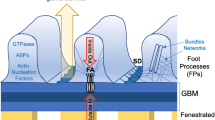
Abstract
The visceral glomerular epithelial cell, also known as the podocyte, plays an important role in the maintenance of renal glomerular function. This cell type is highly specialized and its foot processes together with the interposed slit diaphragm (SD) form the final barrier to urinary protein loss. Effacement of foot processes is associated with the development of proteinuria and—if not reversed in a certain time—with permanent deterioration of the glomerular filter. To maintain an intact glomerular filter barrier, podocyte-podocyte interactions and podocyte interactions with the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) are essential. Recent years have highlighted podocyte functions by unraveling the molecular composition of the SD, but have also clarified the important role of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton, and the podocyte-GBM interaction in the development of foot process (FP) effacement. This review provides an update of podocyte functions with respect to novel podocyte-specific proteins and also focuses on the dynamic interaction between the actin cytoskeleton of podocytes, their cell surface receptors and the GBM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Somlo S, Mundel P (2000) Getting a foothold in nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet 24:333–335
Kerjaschki D (2001) Caught flat-footed: podocyte damage and the molecular bases of focal glomerulosclerosis. J Clin Invest 108:1583–1587
Tryggvason K, Wartiovaara J (2001) Molecular basis of glomerular permselectivity. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10:543–549
Kaplan JM, Kim SH, North KN, Rennke H, Correia LA, Tong HQ, Mathis BJ, Rodriguez-Perez JC, Allen PG, Beggs AH, Pollak MR (2000) Mutations in ACTN4, encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 24:251–256
Mundel P, Shankland SJ (2002) Podocyte biology and response to injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:3005–3015
Topham PS, Kawachi H, Haydar SA, Chugh S, Addona TA, Charron KB, Holzman LB, Shia M, Shimizu F, Salant DJ (1999) Nephritogenic mAb 5-1-6 is directed at the extracellular domain of rat nephrin. J Clin Invest 104:1559–1566
Liu G, Kaw B, Kurfis J, Rahmanuddin S, Kanwar YS, Chugh SS (2003) Neph1 and nephrin interaction in the slit diaphragm is an important determinant of glomerular permeability. J Clin Invest 112:209–221
Simons M, Schwarz K, Kriz W, Miettinen A, Reiser J, Mundel P, Holthofer H (2001) Involvement of lipid rafts in nephrin phosphorylation and organization of the glomerular slit diaphragm. Am J Pathol 159:1069–1077
Verma R, Wharram B, Kovari I, Kunkel R, Nihalani D, Wary KK, Wiggins RC, Killen P, Holzman LB (2003) Fyn binds to and phosphorylates the kidney slit diaphragm component Nephrin. J Biol Chem 278:20716–20723
Regele HM, Fillipovic E, Langer B, Poczewki H, Kraxberger I, Bittner RE, Kerjaschki D (2000) Glomerular expression of dystroglycans is reduced in minimal change nephrosis but not in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:403–412
Raats CJ, Bakker MA, van den Born J, Berden JH (1997) Hydroxyl radicals depolymerize glomerular heparan sulfate in vitro and in experimental nephrotic syndrome. J Biol Chem 272:26734–26741
Kreidberg JA, Donovan MJ, Goldstein SL, Rennke H, Shepherd K, Jones RC, Jaenisch R (1996) Alpha 3 beta 1 integrin has a crucial role in kidney and lung organogenesis. Development 122:3537–3547
Noakes PG, Miner JH, Gautam M, Cunningham JM, Sanes JR, Merlie JP (1995) The renal glomerulus of mice lacking s-laminin/laminin beta 2: nephrosis despite molecular compensation by laminin beta 1. Nat Genet 10:400–406
Miner JH, Lewis RM, Sanes JR (1995) Molecular cloning of a novel laminin chain, alpha 5, and widespread expression in adult mouse tissues. J Biol Chem 270:28523–28526
Kretzler M, Teixeira VP, Unschuld PG, Cohen CD, Wanke R, Edenhofer I, Mundel P, Schlondorff D, Holthofer H (2001) Integrin-linked kinase as a candidate downstream effector in proteinuria. FASEB J 15:1843–1845
Smoyer WE, Mundel P (1998) Regulation of podocyte structure during the development of nephrotic syndrome. J Mol Med 76:172–183
Kos CH, Le TC, Sinha S, Henderson JM, Kim SH, Sugimoto H, Kalluri R, Gerszten RE, Pollak MR (2003) Mice deficient in alpha-actinin-4 have severe glomerular disease. J Clin Invest 111:1683–1690
Orlando RA, Takeda T, Zak B, Schmieder S, Benoit VM, McQuistan T, Furthmayr H, Farquhar MG (2001) The glomerular epithelial cell anti-adhesin podocalyxin associates with the actin cytoskeleton through interactions with ezrin. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1589–1598
Takeda T, McQuistan T, Orlando RA, Farquhar MG (2001) Loss of glomerular foot processes is associated with uncoupling of podocalyxin from the actin cytoskeleton. J Clin Invest 108:289–301
Quaggin SE (2002) Transcriptional regulation of podocyte specification and differentiation. Microsc Res Tech 57:208–211
Dressler GR, Woolf AS (1999) Pax2 in development and renal disease. Int J Dev Biol 43:463–468
Stayner CK, Cunliffe HE, Ward TA, Eccles MR (1998) Cloning and characterization of the human PAX2 promoter. J Biol Chem 273:25472–25479
Quaggin SE, Schwartz L, Cui S, Igarashi P, Deimling J, Post M, Rossant J (1999) The basic-helix-loop-helix protein Pod1 is critically important for kidney and lung organogenesis. Development 126:5771–5783
Lu J, Richardson JA, Olson EN (1998) Capsulin: a novel bHLH transcription factor expressed in epicardial progenitors and mesenchyme of visceral organs. Mech Dev 73:23–32
Imaki J, Onodera H, Tsuchiya K, Imaki T, Mochizuki T, Mishima T, Yamashita K, Yoshida K, Sakai M (2000) Developmental expression of maf-1 messenger ribonucleic acids in rat kidney by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 272:777–782
Sadl V, Jin F, Yu J, Cui S, Holmyard D, Quaggin S, Barsh G, Cordes S (2002) The mouse Kreisler (Krml1/MafB) segmentation gene is required for differentiation of glomerular visceral epithelial cells. Dev Biol 249:16–29
Dreyer SD, Morello R, German MS, Zabel B, Winterpacht A, Lunstrum GP, Horton WA, Oberg KC, Lee B (2000) LMX1B transactivation and expression in nail-patella syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 9:1067–1074
Kume T, Deng K, Hogan BL (2000) Minimal phenotype of mice homozygous for a null mutation in the forkhead/winged helix gene, Mf2. Mol Cell Biol 20:1419–1425
Kestila M, Lenkkeri U, Mannikko M, Lamerdin J, McCready P, Putaala H, Ruotsalainen V, Morita T, Nissinen M, Herva R, Kashtan CE, Peltonen L, Holmberg C, Olsen A, Tryggvason K (1998) Positionally cloned gene for a novel glomerular protein—nephrin—is mutated in congenital nephrotic syndrome PG-575-82. Mol Cell 1:575–582
Ruotsalainen V, Ljungberg P, Wartiovaara J, Lenkkeri U, Kestil M, Jalanko H, Holmberg C, Tryggvason K (1999) Nephrin is specifically located at the slit diaphragm of glomerular podocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7962–7967
Boute N, Gribouval O, Roselli S, Benessy F, Lee H, Fuchshuber A, Dahan K, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Antignac C (2000) NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet 24:349–354
Shih NY, Li J, Cotran R, Mundel P, Miner JH, Shaw AS (2001) CD2AP localizes to the slit diaphragm and binds to nephrin via a novel C-terminal domain. Am J Pathol 159:2303–2308
Kim JM, Wu H, Green G, Winkler CA, Kopp JB, Miner JH, Unanue ER, Shaw AS (2003) CD2-associated protein haploinsufficiency is linked to glomerular disease susceptibility. Science 300:1298–1300
Ciani L, Patel A, Allen ND, Ffrench-Constant C (2003) Mice lacking the giant protocadherin mFAT1 exhibit renal slit junction abnormalities and a partially penetrant cyclopia and anophthalmia phenotype. Mol Cell Biol 23:3575–3582
Hamano Y, Grunkemeyer JA, Sudhakar A, Zeisberg M, Cosgrove D, Morello R, Lee B, Sugimoto H, Kalluri R (2002) Determinants of vascular permeability in the kidney glomerulus. J Biol Chem 277:31154–31162
Rantanen M, Palmen T, Patari A, Ahola H, Lehtonen S, Astrom E, Floss T, Vauti F, Wurst W, Ruiz P, Kerjaschki D, Holthofer H (2002) Nephrin TRAP mice lack slit diaphragms and show fibrotic glomeruli and cystic tubular lesions. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1586–1594
Lahdenpera J, Kilpelainen P, Liu XL, Pikkarainen T, Reponen P, Ruotsalainen V, Tryggvason K (2003) Clustering-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of nephrin by Src family kinases. Kidney Int 64:404–413
Donoviel DB, Freed DD, Vogel H, Potter DG, Hawkins E, Barrish JP, Mathur BN, Turner CA, Geske R, Montgomery CA, Starbuck M, Brandt M, Gupta A, Ramirez-Solis R, Zambrowicz BP, Powell DR (2001) Proteinuria and perinatal lethality in mice lacking neph1, a novel protein with homology to nephrin. Mol Cell Biol 21:4829–4836
Huber TB, Schmidts M, Gerke P, Schermer B, Zahn A, Hartleben B, Sellin L, Walz G, Benzing T (2003) The carboxy terminus of Neph family members binds to the PDZ domain protein Zonula occludens-1. J Biol Chem (in press)
Schnabel E, Anderson JM, Farquhar MG (1990) The tight junction protein ZO-1 is concentrated along slit diaphragms of the glomerular epithelium. J Cell Biol 111:1255–1263
Li C, Ruotsalainen V, Tryggvason K, Shaw AS, Miner JH (2000) CD2AP is expressed with nephrin in developing podocytes and is found widely in mature kidney and elsewhere. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F785–792
Dustin ML, Olszowy MW, Holdorf AD, Li J, Bromley S, Desai N, Widder P, Rosenberger F, van der Merwe PA, Allen PM, Shaw AS (1998) A novel adaptor protein orchestrates receptor patterning and cytoskeletal polarity in T-cell contacts. Cell 94:667–677
Schwarz K, Simons M, Reiser J, Saleem MA, Faul C, Kriz W, Shaw AS, Holzman LB, Mundel P (2001) Podocin, a raft-associated component of the glomerular slit diaphragm, interacts with CD2AP and nephrin. J Clin Invest 108:1621–1629
Lynch DK, Winata SC, Lyons RJ, Hughes WE, Lehrbach GM, Wasinger V, Corthals G, Cordwell S, Daly RJ (2003) A Cortactin-CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) complex provides a novel link between epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis and the actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 278:21805–21813
Cormont M, Meton I, Mari M, Monzo P, Keslair F, Gaskin C, McGraw TE, Le Marchand-Brustel Y (2003) CD2AP/CMS regulates endosome morphology and traffic to the degradative pathway through its interaction with Rab4 and c-Cbl. Traffic 4:97–112
Inoue T, Yaoita E, Kurihara H, Shimizu F, Sakai T, Kobayashi T, Ohshiro K, Kawachi H, Okada H, Suzuki H, Kihara I, Yamamoto T (2001) FAT is a component of glomerular slit diaphragms. Kidney Int 59:1003–1012
Cho EA, Patterson LT, Brookhiser WT, Mah S, Kintner C, Dressler GR (1998) Differential expression and function of cadherin-6 during renal epithelium development. Development 125:803–812
Reiser J, Kriz W, Kretzler M, Mundel P (2000) The glomerular slit diaphragm is a modified adherens junction. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:1–8
Roselli S, Gribouval O, Boute N, Sich M, Benessy F, Attie T, Gubler MC, Antignac C (2002) Podocin localizes in the kidney to the slit diaphragm area. Am J Pathol 160:131–139
Sellin L, Huber TB, Gerke P, Quack I, Pavenstadt H, Walz G (2003) NEPH1 defines a novel family of podocin interacting proteins. FASEB J 17:115–117
Adler S (1992) Characterization of glomerular epithelial cell matrix receptors. Am J Pathol 141:571–578
Raats CJ, van Den Born J, Bakker MA, Oppers-Walgreen B, Pisa BJ, Dijkman HB, Assmann KJ, Berden JH (2000) Expression of agrin, dystroglycan, and utrophin in normal renal tissue and in experimental glomerulopathies. Am J Pathol 156:1749–1765
Suzuki A, Yoshida M, Hayashi K, Mizuno Y, Hagiwara Y, Ozawa E (1994) Molecular organization at the glycoprotein-complex-binding site of dystrophin. Three dystrophin-associated proteins bind directly to the carboxy-terminal portion of dystrophin. Eur J Biochem 220:283–292
Chen YJ, Spence HJ, Cameron JM, Jess T, Ilsley JL, Winder SJ (2003) Direct interaction of beta-dystroglycan with F-actin. Biochem J (in press)
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110:673–687
Hemler ME (1998) Integrin associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10:578–585
Kreidberg JA (2000) Functions of alpha3beta1 integrin. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:548–553
Chen HC, Chen CA, Guh JY, Chang JM, Shin SJ, Lai YH (2000) Altering expression of alpha3beta1 integrin on podocytes of human and rats with diabetes. Life Sci 67:2345–2353
Regoli M, Bendayan M (1997) Alterations in the expression of the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin in certain membrane domains of the glomerular epithelial cells (podocytes) in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 40:15–22
Baraldi A, Furci L, Zambruno G, Rubbiani E, Annessi G, Lusvarghi E (1992) Very late activation-3 integrin is the dominant beta 1-integrin on the glomerular capillary wall: an immunofluorescence study in nephrotic syndrome. Nephron 62:382–388
Kambham N, Tanji N, Seigle RL, Markowitz GS, Pulkkinen L, Uitto J, D’Agati VD (2000) Congenital focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associated with beta4 integrin mutation and epidermolysis bullosa. Am J Kidney Dis 36:190–196
Mayer G, Boileau G, Bendayan M (2003) Furin interacts with proMT1-MMP and integrin alphaV at specialized domains of renal cell plasma membrane. J Cell Sci 116:1763–1773
Miner JH (2001) Mystery solved: discovery of a novel integrin ligand in the developing kidney. J Cell Biol 154:257–259
Giancotti FG (2003) A structural view of integrin activation and signaling. Dev Cell 4:149–151
Ballestrem C, Hinz B, Imhof BA, Wehrle-Haller B (2001) Marching at the front and dragging behind: differential alphaVbeta3-integrin turnover regulates focal adhesion behavior. J Cell Biol 155:1319–1332
Miner JH (1999) Renal basement membrane components. Kidney Int 56:2016–2024
Abbi S, Guan JL (2002) Focal adhesion kinase: protein interactions and cellular functions. Histol Histopathol 17:1163–1171
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420:629–635
Chan YM, Bonnemann CG, Lidov HG, Kunkel LM (1998) Molecular organization of sarcoglycan complex in mouse myotubes in culture. J Cell Biol 143:2033–2044
Hannigan GE, Leung Hagesteijn C, Fitz Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J, Bell JC, Dedhar S (1996) Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature 379:91–96
Shirato I, Sakai T, Kimura K, Tomino Y, Kriz W (1996) Cytoskeletal changes in podocytes associated with foot process effacement in Masugi nephritis. Am J Pathol 148:1283–1296
Seiler MW, Venkatachalam MA, Cotran RS (1975) Glomerular epithelium: structural alterations induced by polycations. Science 189:390–393
Smoyer WE, Ransom RF (2002) Hsp27 regulates podocyte cytoskeletal changes in an in vitro model of podocyte process retraction. FASEB J 16:315–326
Mundel P, Kriz W (1996) Cell culture of podocytes. Exp Nephrol 4:263–266
Mundel P, Gilbert P, Kriz W (1991) Podocytes in glomerulus of rat kidney express a characteristic 44 KD protein. J Histochem Cytochem 39:1047–1056
Kemeny E, Durmuller U, Nickeleit V, Gudat F, Mihatsch MJ (1997) Distribution of podocyte protein (44 KD) in different types of glomerular diseases. Virchows Arch 431:425–430
Srivastava T, Garola RE, Whiting JM, Alon US (2001) Synaptopodin expression in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Kidney Int 59:118–125
Barisoni L, Kriz W, Mundel P, D’Agati V (1999) The dysregulated podocyte phenotype: a novel concept in the pathogenesis of collapsing idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and HIV-associated nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:51–61
Honda K, Yamada T, Endo R, Ino Y, Gotoh M, Tsuda H, Yamada Y, Chiba H, Hirohashi S (1998) Actinin-4, a novel actin-bundling protein associated with cell motility and cancer invasion [published erratum appears in J Cell Biol 1998 Oct 5;143(1):following 276]. J Cell Biol 140:1383–1393
Smoyer WE, Mundel P, Gupta A, Welsh MJ (1997) Podocyte alpha-actinin induction precedes foot process effacement in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Am J Physiol 273:F150–157
Pollak MR (2002) Inherited podocytopathies: FSGS and nephrotic syndrome from a genetic viewpoint. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:3016–3023
Goto H, Wakui H, Komatsuda A, Ohtani H, Imai H, Sawada K, Kobayashi R (2003) Renal alpha-actinin-4: purification and puromycin aminonucleoside-binding property. Nephron Exp Nephrol 93:e27–35
Arrondel C, Vodovar N, Knebelmann B, Grunfeld JP, Gubler MC, Antignac C, Heidet L (2002) Expression of the nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA in the human kidney and screening for MYH9 mutations in Epstein and Fechtner syndromes. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:65–74
Togawa A, Miyoshi J, Ishizaki H, Tanaka M, Takakura A, Nishioka H, Yoshida H, Doi T, Mizoguchi A, Matsuura N, Niho Y, Nishimune Y, Nishikawa S, Takai Y (1999) Progressive impairment of kidneys and reproductive organs in mice lacking Rho GDIalpha. Oncogene 18:5373–5380
Kriz W, Gretz N, Lemley KV (1998) Progression of glomerular diseases: is the podocyte the culprit? Kidney Int 54:687–697
Le Hir M, Keller C, Eschmann V, Hahnel B, Hosser H, Kriz W (2001) Podocyte bridges between the tuft and Bowman’s capsule: an early event in experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2060–2071
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, Ritz E, Atkins RC, Rohde R, Raz I (2001) Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 345:851–860
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S (2001) Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 345:861–869
Parving HH, Hommel E, Jensen BR, Hansen HP (2001) Long-term beneficial effect of ACE inhibition on diabetic nephropathy in normotensive type 1 diabetic patients. Kidney Int 60:228–234
Gloy J, Henger A, Fischer KG, Nitschke R, Mundel P, Bleich M, Schollmeyer P, Greger R, Pavenstadt H (1997) Angiotensin II depolarizes podocytes in the intact glomerulus of the rat. J Clin Invest 99:2772–2781
Mifsud SA, Allen TJ, Bertram JF, Hulthen UL, Kelly DJ, Cooper ME, Wilkinson-Berka JL, Gilbert RE (2001) Podocyte foot process broadening in experimental diabetic nephropathy: amelioration with renin-angiotensin blockade. Diabetologia 44:878–882
Bonnet F, Cooper ME, Kawachi H, Allen TJ, Boner G, Cao Z (2001) Irbesartan normalises the deficiency in glomerular nephrin expression in a model of diabetes and hypertension. Diabetologia 44:874–877
Macconi D, Ghilardi M, Bonassi ME, Mohamed EI, Abbate M, Colombi F, Remuzzi G, Remuzzi A (2000) Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on glomerular basement membrane permeability and distribution of zonula occludens-1 in MWF rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:477–489
Benigni A, Tomasoni S, Gagliardini E, Zoja C, Grunkemeyer JA, Kalluri R, Remuzzi G (2001) Blocking angiotensin II synthesis/activity preserves glomerular nephrin in rats with severe nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:941–948
Mimran A, Ribstein J (1999) Angiotensin receptor blockers: pharmacology and clinical significance. J Am Soc Nephrol 10 Suppl 12:S273–277
Campbell R, Sangalli F, Perticucci E, Aros C, Viscarra C, Perna A, Remuzzi A, Bertocchi F, Fagiani L, Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P (2003) Effects of combined ACE inhibitor and angiotensin II antagonist treatment in human chronic nephropathies. Kidney Int 63:1094–1103
Reeves WB, Andreoli TE (2000) Transforming growth factor beta contributes to progressive diabetic nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:7667–7669
Wendt T, Tanji N, Guo J, Hudson BI, Bierhaus A, Ramasamy R, Arnold B, Nawroth PP, Yan SF, D’Agati V, Schmidt AM (2003) Glucose, glycation, and RAGE: implications for amplification of cellular dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1383–1395
Wendt TM, Tanji N, Guo J, Kislinger TR, Qu W, Lu Y, Bucciarelli LG, Rong LL, Moser B, Markowitz GS, Stein G, Bierhaus A, Liliensiek B, Arnold B, Nawroth PP, Stern DM, D’Agati VD, Schmidt AM (2003) RAGE drives the development of glomerulosclerosis and implicates podocyte activation in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Pathol 162:1123–1137
Sharma K, McCue P, Dunn SR (2003) Diabetic kidney disease in the db/db mouse. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F1138–1144
Tanji N, Markowitz GS, Fu C, Kislinger T, Taguchi A, Pischetsrieder M, Stern D, Schmidt AM, D’Agati VD (2000) Expression of advanced glycation end products and their cellular receptor RAGE in diabetic nephropathy and nondiabetic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:1656–1666
Acknowledgements
J.O. was supported by the DFG and is currently funded by a research fellowship of the Kidney & Urology Foundation of America. P.M. is supported by grants from the NIH/NIDDK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, J., Reiser, J. & Mundel, P. Dynamic (re)organization of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton in the nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 19, 130–137 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1367-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1367-y