Abstract
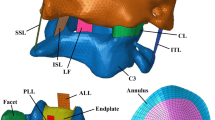
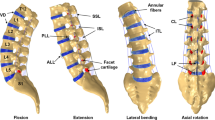
This study pursues the numerical validation of human lumbar spine segments. By means of the finite element (FE) method, computational analyses are carried out of various load cases. In particular Flexion–Extension, Lateral Bending and Axial Torque are considered. By means of a literature review the underlying constitutive data is verified. In this context, the heterogeneity of the annulus fibrosus, the transversely isotropic stress response of the spinal ligaments and aspects of the FE discretization are particularly emphasized. The numerical results show good agreement with experimental investigations for Extension and Axial Torque for a FE model that accounts for intact human lumbar spine response. In Flexion and Lateral Bending, however, the results of the intact FE-model do not properly account for the experimental data. A good correlation for these load cases can be found by taking disc degeneration into account in the FE-model. This fact shows that tissue degeneration plays a key role in the current validation process and must be accounted for if the lumbar spine specimen is employed for spinal implant evaluation. A degenerated FE-model that represents the stage of degeneration of the specimen and fits the experimental data for all load cases could not be found in this study and warrants further work in this area.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors are deeply indebted to Centerpulse Orthopedics Ltd., Winterthur, Switzerland (www.zimmer.com) for financial aid and support of this research. Additionally, the authors thank Darrell Goertzen for his work involving the experimental testing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eberlein, R., Holzapfel, G. & Fröhlich, M. Multi-segment FEA of the human lumbar spine including the heterogeneity of the annulus fibrosus. Computational Mechanics 34, 147–163 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-004-0563-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-004-0563-3