Abstract
Background
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with stent placement is used for the management of many pancreaticobiliary disorders. It is generally safe with a few short-term complications. The risk factors for the development of post-ERCP cholangitis due to stent occlusion have not been previously described. This study identified such risk factors among patients undergoing ERCP and stent placement for pancreatic or biliary obstruction.
Methods
3648 ERCPs performed at the University of Louisville from 2008 to 2016 were reviewed. Data including patient demographics, diagnostic, laboratory, and ERCP related data were included. Patients were classified as having post-ERCP cholangitis if they developed jaundice, fever, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, and confirmatory findings of stent occlusion and/or purulent drainage at the time of repeat ERCP. These patients were compared to those who did not develop post-ERCP cholangitis using univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results
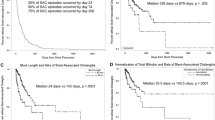
A total of 431 patients met inclusion criteria. Of these, 57 (13.2%) developed post-ERCP cholangitis. The average age of patients was 57 years with 57% women and 43% men. On univariate analysis, patients developing post-ERCP cholangitis were more likely to be of increased age, have higher white blood cell count (WBC), total bilirubin (TBili), AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase (AlkPhos), and a decreased serum albumin level. Risk factors for post-ERCP cholangitis due to stent occlusion identified on multivariate analysis include: a diagnosis of cancer, the placement of multiple biliary stents at index ERCP, and low serum albumin level.
Conclusions
The development of post-ERCP cholangitis due to stent occlusion is strongly associated with the presence of malignancy, the placement of multiple biliary stents, and low serum albumin. A decreased threshold to monitor for stent occlusion, including routine liver function tests and prophylactic stent removal or exchange, should be employed in patients with these characteristics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, Niro G, Valvano MR, Spirito F et al (2007) Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol 102(8):1781–1788
Cotton PB, Garrow DA, Gallagher J, Romagnuolo J (2009) Risk factors for complications after ERCP: a multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. YMGE. Am Soc Gastrointest Endosc 70(1):80–88
Bilbao MK, Dotter CT, Lee TG, Katon RM (1976) Complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). A study of 10,000 cases. Gastroenterology 70(3):314–320
Anderson MA, Fisher L, Jain R, Evans JA, Appalaneni V, Ben-Menachem T et al (2012) Complications of ERCP. YMGE 75(3):467–473
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, Geenen JE, Russell RC, Meyers WC et al (1991) Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. YMGE 37(3):383–393
Cotton PB, Garrow DA, Gallagher J, Romagnuolo J (2009) Risk factors for complications after ERCP: a multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. YMGE 70(1):80–88
Loperfido S, Angelini G, Benedetti G, Chilovi F, Costan F, De Berardinis F et al (1998) Major early complications from diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: a prospective multicenter study. YMGE 48(1):1–10
Vandervoort J, Soetikno RM, Tham TCK, Wong RCK, Ferrari AP, Montes H et al (2002) Risk factors for complications after performance of ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc 56(5):652–656
Kwon C-I, Lehman GA (2016) Mechanisms of biliary plastic stent occlusion and efforts at prevention. Clin Endosc 49(2):139–146
Kwon CI, Gromski MA, Sherman S, Easler JJ, El Hajj II, Watkins J et al (2016) Time sequence evaluation of biliary stent occlusion by dissection analysis of retrieved stents. Dig Dis Sci 61(8):2426–2435
Kullman E, Borch K, Lindstrom E, Ansehn S, Ihse I, Anderberg B (1992) Bacteremia following diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP. YMGE 38(4):444–449
Mollison LC, Desmond PV, Stockman KA, Andrew JH, Watson K, Shaw G et al (1994) A prospective study of septic complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(1):55–59
Kwak M-S, Jang ES, Ryu JK, Kim Y-T, Yoon YB, Park JK (2013) Risk Factors of Post Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Bacteremia. Gut Liver 7(2):228–233
Talukdar R (2016) Complications of ERCP. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 30(5):793–805
Szary NM, Al-Kawas FH (2013) Complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: how to avoid and manage them. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 30:1–9
Khashab MA, Kim K, Hutfless S, Lennon AM, Kalloo AN, Singh VK (2012) Predictors of early stent occlusion among plastic biliary stents. Dig Dis Sci 57(9):2446–2450
Kiriyama S, Takada T, Strasberg SM, Solomkin JS, Mayumi T, Pitt HA et al (2013) TG13 guidelines for diagnosis and severity grading of acute cholangitis (with videos). J HepatoBiliaryPancreatic Sci 20(1):24–34
Buxbaum JL, Biggins SW, Bagatelos KC, Inadomi JM, Ostroff JW (2011) Inoperable pancreatic cancer patients who have prolonged survival exhibit an increased risk of cholangitis. JOP 12(4):377–383
Pola S, Muralimohan R, Cohen B, Fehmi SMA, Savides TJ (2012) Long-term risk of cholangitis in patients with metal stents for malignant biliary obstruction. Dig Dis Sci 57(10):2693–2696
Schaible UE, Kaufmann SH (2007) Malnutrition and infection: complex mechanisms and global impacts. PLoS Med 4(5):e115
Bruera E (1997) ABC of palliative care. Anorexia, cachexia, and nutrition. BMJ 315(7117):1219–1222
Castle SC (2000) Clinical relevance of age-related immune dysfunction. Clin Infect Dis 31(2):578–585
Lawrence C, Romagnuolo J, Payne KM, Hawes RH, Cotton PB (2010) Low symptomatic premature stent occlusion of multiple plastic stents for benign biliary strictures: comparing standard and prolonged stent change intervals. YMGE. 72(3):558–563
Draganov P, Hoffman B, Marsh W, Cotton P, Cunningham J (2002) Long-term outcome in patients with benign biliary strictures treated endoscopically with multiple stents. Gastrointest Endosc 55(6):680–686
De Palma GD, Pezzullo A, Rega M, Persico M, Patrone F, Mastantuono L et al (2003) Unilateral placement of metallic stents for malignant hilar obstruction: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 58(1):50–53
De Palma GD, Galloro G, Siciliano S, Iovino P, Catanzano C (2001) Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic hepatic duct drainage in patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction: results of a prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Gastrointest Endosc 53(6):547–553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Bryce Stamp has no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures. Drs. Joshua Tierney, Neal Bhutiani, John S. Richey, Michael H. Bahr, and Gary C. Vitale have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tierney, J., Bhutiani, N., Stamp, B. et al. Predictive risk factors associated with cholangitis following ERCP. Surg Endosc 32, 799–804 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5746-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5746-z