Abstract
Background
The endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) technique has been gaining popularity, with continued advances in this treatment approach. However, ESD still is associated with potential complications such as severe bleeding and perforation.
Methods
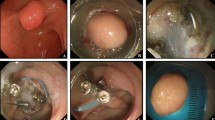
This study was performed to compare the clinical outcomes for macro- and microperforations with ESD procedures and to determine the short-term prognosis after ESD. A macroperforation was defined as a gross perforation that occurred during an ESD procedure, and a microperforation was defined by free air observed on simple radiography after the procedure. Immediate closure of macroperforations was performed using endoclips. From July 2003 through May 2008, 1,711 patients underwent ESD for gastric lesions such as dysplasia, early cancer, and subepithelial lesions.
Results
Among 39 perforation cases (2.3%), macroperforations occurred for 26 patients (67%) and microperforations for 13 patients (33%). All the patients except one who underwent emergency surgery because of severe bleeding and perforation during ESD were managed successfully by intravenous antibiotics and no oral intake. The clinical prognosis and endoscopic characteristics of the patients with macroperforations did not differ from those of the patients with microperforations.
Conclusions
Perforations associated with ESD could be managed safely and successfully by nonsurgical methods. The clinical prognoses for macro- and microperforations were favorable and comparable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soetikno R, Kaltenbach T, Yeh R, Gotoda T (2005) Endoscopic mucosal resection for early cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Oncol 23:4490–4498
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Ono S, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2006) Successful nonsurgical management of perforation complicating endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy 38:1001–1006
Takizawa K, Oda I, Gotoda T, Yokoi C, Matsuda T, Saito Y, Saito D, Ono H (2008) Routine coagulation of visible vessels may prevent delayed bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection: an analysis of risk factors. Endoscopy 40:179–183
Uedo N, Takeuchi Y, Yamada T, Ishihara R, Ogiyama H, Yamamoto S, Kato M, Tatsumi K, Masuda E, Tamai C, Yamamoto S, Higashino K, Iishi H, Tatsuta M (2007) Effect of a proton pump inhibitor or an H2-receptor antagonist on prevention of bleeding from ulcer after endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 102:1610–1616
Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Boku N, Ohtu A, Tajiri H, Yoshida S (2001) New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy 33:221–226
Yamamoto H, Kawata H, Sunada K, Satoh K, Kaneko Y, Ido K, Sugano K (2002) Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc 56:507–512
Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, Mouri R, Hirata M, Kawamura T, Yoshihara M, Chayama K (2006) Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 64:877–883
Jeong G, Lee JH, Yu MK, Moon W, Rhee PL, Paik SW, Rhee JC, Kim JJ (2006) Nonsurgical management of microperforation induced by EMR of the stomach. Dig Liver Dis 38:605–608
Kojima T, Parra-Blanco A, Takahashi H, Fujita R (1998) Outcome of endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer: review of the Japanese literature. Gastrointest Endosc 48:550–554; discussion 554–555
Minami S, Gotoda T, Ono H, Oda I, Hamanaka H (2006) Complete endoscopic closure of gastric perforation induced by endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer using endoclips can prevent surgery (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 63:596–601
Ono H, Kondo H, Gotoda T, Shirao K, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Hosokawa K, Shimoda T, Yoshida S (2001) Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer. Gut 48:225–229
Choi IJ, Kim CG, Chang HJ, Kim SG, Kook MC, Bae JM (2005) The learning curve for EMR with circumferential mucosal incision in treating intramucosal gastric neoplasm. Gastrointest Endosc 62:860–865
Rosch T, Sarbia M, Schumacher B, Deinert K, Frimberger E, Toermer T, Stolte M, Neuhaus H (2004) Attempted endoscopic en bloc resection of mucosal and submucosal tumors using insulated-tip knives: a pilot series. Endoscopy 36:788–801
Jeon SW, Jung MK, Cho CM, Tak WY, Kweon YO, Kim SK, Choi YH (2008) Predictors of immediate bleeding during endoscopic submucosal dissection in gastric lesions. Surg Endosc June 14, Epub ahead of print
Seewald S, Soehendra N (2006) Perforation: part and parcel of endoscopic resection? Gastrointest Endosc 63:602–605
Bittinger M, Messmann H (2007) Is nonsurgical management safe and effective for patients with microperforation caused by EMR? Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:134–135
Kim JJ, Lee JH, Jung HY, Lee GH, Cho JY, Ryu CB, Chun HJ, Park JJ, Lee WS, Kim HS, Chung MG, Moon JS, Choi SR, Song GA, Jeong HY, Jee SR, Seol SY, Yoon YB (2007) EMR for early gastric cancer in Korea: a multicenter retrospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 66:693–700
Takenaka R, Kawahara Y, Okada H, Hori K, Inoue M, Kawano S, Tanioka D, Tsuzuki T, Yagi S, Kato J, Uemura M, Ohara N, Yoshino T, Imagawa A, Fujiki S, Takata R, Yamamoto K (2008) Risk factors associated with local recurrence of early gastric cancers after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc 68:887–894
Disclosures
Drs. Seong Woo Jeon, Min Kyu Jung, Sung Kook Kim, Kwang Bum Cho, Kyung Sik Park, Chang Keun Park, Joong Goo Kwon, Eun Young Kim, Jin Tae Jung, Tae Nyeun Kim, Byung Ik Jang, and Chang Hun Yang have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, S.W., Jung, M.K., Kim, S.K. et al. Clinical outcomes for perforations during endoscopic submucosal dissection in patients with gastric lesions. Surg Endosc 24, 911–916 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0693-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0693-y