Abstract
Background
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes (T2D) includes insulin resistance (IR) and insufficient insulin secretion. Remission in obese patients can be achieved through surgically induced weight loss. Sleeve gastrectomy is a novel technique for the treatment of morbid obesity, and its effects on the metabolic syndrome and T2D have not yet been fully understood.
Methods
From February 2008 to July 2010, sleeve gastrectomy as stand-alone treatment for severe or morbid obesity was performed in 23 patients with T2D or impaired fasting glucose (IFG). No postoperative complications occurred and patients were dismissed from hospital on day 2 after surgery. Body mass index (BMI), fasting blood glucose (FBG) and fasting insulin were determined before and up to 24 months after surgery. IR and beta cell function were calculated using the modified homeostasis model assessment (HOMA2).
Results
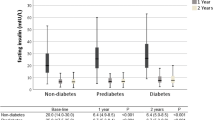
BMI, FBG and fasting insulin improved significantly as early as 3 months after surgery. Threefold increased preoperative insulin resistance (3.05) decreased to near-normal values (1.14) during the same period. Interestingly, overall beta cell function diminished at 12 months of follow-up (79.6 %), in comparison with preoperative values (117.8 %). Patients with a markedly reduced preoperative beta cell function (<40 %) did not achieve a complete remission after surgery.
Conclusions
In obese patients with T2D and IFG, commonly characterized by an augmented beta cell function and an increased insulin resistance, sleeve gastrectomy induces remission through reduction of insulin resistance. Preoperative IR and beta cell function calculated by HOMA2 deserve further studies in patients undergoing metabolic surgery.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
One patient with BMI < 35 kg/m2 at date of surgery due to standard preoperative diet.
One patient on oral antidiabetics with fasting glycemia <100 mg/dl.
References
DeFronzo RA (1992) Pathogenesis of type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus: a balanced overview. Diabetologia 35:389–397
Seppälä-Lindroos A, Vehkavaara S, Häkkinen A-M, Goto T, Westerbacka J, Sovijärvi A et al (2002) Fat accumulation in the liver is associated with defects in insulin suppression of glucose production and serum free fatty acids independent of obesity in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3023–3028
Guo Z (2007) Intramyocellular lipid kinetics and insulin resistance. Lipids Health Dis 6:18
Jiang G, Zhang BB (2003) Glucagon and regulation of glucose metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284:E671–E678
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, Banel D, Jensen MD, Pories WJ et al (2009) Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 122(248–256):e5
Le Roux CW, Aylwin SJB, Batterham RL, Borg CM, Coyle F, Prasad V et al (2006) Gut hormone profiles following bariatric surgery favor an anorectic state, facilitate weight loss, and improve metabolic parameters. Ann Surg 243:108–114
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R (1979) Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol 237:E214–E223
Bonora E, Targher G, Alberiche M, Bonadonna RC, Saggiani F, Zenere MB et al (2000) Homeostasis model assessment closely mirrors the glucose clamp technique in the assessment of insulin sensitivity: studies in subjects with various degrees of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 23:57–63
Benaiges D, Goday A, Ramon JM, Hernandez E, Pera M, Cano JF (2011) Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic gastric bypass are equally effective for reduction of cardiovascular risk in severely obese patients at one year of follow-up. Surg Obes Relat Dis (in press)
De Gordejuela AGR, Pujol Gebelli J, García NVNV, Alsina EFF, Medayo LS, Masdevall Noguera C (2011) Is sleeve gastrectomy as effective as gastric bypass for remission of type 2 diabetes in morbidly obese patients? Surg Obes Relat Dis 7:506–509
Levy JC, Matthews DR, Hermans MP (1998) Correct homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) evaluation uses the computer program. Diabetes Care 21:2191–2192
Reaven GM, Banting lecture (1988) Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988(37):1595–1607
Martin BC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS, Bergman RN, Soeldner JS, Kahn CR (1992) Role of glucose and insulin resistance in development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: results of a 25-year follow-up study. Lancet 340:925–929
Facchini FS, Hua N, Abbasi F, Reaven GM (2001) Insulin resistance as a predictor of age-related diseases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3574–3578
Rizzello M, Abbatini F, Casella G, Alessandri G, Fantini A, Leonetti F et al (2010) Early postoperative insulin-resistance changes after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg 20:50–55
Meier JJ, Gallwitz B, Salmen S, Goetze O, Holst JJ, Schmidt WE et al (2003) Normalization of glucose concentrations and deceleration of gastric emptying after solid meals during intravenous glucagon-like peptide 1 in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:2719–2725
Perseghin G, Scifo P, De Cobelli F, Pagliato E, Battezzati A, Arcelloni C et al (1999) Intramyocellular triglyceride content is a determinant of in vivo insulin resistance in humans: a 1H-13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy assessment in offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. Diabetes 48:1600–1606
Utzschneider KM, Kahn SE (2006) Review: the role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4753–4761
Bhat G, Baba CS, Pandey A, Kumari N, Choudhuri G (2012) Life style modification improves insulin resistance and liver histology in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 4:209–217
Petersen KF, Dufour S, Befroy D, Lehrke M, Hendler RE, Shulman GI (2005) Reversal of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis, hepatic insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia by moderate weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54:603–608
Mari A, Tura A, Natali A, Anderwald C, Balkau B, Lalic N et al (2011) Influence of hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance on in vivo β-cell function: their role in human β-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 60:3141–3147
Prentki M, Nolan CJ (2006) Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 116:1802–1812
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC (2003) Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52:102–110
Prentki M, Joly E, El-Assaad W, Roduit R (2002) Malonyl-CoA signaling, lipid partitioning, and glucolipotoxicity: role in beta-cell adaptation and failure in the etiology of diabetes. Diabetes 51(Suppl 3):S405–S413
Akash MSH, Rehman K, Chen S (2013) Role of inflammatory mechanisms in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cell Biochem 114:525–531
Jørgensen NB, Dirksen C, Bojsen-Møller KN, Jacobsen SH, Worm D, Hansen DL et al (2013) Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide 1 response is important for improved β-cell function and glucose tolerance after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 62:3044–3052
Marinari GM, Papadia FS, Briatore L, Adami G, Scopinaro N (2006) Type 2 diabetes and weight loss following biliopancreatic diversion for obesity. Obes Surg 16:1440–1444
De Paula AL, Stival AR, Macedo A, Ribamar J, Mancini M, Halpern A et al (2010) Prospective randomized controlled trial comparing 2 versions of laparoscopic ileal interposition associated with sleeve gastrectomy for patients with type 2 diabetes with BMI 21–34 kg/m2. Surg Obes Relat Dis 6:296–304
Strader AD, Vahl TP, Jandacek RJ, Woods SC, D’Alessio DA, Seeley RJ (2005) Weight loss through ileal transposition is accompanied by increased ileal hormone secretion and synthesis in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E447–E453
Disclosures
Hans Eickhoff, Ana Guimarães, Teresa Louro, Raquel Seiça, and Francisco Castro e Sousa have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All patients were treated at the Obesity Center of Hospital de Santiago, Setúbal, Portugal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eickhoff, H., Guimarães, A., Louro, T.M. et al. Insulin resistance and beta cell function before and after sleeve gastrectomy in obese patients with impaired fasting glucose or type 2 diabetes. Surg Endosc 29, 438–443 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3675-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3675-7