Abstract
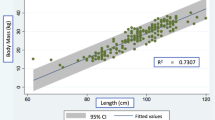
Background: Comparisons of splenic size based on splenic weight are difficult after laparoscopic splenectomy, which results in a morcellated specimen. We report the results of a direct comparison between morcellated and intact splenic weights. Methods: Porcine spleens were harvested via a midline laparotomy, and an intact splenic weight was obtained, which served as the control. The spleen then was placed into an impermeable retrieval bag and returned to the peritoneal cavity. A separate 10-mm incision was made and the spleen mechanically morcellated with a uterine forceps. This design most faithfully recreates the morcellation process during laparoscopic splenectomy in humans. The aggregate weight of the fragments was compared with intact splenic weight. Results: Intact and morcellated weights were obtained from 58 porcine spleens. The mean intact splenic weight was 145 g, and the mean morcellated weight was 78 g. For a given morcellated weight achieved at laparoscopic splenectomy, an estimated intact weight can be determined by the following formula: intact weight (g) = morcellated weight (g) × 1.34 + 45. Conclusions: On the basis of our calculations, a normal spleen weighing 150 g would have a mean morcellated weight of 78 g, and splenomegaly (intact spleen weighing 250 g or more) would be defined by a morcellated weight exceeding 153 g.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
RM Walsh B Chand J Brodsky BT Heniford (2002) ArticleTitleDetermination of intact splenic weight based on morcellated weight. Surg Endosc 16 851–854 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004640080095 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD383lvVagsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11997836
CW Chung WJ Lee JS Choi YW Ko JS Hans YH Min BT Kim (1999) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic splenectomy for immune thrombocytopenic purpura: long-term result of 40 laparoscopic splenectomies. Yonsei Med J 40 578–582 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7is1ykug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10661035
FH DeLand (1970) ArticleTitleNormal spleen size. Radiology 97 589–592 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CS6D2snlt1E%3D Occurrence Handle5491745
A Doini U Baccarani G Terrosu V Corno A Ermacora A Pasqualucci F Bresadola (1999) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic vs open splenectomy in the management of hematologic diseases. Surg Endosc 13 1220–1225 Occurrence Handle10594270
MT Downey (1992) ArticleTitleEstimation of splenic weight from ultrasonographic measurements. Can Assoc Radiol J 43 273–277 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A2cnkt1U%3D Occurrence Handle1638425
N Katkhouda MB Hurwitz (1999) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic splenectomy for hematologic disease. Adv Surg 33 141–161 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FjvVylsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10572565
N Katkhouda E Mavor (2000) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic splenectomy. Surg Clin North Am 80 1285–1297
J Myers RJ Segal (1974) ArticleTitleWeight of the spleen: I. Range of normal in a nonhospital population. Arch Pathol Lab Med 98 33–35 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSuC28fhvVE%3D
RA O’Reilly (1996) ArticleTitleSplenomegaly at a United States County Hospital: diagnostic evaluation of 170 patients. Am J Med Sci 312 160–165 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000441-199610000-00003 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD3crns1E%3D Occurrence Handle8853064
A Park M Marcaccio M Sternbach D Witzke P Fitzgerald (1999) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic vs open splenectomy. Arch Surg 134 1263–1269 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archsurg.134.11.1263 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2Fit1Gksg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10555644
InstitutionalAuthorName. (1974) Spleen. SL Robbins RS Cotran (Eds) Pathologic basis of disease. W.B. Saunders Philadelphia
S Sprogoe-Jakobsen U Sprogoe-Jakobsen (1997) ArticleTitleThe weight of the normal spleen. Forensic Sci Int 88 21–23
CJ Stanton (1999) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic splenectomy for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP): a five-year experience. Surg Endosc 13 1083–1086 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004649901178 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FivVCjtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10556443
A Szold B Sagi H Merhav JM Klausner (1998) ArticleTitleOptimizing laparoscopic splenectomy: technical details and experience in 59 patients. Surg Endosc 12 1078–1081 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004649900784 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czls1ersg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9685546
EM Targarona JJ Espert G Cerdan C Balague J Piulachs G Sugranes V Artigas M Trias (1999) ArticleTitleEffect of spleen size on splenectomy outcome: a comparison of open and laparoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 13 559–562 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004649901040 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3nvVGgtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10347290
V Velanovich (2000) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic vs open surgery: a preliminary comparison of quality-of-life outcomes. Surg Endosc 14 16–21 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004649900003 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7hs12gsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10653229
RM Walsh BT Heniford F Brody JL Ponsky (2000) ArticleTitleThe ascendance of laparoscopic splenectomy. Am Surg 67 48–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walsh, R., Chand, B., Brodsky, J. et al. Determination of intact splenic weight based on morcellated weight . Surg Endosc 17, 1266–1268 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-001-8223-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-001-8223-6