Abstract
Background
This cohort study investigates the association between insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1), bone mineral density, and frailty phenotype in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
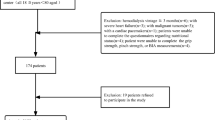
Forty-six patients (median age 14.5 years) were prospectively enrolled. Frailty phenotype was defined as the presence ≥ 3 of the following indicators: suboptimal growth/weight gain (body mass index height age < 5th percentile or height < 3rd percentile or loss of ≥ 10 percentiles/year in at least one parameter), low muscle mass (lean tissue mass height age < 5th percentile or loss of ≥ 10 percentiles/year), general fatigue reported by parent or child, and C-reactive protein > 3 mg/l. Lumbar bone mineral apparent density (LBMAD) was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, body composition by bioimpedance spectroscopy, and IGF-1 by enzyme-labeled chemiluminescent immunometric assay.
Results
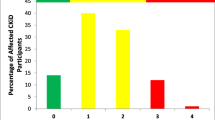
Frailty phenotype (seven patients) was more frequent in advanced CKD (estimated glomerular filtration rate < 30 ml/min/1.73m2) (p = 0.014). IGF-1 and LBMAD z-scores were lower in patients with suboptimal growth/weight gain (14 patients) (p = 0.013, p = 0.012), low muscle mass (nine patients) (p = 0.001, p = 0.009), and general fatigue (eight patients) (p < 0.001, p = 0.004). IFG-1 and LBMAD z-scores were associated with frailty phenotype (OR 0.109, 95% CI 0.015–0.798 and OR 0.277, 95% CI 0.085–0.903) after adjustment for CKD stage. IGF-1 z-score was associated with LBMAD < 5th percentile (six patients) (OR 0.020, 95% CI 0.001–0.450) after adjustment for CKD stage. The association between LBMAD and frailty phenotype lost significance after adjustment for IGF-1.
Conclusion
Frailty phenotype is more frequent in advanced pediatric CKD. IGF-1 is negatively associated with frailty phenotype and interferes in the association between frailty and LBMAD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, Seeman T, Tracy R, Kop WJ, Burke G, McBurnie MA, Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group (2001) Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 56:M146–MM56
Nixon AC, Bampouras TM, Pendleton N, Woywodt A, Mitra S, Dhaygude A (2018) Frailty and chronic kidney disease: current evidence and continuing uncertainties. Clin Kidney J 11:236–245
Sgambat K, Matheson MB, Hooper SR, Warady B, Furth S, Moudgil A (2019) Prevalence and outcomes of fragility: a frailty-inflammation phenotype in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 34:2563–2569
Greco EA, Pietschmann P, Migliaccio S (2019) Osteoporosis and sarcopenia increase frailty syndrome in the elderly. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10:255
Clegg A, Hassan-Smith Z (2018) Frailty and the endocrine system. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 6:743–752
Leng S, Chen X, Mao G (2014) Frailty syndrome: an overview. Clin Interv Aging 9:433
Kim JC, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD (2013) Frailty and protein-energy wasting in elderly patients with end stage kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:337–351
Bikle DD, Tahimic C, Chang W, Wang Y, Philippou A, Barton ER (2015) Role of IGF-I signaling in muscle bone interactions. Bone 80:79–88
Oh Y (2012) The insulin-like growth factor system in chronic kidney disease: pathophysiology and therapeutic opportunities. Kidney Res Clin Pract 31:26–37
Bacchetta J, Harambat J, Cochat P, Salusky IB, Wesseling-Perry K (2012) The consequences of chronic kidney disease on bone metabolism and growth in children. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:3063–3071
Blum WF (1991) Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF binding proteins in chronic renal failure: evidence for reduced secretion of IGFs. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 379:24–31
Tönshoff B, Blum WF, Mehls O (1997) Derangements of the somatotropic hormone axis in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int Suppl 58:S106–SS13
Doi T, Makizako H, Tsutsumimoto K, Hotta R, Nakakubo S, Makino K, Suzuki T, Shimada H (2018) Association between insulin-like growth factor-1 and frailty among older adults. J Nutr Health Aging 22:68–72
Leng SX, Cappola AR, Andersen RE, Blackman MR, Koenig K, Blair M, Walston JD (2004) Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), and their relationships with serum interleukin-6, in the geriatric syndrome of frailty. Aging Clin Exp Res 16:153–157
Li G, Thabane L, Papaioannou A, Ioannidis G, Levine MA, Adachi JD (2017) An overview of osteoporosis and frailty in the elderly. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18:46
Kojima G (2016) Frailty as a predictor of fractures among community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone 90:116–122
Bakkaloglu SA, Wesseling-Perry K, Pereira RC, Gales B, Wang HJ, Elashoff RM, Salusky IB (2010) Value of the new bone classification system in pediatric renal osteodystrophy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1860–1866
Denburg MR, Tsampalieros AK, de Boer IH, Shults J, Kalkwarf HJ, Zemel BS, Foerster D, Stokes D, Leonard MB (2013) Mineral metabolism and cortical volumetric bone mineral density in childhood chronic kidney disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1930–1938
Lalayiannis AD, Crabtree NJ, Fewtrell M, Biassoni L, Milford DV, Ferro CJ, Shroff R (2019) Assessing bone mineralisation in children with chronic kidney disease: what clinical and research tools are available? Pediatr Nephrol 35:937–957
Wells JCK, Williams JE, Chomtho S, Darch T, Grijalva-Eternod C, Kennedy K, Haroun D, Wilson C, Cole TJ, Fewtrell MS (2012) Body-composition reference data for simple and reference techniques and a 4-component model: a new UK reference child. Am J Clin Nutr 96:1316–1326
Crichton A, Knight S, Oakley E, Babl FE, Anderson V (2015) Fatigue in child chronic health conditions: a systematic review of assessment instruments. Pediatrics 135:e1015–e1031
Roumelioti ME, Wentz A, Schneider MF, Gerson AC, Hooper S, Benfield M, Warady BA, Furth SL, Unruh ML (2010) Sleep and fatigue symptoms in children and adolescents with CKD: a cross-sectional analysis from the chronic kidney disease in children (CKiD) study. Am J Kidney Dis 55:269–280
Crabtree NJ, Shaw NJ, Bishop NJ, Adams JE, Mughal MZ, Arundel P, Fewtrell MS, Ahmed SF, Treadgold LA, Högler W, Bebbington NA, Ward KA (2017) Amalgamated reference data for size-adjusted bone densitometry measurements in 3598 children and young adults—the ALPHABET study. J Bone Miner Res 32:172–180
Löfqvist C, Andersson E, Gelander L, Rosberg S, Blum WF, Albertsson Wikland K (2001) Reference values for IGF-I throughout childhood and adolescence: a model that accounts simultaneously for the effect of gender, age, and puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:5870–5876
Onder G, Vetrano DL, Marengoni A, Bell JS, Johnell K, Palmer K (2018) Accounting for frailty when treating chronic diseases. Eur J Intern Med 56:49–52
Worthen G, Tennankore K (2019) Frailty screening in chronic kidney disease: current perspectives. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 12:229–239
Kim JC, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD (2013) Frailty and protein-energy wasting in elderly patients with end stage kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:337–351
Jia T, Axelsson TG, Heimbürger O, Bárány P, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P, Qureshi AR (2014) IGF-1 and survival in ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:120–127
Rashid Qureshi A, Alvestrand A, Divino-Filho JC, Gutierrez A, Heimbürger O, Lindholm B, Bergström J (2001) Inflammation, malnutrition, and cardiac disease as predictors of mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:S28–S36
Fernández-Reyes MJ, Alvarez-Ude F, Sánchez R, Mon C, Iglesias P, Díez JJ, Vázquez A (2002) Inflammation and malnutrition as predictors of mortality in patients on hemodialysis. J Nephrol 15:136–143
Qureshi AR, Alvestrand A, Danielsson A, Divino-Filho JC, Gutierrez A, Lindholm B, Bergström J (1998) Factors predicting malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study. Kidney Int 53:773–782
Ascenzi F, Barberi L, Dobrowolny G, Villa Nova Bacurau A, Nicoletti C, Rizzuto E, Rosenthal N, Scicchitano BM, Musarò A (2019) Effects of IGF-1 isoforms on muscle growth and sarcopenia. Aging Cell 18:e12954
Allain TJ, Bearn JA, Coskeran P, Jones J, Checkley A, Butler J, Wessely S, Miell JP (1997) Changes in growth hormone, insulin, insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), and IGF-binding protein-1 in chronic fatigue syndrome. Biol Psychiatry 41:567–573
Lucia Casadonte CJ, Brown J, Strople J, Neighbors K, Fei L, Alonso EM (2018) Low insulin-like growth factor-1 influences fatigue and quality of life in children with inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 67:616–621
Szczêsny E, OElusarczyk J, Glombik K, Budziszewska B, Kubera M, Lasoń W, Basta-Kaim A (2013) Possible contribution of IGF-1 to depressive disorder. Pharmacol Rep 65:1622–1631
Chennaoui M, Léger D, Gomez-Merino D (2020) Sleep and the GH/IGF-1 axis: consequences and countermeasures of sleep loss/disorders. Sleep Med Rev 49:101223
Bartosch P, McGuigan FE, Akesson KE (2018) Progression of frailty and prevalence of osteoporosis in a community cohort of older women—a 10-year longitudinal study. Osteoporos Int 29:2191–2199
Kenny AM, Waynik IY, Smith JA, Fortinsky R, Kleppinger A, McGee D (2006) Association between level of frailty and bone mineral density in community-dwelling men. J Clin Densitom 9:309–314
Wasserman H, O’Donnell JM, Gordon CM (2017) Use of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in pediatric patients. Bone 104:84–90
Tsampalieros A, Kalkwarf HJ, Wetzsteon RJ, Shults J, Zemel BS, Foster BJ, Foerster DL, Leonard MB (2013) Changes in bone structure and the muscle-bone unit in children with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 83:495–502
Swolin-Eide D, Magnusson P, Hansson S (2007) Bone mass, biochemical markers and growth in children with chronic kidney disease: a 1-year prospective study. Acta Paediatr 96:720–725
van der Sluis IM, Boot AM, Nauta J, Hop WC, de Jong MC, Lilien MR, Groothoff JW, van Wijk AE, Pols HA, Hokken-Koelega AC, de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM (2000) Bone density and body composition in chronic renal failure: effects of growth hormone treatment. Pediatr Nephrol 15:221–228
Van Dyck M, Gyssels A, Proesmans W, Nijs J, Eeckels R (2001) Growth hormone treatment enhances bone mineralisation in children with chronic renal failure. Eur J Pediatr 160:359–363
Kovács GT, Oh J, Kovács J, Tönshoff B, Hunziker EB, Zapf J, Mehls O (1996) Growth promoting effects of growth hormone and IGF-I are additive in experimental uremia. Kidney Int 49:1413–1421
Sun DF, Chen Y, Rabkin R (2006) Work-induced changes in skeletal muscle IGF-1 and myostatin gene expression in uremia. Kidney Int 70:453–459
Moinuddin I, Leehey DJ (2008) A comparison of aerobic exercise and resistance training in patients with and without chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 15:83–96
Bacchetta J, Salusky IB (2016) Combining exercise and growth hormone therapy: how can we translate from animal models to chronic kidney disease children? Nephrol Dial Transplant 31:1191–1194
Weber LT, Mehls O (2010) Limitations of dual x-ray absorptiometry in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 25:3–5
Crabtree NJ, Arabi A, Bachrach LK, Fewtrell M, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Kecskemethy HH, Jaworski M, Gordon CM, International Society for Clinical Densitometry (2014) Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry interpretation and reporting in children and adolescents: the revised 2013 ISCD pediatric official positions. J Clin Densitom 17:225–242
Milani GP, Groothoff JW, Vianello FA, Fossali EF, Paglialonga F, Consolo S, Edefonti A, Consonni D, van Harskamp D, van Goudoever JB, Schierbeek H, Agostoni C, Oosterveld MJS (2018) Bioimpedance spectroscopy imprecisely assesses lean body mass in pediatric dialysis patients. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 67:533–537
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karava, V., Dotis, J., Christoforidis, A. et al. Association between insulin growth factor-1, bone mineral density, and frailty phenotype in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 36, 1861–1870 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-04918-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-04918-y