cytometry of nuclear DNA. In: Darzynkiewiez Z, Crissman HA, 671 Robinson JP (eds) Methods in cell biology, vol 33. Academic 672, San Diego, pp 105–110
Otto SP, Whitton J (2000) Polyploid incidence and evolution. Annu Rev Genet 34:401–437. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.34.1.401
Peixoto AL, Maia LC (2013) Manual de procedimentos para herbários. Recife. Editora Universitária UFPE
Petrov DA (2002) DNA loss and evolution of genome size in Drosophila. Genetica 115:81–91
Praça-Fontes MM, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2011) C-value reassessment of plant standards: an image cytometry approach. Plant Cell Rep 30:2303–2312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1135-6
Rivero G, Salazar G, Pacheco D, Sánchez A, Quirós M, Sthormes G (2012) Relaciones filogeneticas entre especies de Psidium (Myrtaceae) presentes en el occidente de venezuela a partir de secuencias de adn nuclear (ITS) y plastidial (trnH-psbA). Interciencia 37:838–844
Rye BL (1979) Chromosome number variation in the Myrtaceae and its taxonomic implications. Aust J Bot 27:547–573. https://doi.org/10.1071/BT9790547
Sattler MC, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2016) The polyploidy and its key role in plant breeding. Planta 243:281–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2450-x
Segraves KA (2017) The effects of genome duplications in a community context. New Phytol 215:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14564
Shu Z, Row S, Deng W (2018) Endoreplication: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Trends Cell Biol 28:465–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2018.02.006
Silveira RM, Machado RM, Forni-Martins ER, Verola CF, Costa IR (2017) Environmental variations drive polyploid evolution in neotropical Eugenia species (Myrtaceae). Genet Mol Res 15:gmr15048842
Slijepcevic P (2018) Genome dynamics over evolutionary time: “C-value enigma” in light of chromosome structure. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2018.05.005
Soares-Silva LH, Proença CE (2006) An old species revisited and a new combination proposed in Psidium (Myrtaceae). Kew Bull 61:199–204
Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2000) The role of genetic and genomic attributes in the success of polyploids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7051–7057. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.13.7051
Soltis DE, Solti PS, Tate JA (2003) Advances in the study of polyploidy since plant speciation. New Phytol 161:173–191. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00948.x
Souza AG, Resende LV, Lima IP, Martins LSS, Techio VH (2015) Chromosome number and nuclear DNA amount in Psidium spp. resistant and susceptible to Meloidogyne enterolobii and its relation with compatibility between rootstocks and commercial varieties of guava tree. Plant Syst Evol 301:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-014-1068-y
Spoelhof JP, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2017) Pure polyploidy: closing the gaps in autopolyploid research. J Syst Evol 55:340–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12253
Staggemeier VG, Cazetta E, Morellato LPC (2016) Hyperdominance in fruit production in the Brazilian Atlantic rain forest: the functional role of plants in sustaining frugivores. Biotropica 49:71–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/btp.12358
Stebbins GL (1947) The origin of the complex of Bromus carinatus and its phylogeographic implications. Contr Gray Herb Harv Univ 165:42–55
Stebbins GL (1950) Variation and evolution in plants. Oxford University Press, London
Stebbins GL (1985) Polyploidy, hybridization, and the invasion of new habitats. Ann Mo Bot Gard 72:824–832
Thompson JD, Lumaret R (1992) The evolutionary dynamics of polyploidy plants: origins, establishment and persistence. Trends Ecol Evol 7:302–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(92)90228-4
Thornhill AH, Ho SYW, Külheim C, Crisp MD (2015) Interpreting the modern distribution of Myrtaceae using a dated molecular phylogeny. Mol Phylogenet Evol 93:29–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.007
Treier UA, Broennimann O, Normand S et al (2009) Shift in cytotype frequency and niche space in the invasive plant Centaurea maculosa. Ecology 90:1366–1377
Tuler AC, Carrijo TT, Nóia LR, Ferreira A, Peixoto AL, Ferreira MFS (2015) SSR markers: a tool for species identification in Psidium (Myrtaceae). Mol Biol Rep 42:1501–1513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-015-3927-1
Van Dijk P, Bakx-Schotman T (1997) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography and cytotype geography in autopolyploid Plantago media. Mol Ecol 6:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.1997.00199.x
Vasconcelos TNC, Proença CEB, Ahmad B et al (2017) Myrteae phylogeny, calibration, biogeography and diversification patterns: increased understanding in the most species rich tribe of Myrtaceae. Mol Phylogenet Evol 109:113–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2017.01.002
Watanabe K (1986) The cytogeography of the genus Eupatorium (Compositae): a review. Plant Spec Biol 1:99–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-1984.1986.tb00019.x
WCSP (2017) World checklist of selected plant families. http://apps.kew.org/wcsp/. Accessed 13 May 2017
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, Brasília—DF, Brazil; Grants 443801/2014-2 and 308828/2015-1, 305821/2016-4), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Espírito Santo (FAPES/VALE, Vitória—ES, Brazil; Grant 75516586/16), Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ, Rio de Janeiro—RJ, Brazil) and VALE for financial support. This study was financid in part by the Coordernação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Alia.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuler, A.C., Carrijo, T.T., Peixoto, A.L. et al. Diversification and geographical distribution of Psidium (Myrtaceae) species with distinct ploidy levels. Trees 33, 1101–1110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-019-01845-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-019-01845-2