Abstract
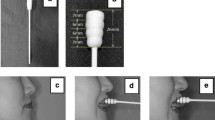
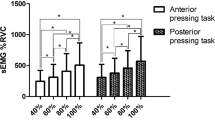
Although effortful swallow and the Mendelsohn maneuver are commonly used in dysphagia rehabilitation, little is known about their effects on tongue-palate pressure production. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of effortful swallow and the Mendelsohn maneuver on tongue pressure production. Fourteen healthy volunteers (10 men, 4 women; age range = 21–41 years) participated. Tongue pressures during dry swallow, water swallow, effortful swallow, and the Mendelsohn maneuver were measured using a sensor sheet system with five measurement points on the hard palate. Sequential order, duration, maximal magnitude, and the integrated value of tongue pressure at each measurement point were compared among the four tasks. Onset of tongue pressure at the posterior-circumferential parts occurred first in the Mendelsohn maneuver; that at the anterior-median part was earlier than at other parts in the effortful swallow. At all measurement points, tongue pressure duration was significantly longer in the Mendelsohn maneuver than in other tasks. Effortful swallow was most effective in increasing tongue pressure. The integrated value of tongue pressure at the posterior-circumferential parts in the Mendelsohn maneuver and at the median parts in the effortful swallow showed a tendency to increase. These results suggest that tongue pressure increases along a wide part of the hard palate in effortful swallow because the anchor of tongue movement is emphasized at the anterior part of the hard palate. The Mendelsohn maneuver provides prolonged and accentuated tongue-palate contact at the posterior-circumferential parts, which might be important for hyoid-laryngeal elevation during swallowing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin: Pro-Ed; 1998.
Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Song CW, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of voluntary maneuvers on tongue base function for swallowing. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2002;54(4):171–6.
Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Krugler C, Flanagan E. Volitional augmentation of upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:G450–6.
Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Gibbons P. Effects of maneuvers on swallowing function in a dysphagic oral cancer patient. Head Neck. 1993;15(5):419–24.
Ding R, Larson CR, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW. Surface electromyographic and electroglottographic studies in normal subjects under two swallow conditions: normal and during the Mendelsohn manuever. Dysphagia. 2002;17:1–12.
Bodén K, Hallgren A, Witt Hedström H. Effects of three different swallow maneuvers analyzed by videomanometry. Acta Radiol. 2006;47(7):628–33.
Bulow M, Olsson R, Ekberg O. Videomanometric analysis of supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck in healthy volunteers. Dysphagia. 1999;14:67–72.
Bulow M, Olsson R, Ekberg O. Videomanometric analysis of supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia. 2001;16:190–5.
Hind JA, Nicosia MA, Roecker EB, Carnes ML, Robbins J. Comparison of effortful and noneffortful swallows in healthy middleaged and older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82:1661–5.
Bulow M, Olsson R, Ekkberg O. Supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck did not alter hypopharyngeal intrabolus pressure in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia. 2002;17:197–201.
Huckabee ML, Butler SG, Barclay M, Jit S. Submental surface electromyographic measurement and pharyngeal pressures during normal and effortful swallowing. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86:2144–9.
Hiss SG, Huckabee ML. Timing of pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter pressures as a function of normal and effortful swallowing in young healthy adults. Dsyphagia. 2005;20:149–56.
Witte U, Huckabee ML, Doeltgen SH, Gumbley F, Robb M. The effect of effortful swallow on pharyngeal manometric measurements during saliva and water swallowing in healthy participants. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89:822–8.
Cerenko D, McConnel MS, Jackson RT. Quantitative assessment of pharyngeal bolus driving forces. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1988;100:57–63.
Shaker R, Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ. Pressure-flow dynamics of the oral phase of swallowing. Dysphagia. 1988;3(2):79–84.
Kahrilas P, Lin S, Logemann JA, Ergun G, Facchini F. Deglutitive tongue action: volume accommodation and bolus propulsion. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:152–62.
Hori K, Ono T, Iwata H, Nokubi T, Kumakura I. Tongue pressure against hard palate during swallowing in post-stroke patients. Gerodontology. 2005;22:227–33.
Hori K, Ono T, Tamine K, Kondo J, Hamanaka S, Maeda Y, Dong J, Hatsuda M. Newly developed sensor sheet for measuring tongue pressure in swallowing. J Prosthodont Res. 2009;53:28–32.
Hirota N, Konaka K, Ono T, Tamine K, Kondo J, Hori K, Yoshimuta Y, Maeda Y, Sakoda S, Naritomi H. Reduced tongue pressure against the hard palate on the paralyzed side during swallowing predicts dysphagia in patients with acute stroke. Stroke. 2010;41(12):2982–4.
Hori K, Tamine K, Barbezat C, Maeda Y, Yamori M, Müller F, Ono T. Influence of chin-down posture on tongue pressure during dry swallow and bolus swallows in healthy subjects. Dysphagia. 2011;26(3):238–45.
Huckabee ML, Steele CM. An analysis of lingual contribution to submental surface electromyographic measures and pharyngeal pressure during effortful swallow. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006;87:1067–72.
Logemann JA. Behavioral management for oropharyngeal dysphagia. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 1999;51:199–212.
Wheeler-Hegland KM, Rosenbek JC, Sapienza CM. Submental sEMG and hyoid movement during Mendelsohn maneuver, effortful swallow, and expiratory muscle strength training. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2008;51:1072–87.
Robbins J, Levine R, Wood J, Roecker EB, Luschei E. Age effects on lingual pressure generation as a risk factor for dysphagia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1995;50:M257–62.
Hayashi R, Tsuga K, Hosokawa R, Yoshida M, Sato Y, Akagawa Y. A novel handy probe for tongue pressure measurement. Int J Prosthodont. 2002;15:385–8.
Robbins J, Gangnon RE, Theis SM, Kays SA, Hewitt AL, Hind JA. The effects of lingual exercise on swallowing in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:1483–9.
Robbins J, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, Taylor AJ. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88:150–8.
Steel CM, Huckabee ML. The influence of orolingual pressure on the timing of pharyngeal pressure events. Dysphagia. 2007;22:30–6.
Yeates EM, Steele CM, Pelletier CA. Tongue pressure and submental surface electromyography measures during noneffortful and effortful saliva swallows in healthy women. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2010;19(3):274–81.
Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Hurst P, Davis J, Krugler C. Effects of intraoral prosthetics on swallowing in patients with oral cancer. Dysphagia. 1989;4:118–20.
Hoffman MR, Mielens JD, Ciucci MR, Jones CA, Jiang JJ, McCulloch TM. High-resolution manometry of pharyngeal swallow pressure events associated with effortful swallow and the Mendelsohn maneuver. Dysphagia. 2012;27(3):418–26.
Crary MA, Baldwin BO. Surface electromyographic characteristics of swallowing in dysphagia secondary to brainstem stroke. Dysphagia. 1997;12(4):180–7.
Coulas VL, Smith RC, Qadri SS, Martin RE. Differentiating effortful and non-effortful swallowing with a neck force transducer: Implications for the development of a clinical feedback system. Dysphagia. 2009;24:7–12.
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (No. 24659859).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuoka, T., Ono, T., Hori, K. et al. Effect of the Effortful Swallow and the Mendelsohn Maneuver on Tongue Pressure Production against the Hard Palate. Dysphagia 28, 539–547 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-013-9464-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-013-9464-y