Abstract
Rituximab has emerged as an effective and important therapy in children with complicated frequently relapsing and steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome to induce long-term disease remission and avoid steroid toxicities. The optimal rituximab regimen is not totally well defined, and there are many varying practices worldwide. We will in this review describe how patient factors, rituximab dose, and use of maintenance immunosuppression affect treatment outcomes. Specifically, low-dose rituximab without concomitant immunosuppression is associated with shorter relapse-free duration while other regimens have comparable outcomes. Patients with more severe disease generally have worse response to rituximab. Although rituximab appears to be generally safe, there are growing concerns of chronic hypogammaglobulinemia and impaired immunity especially in young children. Reliable prognostications and biomarkers for guiding subsequent treatments to avoid excessive treatments are yet to be identified. In this review, we will outline the, as we see it, best approach of rituximab in childhood steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome at the present state of knowledge.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chanchlani R, Parekh RS (2016) Ethnic differences in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Front Pediatr 4:39
Webb N, Woolley R, Lambe T, Frew E, Brettell E, Barsoum E, Trompeter R, Cummins C, Deeks J, Wheatley K (2019) Long term tapering versus standard prednisolone treatment for first episode of childhood nephrotic syndrome: phase III randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation. Bmj 365:I1800
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K (2017) Rituximab for nephrotic syndrome in children. Clin Exp Nephrol 21(2):193–202
Benz K, Dötsch J, Rascher W, Stachel D (2004) Change of the course of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19(7):794–797
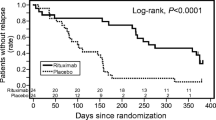
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, Miura K, Aya K, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y (2014) Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet 384(9950):1273–1281
Ravani P, Rossi R, Bonanni A, Quinn RR, Sica F, Bodria M, Pasini A, Montini G, Edefonti A, Belingheri M (2015) Rituximab in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter, open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(9):2259–2266
Ruggenenti P, Ruggiero B, Cravedi P, Vivarelli M, Massella L, Marasà M, Chianca A, Rubis N, Ene-Iordache B, Rudnicki M (2014) Rituximab in steroid-dependent or frequently relapsing idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 25(4):850–863
Basu B, Sander A, Roy B, Preussler S, Barua S, Mahapatra T, Schaefer F (2018) Efficacy of rituximab vs. tacrolimus in pediatric corticosteroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr 172(8):757–764
Prytuła A, Iijima K, Kamei K, Geary D, Gottlich E, Majeed A, Taylor M, Marks SD, Tuchman S, Camilla R (2010) Rituximab in refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25(3):461–468
Deschênes G, Vivarelli M, Peruzzi L (2017) Variability of diagnostic criteria and treatment of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome across European countries. Eur J Pediatr 176(5):647–654
Kamei K, Ogura M, Sato M, Sako M, Iijima K, Ito S (2016) Risk factors for relapse and long-term outcome in steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome treated with rituximab. Pediatr Nephrol 31(1):89–95
Ito S, Kamei K, Ogura M, Udagawa T, Fujinaga S, Saito M, Sako M, Iijima K (2013) Survey of rituximab treatment for childhood-onset refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28(2):257–264
Ito S, Kamei K, Ogura M, Sato M, Fujimaru T, Ishikawa T, Udagawa T, Iijima K (2011) Maintenance therapy with mycophenolate mofetil after rituximab in pediatric patients with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 26(10):1823–1828
Sinha A, Bhatia D, Gulati A, Rawat M, Dinda AK, Hari P, Bagga A (2014) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in children with difficult-to-treat nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transpl 30(1):96–106
Kemper MJ, Gellermann J, Habbig S, Krmar RT, Dittrich K, Jungraithmayr T, Pape L, Patzer L, Billing H, Weber L (2011) Long-term follow-up after rituximab for steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transpl 27(5):1910–1915
Chan EY-H, Webb H, Yu E, Ghiggeri GM, Kemper MJ, Ma AL-T, Yamamura T, Sinha A, Bagga A, Hogan J (2020) Both the rituximab dose and maintenance immunosuppression in steroid-dependent/frequently-relapsing nephrotic syndrome have important effects on outcomes. Kidney Int 97(2):393–401
Fujinaga S, Hirano D, Mizutani A, Sakuraya K, Yamada A, Sakurai S, Shimizu T (2017) Predictors of relapse and long-term outcome in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab treatment. Clin Exp Nephrol 21(4):671–676
Hogan J, Dossier C, Kwon T, Macher M-A, Maisin A, Couderc A, Niel O, Baudouin V, Deschênes G (2018) Effect of different rituximab regimens on B cell depletion and time to relapse in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 34(2):253–259
Ahn YH, Kim SH, Han KH, Choi HJ, Cho H, Lee JW, Shin JI, Cho MH, Lee JH, Park YS (2018) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in childhood-onset, difficult-to-treat nephrotic syndrome: A multicenter open-label trial in Korea. Medicine (Baltimore) 97(46)
Webb H, Jaureguiberry G, Dufek S, Tullus K, Bockenhauer D (2016) Cyclophosphamide and rituximab in frequently relapsing/steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 31(4):589–594
Maxted AP, Dalrymple RA, Chisholm D, McColl J, Tse Y, Christian MT, Reynolds BC (2019) Low-dose rituximab is no less effective for nephrotic syndrome measured by 12-month outcome. Pediatr Nephrol 34(5):855–863
Basu B, Mahapatra T, Mondal N (2015) Mycophenolate mofetil following rituximab in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatrics 136(1):e132–e139
Fujinaga S, Someya T, Watanabe T, Ito A, Ohtomo Y, Shimizu T, Kaneko K (2013) Cyclosporine versus mycophenolate mofetil for maintenance of remission of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after a single infusion of rituximab. Eur J Pediatr 172(4):513–518
Horinouchi T, Sako M, Nakanishi K, Ishikura K, Ito S, Nakamura H, Oba MS, Nozu K, Iijima K (2018) Study protocol: mycophenolate mofetil as maintenance therapy after rituximab treatment for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently-relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (JSKDC07). BMC nephrol 19(1):302
Bonanni A, Calatroni M, D'alessandro M, Signa S, Bertelli E, Cioni M, Di Marco E, Biassoni R, Caridi G, Ingrasciotta G (2018) Adverse events linked with the use of chimeric and humanized anti-CD20 antibodies in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Br J Clin Pharmacol 84(6):1238–1249
Parmentier C, Delbet J-D, Decramer S, Boyer O, Hogan J, Ulinski T (2019) Immunoglobulin serum levels in rituximab-treated patients with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 35(3):455–462
Fujinaga S, Sakuraya K, Yamada A, Urushihara Y, Ohtomo Y, Shimizu T (2015) Positive role of rituximab in switching from cyclosporine to mycophenolate mofetil for children with high-dose steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 30(4):687–691
Kamei K, Ogura M, Sato M, Ito S, Ishikura K (2018) Infusion reactions associated with rituximab treatment for childhood-onset complicated nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 33(6):1013–1018
Tsutsumi Y, Kanamori H, Mori A, Tanaka J, Asaka M, Imamura M, Masauzi N (2005) Reactivation of hepatitis B virus with rituximab. Expert Opin Drug Saf 4(3):599–608
Chaumais M-C, Garnier A, Chalard F, Peuchmaur M, Dauger S, Jacqz-Agrain E, Deschênes G (2009) Fatal pulmonary fibrosis after rituximab administration. Pediatr Nephrol 24(9):1753–1755
Boren EJ, Cheema GS, Naguwa SM, Ansari AA, Gershwin ME (2008) The emergence of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in rheumatic diseases. J Autoimmun 30(1-2):90–98
Gea-Banacloche JC (2010) Rituximab-associated infections. Seminars in hematology 47(2):187–198
Sellier-Leclerc A-L, Belli E, Guérin V, Dorfmüller P, Deschênes G (2013) Fulminant viral myocarditis after rituximab therapy in pediatric nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28(9):1875–1879
Sato M, Ito S, Ogura M, Kamei K, Miyairi I, Miyata I, Higuchi M, Matsuoka K (2013) Atypical Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia with multiple nodular granulomas after rituximab for refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28(1):145–149
Kamei K, Takahashi M, Fuyama M, Saida K, Machida H, Sato M, Ogura M, Ito S (2014) Rituximab-associated agranulocytosis in children with refractory idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: case series and review of literature. Nephrol Dial Transpl 30(1):91–96
Peuvrel L, Chiffoleau A, Quéreux G, Brocard A, Saint-Jean M, Batz A, Jolliet P, Dréno B (2013) Melanoma and rituximab: an incidental association? Derm 226(3):274–278
Velter C, Pagès C, Schneider P, Osio A, Brice P, Lebbé C (2014) Four cases of rituximab-associated melanoma. Melanoma Res 24(4):401–403
Tarella C, Passera R, Magni M, Benedetti F, Rossi A, Gueli A, Patti C, Parvis G, Ciceri F, Gallamini A (2010) Risk factors for the development of secondary malignancy after high-dose chemotherapy and autograft, with or without rituximab: a 20-year retrospective follow-up study in patients with lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 29(7):814–824
Colucci M, Carsetti R, Serafinelli J, Rocca S, Massella L, Gargiulo A, Lo Russo A, Capponi C, Cotugno N, Porzio O (2019) Prolonged impairment of immunological memory after anti-CD20 treatment in pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Front Immunol 10:1653
Wijetilleka S, Jayne DR, Mukhtyar C, Ala A, Bright PD, Chinoy H, Harper L, Kazmi MA, Kiani-Alikhan S, Li CK (2019) Recommendations for the management of secondary hypogammaglobulinaemia due to B cell targeted therapies in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology 58(5):889–896
Kamei K, Ishikura K, Sako M, Aya K, Tanaka R, Nozu K, Kaito H, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Miura K (2017) Long-term outcome of childhood-onset complicated nephrotic syndrome after a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of rituximab. Pediatr Nephrol 32(11):2071–2078
Basu B, Sander A, Preussler S, Sinha Mahapatra T, Schaefer F (2019) IPN11036-82 Long-term efficacy of rituximab & MMF maintenance - therapy in childhood SDNS. Abstracts of the 18th Congress of the International Pediatric Nephrology Association, Venice (Italy), October 2019. Pediatr Nephrol 34:1821–2260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04325-4
Kim JH, Park E, Hyun HS, Cho MH, Ahn YH, Choi HJ, Kang HG, Ha I-S, Cheong HI (2017) Long-term repeated rituximab treatment for childhood steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Res Clin Pract 36(3):257
Ramachandran R, Bharati J, Rao I, Kashif AW, Nada R, Minz R, Gupta KL, Kohli HS (2019) Persistent CD-19 depletion by rituximab is cost-effective in maintaining remission in calcineurin-inhibitor dependent podocytopathy. Nephrology (Carlton) 24(12):1241–1247
Delbet JD, Leclerc G, Ulinski T (2019) Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome and rituximab: may we predict circulating B lymphocytes recovery? Pediatr Nephrol 34(3):529–532
Sato M, Kamei K, Ogura M, Ishikura K, Ito S (2018) Relapse of nephrotic syndrome during post-rituximab peripheral blood B-lymphocyte depletion. Clin Exp Nephrol 22(1):110–116
Colucci M, Corpetti G, Emma F, Vivarelli M (2018) Immunology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 33(4):573–584
Colucci M, Carsetti R, Cascioli S, Serafinelli J, Emma F, Vivarelli M (2019) B cell phenotype in pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 34(1):177–181
Colucci M, Carsetti R, Cascioli S, Casiraghi F, Perna A, Ravà L, Ruggiero B, Emma F, Vivarelli M (2016) B cell reconstitution after rituximab treatment in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(6):1811–1822
Kimata T, Hasui M, Kino J, Kitao T, Yamanouchi S, Tsuji S, Kaneko K (2013) Novel use of rituximab for steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. Am J Npehrol 38(6):483–488
Takahashi T, Okamoto T, Sato Y, Yamazaki T, Hayashi A, Aoyagi H, Ueno M, Kobayashi N, Uetake K, Nakanishi M (2019) Periodically repeated rituximab administrations in children with refractory nephrotic syndrome: 2-year multicenter observational study. Pediatr Nephrol 34(1):87–96
Ahn YH, Kang HG, Lee JM, Choi HJ, Ha I-S, Cheong HI (2014) Development of antirituximab antibodies in children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 29(8):1461–1464
Chan C-Y, Liu ID, Resontoc LP, Ng K-H, Chan Y-H, Lau PY-W, Than M, Jordan SC, Lam K-P, Yeo W-S (2016) T lymphocyte activation markers as predictors of responsiveness to rituximab among patients with FSGS. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(8):1360–1368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, E.Yh., Tullus, K. Rituximab in children with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome: in quest of the optimal regimen. Pediatr Nephrol 36, 1397–1405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04609-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04609-0