Abstract
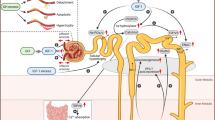
Renal disease in children disrupts the growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis and causes growth failure. Although GH therapy stimulates growth in these children, their short stature is likely due to a form of IGF-1 deficiency (IGFD) rather than GH deficiency. Recent experimental data have caused us to reconsider the importance of IGF-1 and IGFD to human growth. Pharmacology studies in rodents, as well as studies in patients with no functional GH receptors and primary IGFD, have shown that IGF-1 is an effective growth-promoting therapy. Gene knockout studies in mice have shown that IGF-1, rather than GH, is the major hormone controlling growth. In addition, both pharmacological and genetic studies have shown that there are effects of GH and IGF-1 that require their combined presence. In children with primary IGFD, where there is no GH signaling, recombinant human (rh)IGF-1 produces a large growth response, while in children who are GH and IGF-1 deficient, treatment with rhGH is the most-appropriate therapy. Children with short stature due to renal failure are GH sufficient and have some GH receptor signaling capacity, so that rhIGF-1, or rhIGF-1 plus rhGH, are logical therapeutic options and merit clinical testing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daughaday WH (1989) A personal history of the origin of the somatomedin hypothesis and recent challenges to its validity. Perspect Biol Med 32:194–211
Salmon WD Jr, Daughaday WH (1990) A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J Lab Clin Med 116:408–419
Rinderknecht E, Humbel RE (1978) The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem 253:2769–2776
Isaksson OG, Jansson JO, Gause IA (1982) Growth hormone stimulates longitudinal bone growth directly. Science 216:1237–1239
Isaksson OG, Lindahl A, Nilsson A, Isgaard J (1987) Mechanism of the stimulatory effect of growth hormone on longitudinal bone growth. Endocr Rev 8:426–438
Skottner A, Clark RG, Robinson IC, Fryklund L (1987) Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor: testing the somatomedin hypothesis in hypophysectomized rats. J Endocrinol 112:123–132
Laron Z (1999) The essential role of IGF-I: lessons from the long-term study and treatment of children and adults with Laron syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:4397–4404
Mehls O, Schaefer F, Tonshoff B (2003) Growth disorders in chronic renal failure. Oxford PharmaGenesis, Oxford, pp 1–119
Powell-Braxton L, Hollingshead P, Giltinan D, Pitts-Meek S, Stewart T (1993) Inactivation of the IGF-I gene in mice results in perinatal lethality. Ann N Y Acad Sci 692:300–301
Liu JL, Yakar S, LeRoith D (2000) Conditional knockout of mouse insulin-like growth factor-1 gene using the Cre/loxP system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 223:344–351
Woods KA, Camacho-Hubner C, Savage MO, Clark AJ (1996) Intrauterine growth retardation and postnatal growth failure associated with deletion of the insulin-like growth factor I gene. N Engl J Med 335:1363–1367
Sjogren K, Liu JL, Blad K, Skrtic S, Vidal O, Wallenius V, LeRoith D, Tornell J, Isaksson OG, Jansson JO, Ohlsson C (1999) Liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is the principal source of IGF-I in blood but is not required for postnatal body growth in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7088–7092
Yakar S, Liu JL, Stannard B, Butler A, Accili D, Sauer B, LeRoith D (1999) Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7324–7329
LeRoith D, Bondy C, Yakar S, Liu J-L, Butler A (2001) The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr Rev 22:53–74
Clark RG, Robinson IC (1996) Up and down the growth hormone cascade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 7:65–80
Firth SM, Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23:824–854
Yakar S, Rosen CJ, Beamer WG, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Wu Y, Liu JL, Ooi GT, Setser J, Frystyk J, Boisclair YR, LeRoith D (2002) Circulating levels of IGF-1 directly regulate bone growth and density. J Clin Invest 110:771–781
Tonshoff B, Blum WF, Wingen AM, Mehls O (1995) Serum insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF binding proteins 1, 2, and 3 in children with chronic renal failure: relationship to height and glomerular filtration rate. The European Study Group for Nutritional Treatment of Chronic Renal Failure in Childhood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:2684–2691
Tonshoff B, Veldhuis JD, Heinrich U, Mehls O (1995) Deconvolution analysis of spontaneous nocturnal growth hormone secretion in prepubertal children with preterminal chronic renal failure and with end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Res 37:86–93
Lupu F, Terwilliger JD, Lee K, Segre GV, Efstratiadis A (2001) Roles of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in mouse postnatal growth. Dev Biol 229:141–162
Clark RG, Mortensen DL, Carlsson LMS (1995) Insulin-like growth factor-1 and growth hormone (GH) have distinct and overlapping anabolic effects in GH-deficient rats. Endocrine 3:297–304
Clark RG, Thomas GB, Mortensen DL, Won WB, Ma YH, Tomlinson EE, Fairhall KM, Robinson IC (1997) Growth hormone secretagogues stimulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and are diabetogenic in the Zucker diabetic fatty rat. Endocrinology 138:4316–4323
Rosenfeld RG (1996) Biochemical diagnostic strategies in the evaluation of short stature: the diagnosis of insulin-like growth factor deficiency. Horm Res 46:170–173
Attie KM, Carlsson LM, Rundle AC, Sherman BM (1995) Evidence for partial growth hormone insensitivity among patients with idiopathic short stature. The National Cooperative Growth Study. J Pediatr 127:244–250
Rogol AD, Blethen SL, Sy JP, Veldhuis JD (2003) Do growth hormone (GH) serial sampling, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) or auxological measurements have an advantage over GH stimulation testing in predicting the linear growth response to GH therapy? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 58:229–237
Hazel SJ, Gillespie CM, Moore RJ, Clark RG, Jureidini KF, Martin AA (1994) Enhanced body growth in uremic rats treated with IGF-I and growth hormone in combination. Kidney Int 46:58–68
Kovacs GT, Oh J, Kovacs J, Tonshoff B, Hunziker EB, Zapf J, Mehls O (1996) Growth promoting effects of growth hormone and IGF-I are additive in experimental uremia. Kidney Int 49:1413–1421
Vijayan A, Franklin SC, Behrend T, Hammerman MR, Miller SB (1999) Insulin-like growth factor I improves renal function in patients with end-stage chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol 276:R929–R934
Guler HP, Schmid C, Zapf J, Froesch ER (1989) Effects of recombinant insulin-like growth factor I on insulin secretion and renal function in normal human subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2868–2872
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the IPNA Seventh Symposium on Growth and Development in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Molecular Basis of Skeletal Growth, 1–3 April 2004, Heidelberg, Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, R.G. Recombinant insulin-like growth factor-1 as a therapy for IGF-1 deficiency in renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 290–294 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1714-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1714-7