Abstract
Key message
Based on above- and below-ground biomass measurements from 604 and 212 sample trees respectively, aboveground biomass models for different origins didn’t have significant difference while belowground biomass models did.
Abstract
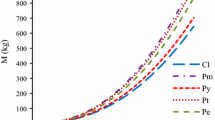
Based on the measurement data of aboveground biomass from 604 sample trees and belowground biomass from 212 sample trees of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) and Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) in southern China, the individual tree above- and below-ground biomass models involving forest origin were developed using nonlinear mixed model and dummy variable model approaches, and the effect of forest origin on biomass models was analyzed. The results showed that the aboveground biomass models for different origins had no significant difference, while the belowground biomass models were significantly different; and the belowground biomass estimate of a natural tree was highly greater than that of a planted tree with the same diameter and height. Specially, the belowground biomass estimates of natural trees were nearly 30 % and about 45 % greater than those of planted trees for Chinese fir and Masson pine, respectively. The mean prediction errors of aboveground biomass models and belowground biomass models developed in this study were less than 5 % and 15 %, respectively, which meant the biomass models could be applied to estimate forest biomass of the two species at large scale.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blujdea VNB, Pilli R, Dutca I et al (2012) Allometric biomass equations for young broadleaved trees in plantations in Romania. For Ecol Manage 264:172–184
Chojnacky DC (2002) Allometric scaling theory applied to FIA biomass estimation: GTR NC-230. North Central Research Station, Forest Service USDA. pp 96–102
Fayolle A, Doucet JL, Gillet JF et al (2013) Tree allometry in central Africa: testing the validity of pantropical multi-species allometric equations for estimating biomass and carbon stocks. For Ecol Manage 305:29–37
Feng ZW, Wang XK, Wu G (1999) Biomass and productivity of forest ecosystems in China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Fu LY, Zeng WS, Tang SZ et al (2012) Using linear mixed model and dummy variable model approaches to construct compatible single-tree biomass equations at different scales— a case study for Masson pine in southern China. J For Sci 58(3):101–115
Fu LY, Zhang HR, Li CM et al (2013) Analysis of nonlinear mixed effects model parameter estimation methods. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 49(1):114–119 (in Chinese)
IUFRO (1994) International guidelines for forest monitoring, 5th edn. IUFRO World Series, Vienna
Jenkins JC, Chojnacky DC, Heath LS et al (2003) National-scale biomass estimators for United States tree species. For Sci 49(1):12–35
Li HK, Ning JK (2012) Individual tree biomass model by tree origin, site classes and age groups. Acta Ecologica Sinica 32(3):740–757 (in Chinese)
Li CM, Zhang HR (2010) Modeling dominant height for Chinese fir plantation using a nonlinear mixed-effects modeling approach. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 46(3):89–95 (in Chinese)
Li D, Chen HW, Li GQ et al (2011) Comparative analysis of artificial forest and natural forest in China. For Inventory Plan 36(6):59–63. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-3168.2011.06.016 (in Chinese)
Luo YJ, Wang XK, Zhang XQ (2012) Root:shoot ratios across China’s forests: forest type and climatic effects. For Ecol Manage 269:19–25
Meng SX, Huang S, Lieffers VJ et al (2008) Wind speed and crown class influence the height–diameter relationship of lodgepole pine: nonlinear mixed effects modeling. For Ecol Manage 256:570–577
Muukkonen P (2007) Generalized allometric volume and biomass equations for some tree species in Europe. Eur J Forest Res 126:157–166
Návar J (2009) Allometric equations for tree species and carbon stocks for forests of northwestern Mexico. For Ecol Manage 257:427–434
Parresol BR (1999) Assessing tree and stand biomass: a review with examples and, critical comparisons. For Sci 45(4):573–593
Snorrason A, Einarsson SF (2006) Single-tree biomass and stem volume functions for eleven tree species used in Icelandic forestry. Icel Agric Sci 19:15–24
Tang SZ, Lang KJ, Li HK (2008) Statistics and computation of biomathematical models. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang ZF (2006) On the forest biomass’s modeling and precision analysis. Dissertation, Beijing Forestry University
Wang M, Borders BE, Zhao D (2008a) An empirical comparison of two subject-specific approaches to dominant heights modeling the dummy variable method and the mixed model method. For Ecol Manage 255:2659–2669
Wang XP, Fang JY, Zhu B (2008b) Forest biomass and root—shoot allocation in northeast China. For Ecol Manage 255:4007–4020
Wang WB, Dang YF, Zeng WS (2012) Compatible tree volume and aboveground biomass equations for larch (Larix spp.) in northeastern China. For Res Manage 2:69–73 (in Chinese)
Wu P, Ding FJ, Chen J (2012) Study on the biomass and productivity of forest in southwest China. Hubei Agric Sci 15(8):1513–1518 (in Chinese)
Xiang WH, Tian DL, Yan WD (2003) Reviews of researches on forest biomass and productivity. Cent South For Inventory Plan 22(3):57–60 (in Chinese)
Xue L, Yang P (2004) Summary of research on forest biomass. J Fujian Coll For 24(3):283–288 (in Chinese)
Yin YB, Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2010) Modeling of standing tree biomass for Larix in northeast China. J Northeast For Univ 38(9):23–26 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS (2011) Methodology on modeling single-tree biomass equations for national biomass estimation in China. Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Forestry [in Chinese]
Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2010a) Using mixed-effects modeling method to establish compatible national and regional single-tree biomass equations. Cent South For Inventory Plan 29(4):1–6 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2010b) Using measurement error modeling method to establish compatible single-tree biomass equations system. For Res 23(6):797–803 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2011a) Bias correction in logarithmic regression and comparison with weighted regression for nonlinear models. For Res 24(2):137–143 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2011b) Goodness evaluation and precision analysis of tree biomass equations. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 47(11):106–113 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2011c) Establishment of belowground biomass equations for larch in northeastern and Masson pine in southern China. J Beijing For Univ 33(2):1–6 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2012) Modeling compatible single-tree biomass equations of Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) in southern China. J For Res 23(4):593–598
Zeng WS, Tang SZ, Huang GS et al (2010a) Population classification and sample structure on modeling of single-tree biomass equations for national biomass estimation in China. For Res Manage 3:16–23 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Xiao QH, Hu J et al (2010b) Establishment of single-tree biomass equations for Pinus massoniana in southern China. J Cent South Univ For Technol 30(5):50–56 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Tang SZ, Xia ZS et al (2011a) Using linear mixed model and dummy variable model approaches to construct generalized single-tree biomass equations in Guizhou. For Res 24(3):285–291 (in Chinese)
Zeng WS, Zhang HR, Tang SZ (2011b) Using the dummy variable model approach to construct compatible single-tree biomass equations at different scales—a case study for Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) in southern China. Can J For Res 41(7):1547–1554
Zeng M, Nie XY, Zeng WS (2013) Compatible tree volume and aboveground biomass equations of Chinese fir in China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 49(10):74–79 (in Chinese)
Zianis D, Muukkonen P, Mäkipää R, Mencuccini M (2005) Biomass and stem volume equations for tree species in Europe. Silva Fennica (Monographs 4)
Author contribution statement
The author made substantial contributions to conception and design, model development, and analysis and discussion of results; and drafted the manuscript and gave final approval of the version to be submitted and any revised version.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges the Forest Biomass Modeling Project of the National Forest Inventory and Monitoring Program (No: 2030208), which was funded by the State Forestry Administration of China, for providing biomass mensuration data of C. lanceolata and P. massoniana, and thanks the project staff of East China Forest Inventory and Planning Institute and Central South Forest Inventory and Planning Institute for biomass data collection.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Matyssek.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, WS. Using nonlinear mixed model and dummy variable model approaches to develop origin-based individual tree biomass equations. Trees 29, 275–283 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1112-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1112-0