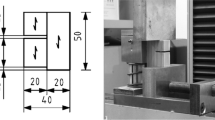
Abstract
The physical characteristics of wood are not usually considered as selection criteria when breeding perennial species that are grown for their fruits or seeds. In the coffee tree, stem breakage during harvesting and lodging during the growth period are major defects in some cultivars. These defects are linked to certain physical and mechanical properties of the wood, such as density or rigidity, which can be characterized by a parameter used in the resistance of materials: the Modulus of Elasticity (MOE). Wood density and the longitudinal MOE were studied on the stems of coffee trees of the species Coffee arabica L., derived from a diallel mating design. The MOE was measured by an acoustic system based on an analysis of the vibrations produced by a blow to the end of a piece of wood of known geometry. The MOE obtained in that way, along with the density of coffee tree stem wood, displayed substantial heritability. A strong link between the average internode length and the yield cumulated over 4 years was detected. Wood density was also correlated to yield and wood elasticity. Classification of parents according to the wood characteristics of their progenies depended on their degree of introgression by the species C. canephora. These traits could therefore be used to measure introgression, possibly as predictors of traits of agronomic interest, and as target traits in the creation of tall C. arabica varieties.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Tendency of a body to resume the shape and dimensions it had before stress, when that stress is removed.
Property of a solid characterizing the degree of deformation undergone for a given increase in stress. The slighter the deformation, the stiffer the body.
The name Bing is a registered trademark. A description of the system can be found at www.indexld.com.
References
Baillères H, Calchera G, Demay L, Fouquet D, Vernay M (1996) Classement des bois guyanais de structure. Comparaison de trois techniques non-destructives: visuelle, ultrasonore et analyse modale. In: ARBOLOR. – 4ème Colloque sciences et industries du bois, Nancy, 1996/09/11–13:369–376
Baillères H, Calchera G, Demay L, Vernay M (1998) Mechanical grading of Guianese structural timber using three non-destructive techniques. Bois et Forêts des Tropiques. Special issue: 1997–1998 highlights: 54–64
Baillères H, Verhaegen D, Gion J-M, Grima-Pettenati J, Plomion C, Rozenberg P, Chantre G, Ham-Pichavant F, Pardon P, Doignie J-C (2000) Introducing biotechnology to improve the selection efficiency of wood quality traits in Eucalyptus: description of a French research project. In: Proceedings of the first IUFRO workshop on the future of eucalypts for wood products. Country Club Casino, Launceston, Tasmania, 19–24 March 2000, pp 271–282
Baradat Ph, Desprez-Loustau ML (1997) Analyse diallèle et intégration de la sensibilité à la rouille courbeuse dans le programme d’amélioration du pin maritime. Ann Sci For 54(1):83–106
Baradat Ph, Labbé Th (1995) OPEP (Diogène), un logiciel intégré pour l’amélioration des plantes pérennes. In: Cirad CP (ed) Traitements statistiques des essais de sélection. Montpellier, France, pp 303–330
Bordonné PA (1989) Module dynamique et frottement intérieur dans le bois. Mesures sur poutres flottantes en vibrations naturelles. PhD thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine, Nancy, 109 p
Bouvet J-M, Baillères H (1995) Expression of some growth and wood property traits among Eucalyptus urophylla grandis clones in Congo. In: Vigneron P, Gérard J, Bouvet JM, Baillères H, Verhaegen D, Kremer A (eds) CIRAD-Forêt. – Eucalyptus plantations: improving fibre yield and quality. CRC IUFRO, Nogent sur Marne, France, pp 1–6
Brancheriau L, Baillères H (2002) Natural vibration analysis of clear wooden beams: a theorical review. Wood Sci Technol 36:347–365
Brashaw BK, Wang X, Ross RJ, Pellerin RF (2004) Relationship between stress wave velocities of green and dry veneer. For Prod J 54:85–89
Cestac Y, Snoeck J (1982) Les essais de densités, de dispositifs de plantation et de taille sur caféiers Robusta en Côte d’Ivoire. Résultats et perspectives. Café Cacao Thé 26:183–198
Cilas C, Godin C, Grenier D, Montagnon C, Baillères H (2002) Variability in the rigidity of Coffea canephora Pierre stems determined by acoustic analysis. Trees Struct Funct 16:23–27
Cilas C, Montagnon C, Bertrand B, Godin C (2000) Wood elasticity of several Coffea canephora Pierre clones. A new trait to include in selection schemes. Agronomie 20:439–444
Coste R (1989) Caféiers et cafés. Ed. Maisonneuve et Larose. Paris, France, 373 p
De Reffye Ph (1976) Modélisation et simulation de la verse du caféier à l’aide de la théorie de la résistance des matériaux. Café Cacao Thé 20:251–272
De Reffye Ph (1977) Amélioration de la résistance à la verse du caféier à l’aide de la théorie de la résistance des matériaux. In: 8th international scientific colloquium on coffee, Côte d’Ivoire, ASIC Ed, France, pp 439–445
Keuls M, Garretsen F (1977) A general method for the analysis of genetic variation in complete and incomplete diallels and North Carolina II designs. Part 1: Procedures and general formulas for the random model. Euphytica 26:537–511
Gérard J (1994) Contraintes de croissance, variations internes de densité et de module d’élasticité longitudinal, et déformations de sciage chez les Eucalyptus de plantation. Thèse de Doctorat en Sciences du Bois, Université de Bordeaux I, France
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids: structures and properties, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, 510 p
Guitard D, El Amri F (1987) Modèles prévisionnels de comportement élastique tridimensionnel pour les bois feuillus et les bois résineux. Ann Sci For 44:335–358
Halabe UB, Bidigalu GM, Gangarao HVS, Ross RJ (1997) Nondestructive evaluation of green wood using stress wave and transverse vibration techniques. Mater Eval 55(9):1013–1018
Koizumi A, Ueda K (1986) Estimation of the mechanical properties of standing trees by bending test 1 – Test method to measure the stiffness of a tree trunk. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 9:669–676
Kollmann FFP, Côté WA (1968) Principles of wood science. I – Solid wood. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 592 p
Pâques LE (2004) Roles of European and Japanese larch in the genetic control of growth, architecture and wood quality traits in interspecific hybrids (Larix x eurolepis Henry). Ann For Sci 61(1):25–33
Kumar S (2004) Genetic parameter estimates for wood stiffness, strength, internal checking, and resin bleeding for radiata pine. Can J For Res 34(12):2601–2610
Searle RS (1971) Linear Models, Wiley New York 532 p
Shao J, Tu D (1995) The Jackknife and Bootstrap. Springer, New York, 516 pp
Zhang SY, Yu QiBin, Beaulieu J (2004) Genetic variation in veneer quality and its correlation to growth in white spruce. Can J For Res 34(6):1311–1318
Zobel BJ, van Buijtenen JP (1989) Wood variation. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 502 p
Zobel BJ, Jett JB (1995) Genetics of wood production. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 526 p
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Zwieniecki
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cilas, C., Godin, C., Bertrand, B. et al. Genetic study on the physical properties of Coffea arabica L. wood. Trees 20, 587–592 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-006-0073-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-006-0073-3