Abstract
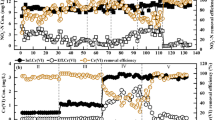
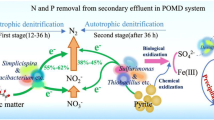
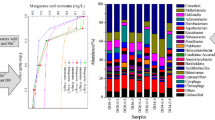
This study aims to explore the effect mechanism of micron-scale zero-valent iron (mZVI) to improve nitrogen and phosphorus removal in a pyrite (FeS2)-driven denitrification biofilter (DNBF) for the secondary effluent treatment. Two similar DNBFs (DNBF-A with FeS2 as fillers and DNBF-B with the mixture mZVI and FeS2 as carrier) were developed. The results showed that NO3−–N, total nitrogen (TN) and PO43−–P removal efficiencies were up to 91.64%, 67.44% and 80.26% in DNBF-B, which were obviously higher than those of DNBF-A (with NO3−–N, TN and PO43−–P removal efficiencies of 38.39%, 44.89% and 53.02%, respectively). Kinetic analysis of both PO43−–P and NO3−–N showed an increase in the rate constant (K) for DNBF-B compared to DNBF-A. The addition of mZVI not only improved the electron transport system activity (ETSA), but also achieved system Fe(II)/Fe(III) redox cycle in DNBF-B. In addition, the high-throughput sequencing analysis indicated that the addition of mZVI could obviously stimulate the enrichment of functional bacteria, such as Thiobacillus (11.99%), Mesotoga (7.50%), JGI-0000079D21 (6.37%), norank_f__Bacteroidetes_vadinHA17 (6.19%), Aquimonas (5.93%) and Arenimonas (3.97%). These genus played the important role in nitrogen and phosphorus removal in DNBF-B. Addition mZVI in the FeS2-driven denitrification biofilter is highly promising for TN and TP removal during secondary effluent treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Ministry of housing and urban-rural development of China. Ministry of housing and urban-rural development, Beijing, China. (2018).
Wu L, Ning D, Zhang B, Li Y, Zhang P, Shan X, Zhang Q, Brown MR, Li Z, Van Nostrand JD, Ling F, Xiao N, Zhang Y, Vierheilig J, Wells GF, Yang Y, Deng Y, Tu Q, Wang A, Global Water Microbiome C, Zhang T, He Z, Keller J, Nielsen PH, Alvarez PJJ, Criddle CS, Wagner M, Tiedje JM, He Q, Curtis TP, Stahl DA, Alvarez-Cohen L, Rittmann BE, Wen X, Zhou J (2019) Global diversity and biogeography of bacterial communities in wastewater treatment plants. Nat microbiol 4:1183–1195. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0426-5
Li H, Li Y, Guo J, Song Y, Hou Y, Lu C, Han Y, Shen X, Liu B (2021) Effect of calcinated pyrite on simultaneous ammonia, nitrate and phosphorus removal in the BAF system and the Fe2+ regulatory mechanisms: electron transfer and biofilm properties. Environ Res 194:110708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110708
Gao L, Zhou W, Huang J, He S, Yan Y, Zhu W, Wu S, Zhang X (2017) Nitrogen removal by the enhanced floating treatment wetlands from the secondary effluent. Bioresour Technol 234:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.036
Peng C, Gao Y, Fan X, Peng P, Huang H, Zhang X, Ren H (2019) Enhanced biofilm formation and denitrification in biofilters for advanced nitrogen removal by rhamnolipid addition. Bioresour Technol 287:121387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121387
Zhou Q, Sun H, Jia L, Wu W, Wang J (2022) Simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from secondary effluent of wastewater treatment plants by advanced treatment: a review. Chemosphere 296:134054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134054
Fu J, Lin Z, Zhao P, Wang Y, He L, Zhou J (2019) Establishment and efficiency analysis of a single-stage denitrifying phosphorus removal system treating secondary effluent. Bioresour Technol 288:121520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121520
Zhang S, Zhu C, Xia S, Li M (2019) Impact of different running conditions on performance of biofilters treating secondary effluent during start-up. Bioresour Technol 281:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.094
Peng C, Huang H, Gao Y, Fan X, Peng P, Zhang X, Ren H (2020) A novel start-up strategy for mixotrophic denitrification biofilters by rhamnolipid and its performance on denitrification of low C/N wastewater. Chemosphere 239:124726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124726
Šereš M, Mocová KA, Moradi J, Kriška M, Kočí V, Hnátková T (2019) The impact of woodchip-gravel mixture on the efficiency and toxicity of denitrification bioreactors. Sci Total Environ 647:888–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.042
Ge Z, Wei D, Zhang J, Hu J, Liu Z, Li R (2019) Natural pyrite to enhance simultaneous long-term nitrogen and phosphorus removal in constructed wetland: three years of pilot study. Water Res 148:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.037
Hu Y, Wu G, Li R, Xiao L, Zhan X (2020) Iron sulphides mediated autotrophic denitrification: an emerging bioprocess for nitrate pollution mitigation and sustainable wastewater treatment. Water Res 179:115914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115914
Xu Z, Li Y, Zhou P, Song X, Wang Y (2022) New insights on simultaneous nitrate and phosphorus removal in pyrite-involved mixotrophic denitrification biofilter for a long-term operation: performance change and its underlying mechanism. Sci Total Environ 845:157403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157403
Wang Y, Wu G, Zheng X, Mao W, Guan Y (2022) Synergistic ammonia and nitrate removal in a novel pyrite-driven autotrophic denitrification biofilter. Bioresour Technol 355:127223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127223
Chen Y, Shao Z, Kong Z, Gu L, Fang J, Chai H (2020) Study of pyrite based autotrophic denitrification system for low-carbon source stormwater treatment. J Water Process Eng 37:101414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101414
Yang Y, Chen T, Morrison L, Gerrity S, Collins G, Porca E, Li R, Zhan X (2017) Nanostructured pyrrhotite supports autotrophic denitrification for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal from secondary effluents. Chem Eng J 328:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.061
Tong S, Rodriguez-Gonzalez LC, Feng C, Ergas SJ (2016) Comparison of particulate pyrite autotrophic denitrification (PPAD) and sulfur oxidizing denitrification (SOD) for treatment of nitrified wastewater. Water Sci Technol 75:239–246. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.502
Di Capua F, Mascolo MC, Pirozzi F, Esposito G (2020) Simultaneous denitrification, phosphorus recovery and low sulfate production in a recirculated pyrite-packed biofilter (RPPB). Chemosphere 255:126977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126977
Li R, Morrison L, Collins G, Li A, Zhan X (2016) Simultaneous nitrate and phosphate removal from wastewater lacking organic matter through microbial oxidation of pyrrhotite coupled to nitrate reduction. Water Res 96:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.034
Li Y, Guo J, Li H, Song Y, Chen Z, Lu C, Han Y, Hou Y (2020) Effect of dissolved oxygen on simultaneous removal of ammonia, nitrate and phosphorus via biological aerated filter with sulfur and pyrite as composite fillers. Bioresour Technol 296:122340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122340
Shi X, Wei W, Wu L, Ni B-J (2021) Zero-valent iron mediated biological wastewater and sludge treatment. Chem Eng J 426:130821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130821
Cao J, Xiong Z, Lai B (2018) Effect of initial pH on the tetracycline (TC) removal by zero-valent iron: adsorption, oxidation and reduction. Chem Eng J 343:492–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.036
Wei K, Li H, Gu H, Liu X, Ling C, Cao S, Li M, Liao M, Peng X, Shi Y, Shen W, Liang C, Ai Z, Zhang L (2022) Strained zero-valent iron for highly efficient heavy metal removal. Adv Funct Mater 32:2200498. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202200498
Peng Y, He S, Wu F (2021) Biochemical processes mediated by iron-based materials in water treatement: enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus removal in low C/N ratio wastewater. Sci Total Environ 775:145137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145137
Zhang Y, Douglas GB, Kaksonen AH, Cui L, Ye Z (2019) Microbial reduction of nitrate in the presence of zero-valent iron. Sci Total Environ 646:1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.112
Lü Y, Li J, Li Y, Liang L, Dong H, Chen K, Yao C, Li Z, Li J, Guan X (2019) The roles of pyrite for enhancing reductive removal of nitrobenzene by zero-valent iron. Appl Catal B 242:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.086
Du M, Zhang Y, Hussain I, Du X, Huang S, Wen W (2019) Effect of pyrite on enhancement of zero-valent iron corrosion for arsenic removal in water: a mechanistic study. Chemosphere 233:744–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.197
Phenrat T, Lowry GV, Babakhani P (2019). In: Phenrat T, Lowry GV (eds) Nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for environmental restoration: from fundamental science to field scale engineering applications. Springer International Publishing, pp 1–43
Perini JAdL, Silva BF, Nogueira RFP (2014) Zero-valent iron mediated degradation of ciprofloxacin – assessment of adsorption, operational parameters and degradation products. Chemosphere 117:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.071
Zhao Y, Li Q, Shi Q, Xi B, Zhang X, Jian Z, Zhou G, Meng X, Mao X, Kang D, Gong B (2023) Mechanisms of phosphate removal by micron-scale zero-valent iron. Sep Purif Technol 319:123706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123706
Xin X, Li B, Liu X, Yang W, Liu Q (2023) Starting-up performances and microbial community shifts in the coupling process (SAPD-A) with sulfide autotrophic partial denitrification (SAPD) and anammox treating nitrate and ammonium contained wastewater. J Environ Manag 331:117298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117298
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edition. American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), Water Pollution Control Federation (WPCF), Washington, DC, USA
Lizama AC, Figueiras CC, Pedreguera AZ, Ruiz Espinoza JE (2019) Enhancing the performance and stability of the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge by zero valent iron nanoparticles dosage. Bioresour Technol 275:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.086
Boleij M, Pabst M, Neu TR, van Loosdrecht MCM, Lin Y (2018) Identification of glycoproteins isolated from extracellular polymeric substances of full-scale anammox granular sludge. Environ Sci Technol 52:13127–13135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b03180
Zhang R-C, Xu X-J, Chen C, Xing D-F, Shao B, Liu W-Z, Wang A-J, Lee D-J, Ren N-Q (2018) Interactions of functional bacteria and their contributions to the performance in integrated autotrophic and heterotrophic denitrification. Water Res 143:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.06.053
Usepa (2013) Secondary Drinking Water Standards: Guidance for Nuisance Chemicals. Accessed by April 2022.
Li Q, Jiang Z, Zheng J, Xie Y, Liao Q, Zhao F, Yang Z, Lin Z, Si M, Yang W (2022) Interaction of pyrite with zerovalent iron with superior reductive ability via Fe(ii) regeneration. Environ Sci Nano 9:2713–2725. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00349J
Zhang C, Guo J, Lian J, Song Y, Lu C, Li H (2018) Bio-mixotrophic perchlorate reduction to control sulfate production in a step-feed sulfur-based reactor: a study of kinetics, ORP and bacterial community structure. Bioresour Technol 269:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.084
Wang J, Li G, Yin H, An T (2020) Bacterial response mechanism during biofilm growth on different metal material substrates: EPS characteristics, oxidative stress and molecular regulatory network analysis. Environ Res 185:109451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109451
Uhlig I, Szargan R, Nesbitt HW, Laajalehto K (2001) Surface states and reactivity of pyrite and marcasite. Appl Surf Sci 179:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(01)00283-5
Biesinger MC, Payne BP, Grosvenor AP, Lau LWM, Gerson AR, Smart RSC (2011) Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl Surf Sci 257:2717–2730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051
Wang C, Xu Y, Hou J, Wang P, Zhang F, Zhou Q, You G (2019) Zero valent iron supported biological denitrification for farmland drainage treatments with low organic carbon: performance and potential mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 689:1044–1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.488
Tian T, Zhou K, Xuan L, Zhang J-X, Li Y-S, Liu D-F, Yu H-Q (2020) Exclusive microbially driven autotrophic iron-dependent denitrification in a reactor inoculated with activated sludge. Water Res 170:115300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115300
Xin X, Liu S, Qin J, Ye Z, Liu W, Fang S, Yang J (2021) Performances of simultaneous enhanced removal of nitrogen and phosphorus via biological aerated filter with biochar as fillers under low dissolved oxygen for digested swine wastewater treatment. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:1741–1753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02557-z
Zhang M, Qiao S, Shao D, Jin R, Zhou J (2018) Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal by combined anammox and denitrifying phosphorus removal process. J Chem Technol Biot 93:94–104. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5326
Zhao Q, Chen K, Li J, Sun S, Jia T, Huang Y, Peng Y, Zhang L (2021) Pilot-scale evaluation of partial denitrification/anammox on nitrogen removal from low COD/N real sewage based on a modified process. Bioresour Technol 338:125580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125580
Xin X, Liu Q, Werner D, Lu H, Qin J (2020) Start-up strategy and bacterial community analysis of SNAD process for treating anaerobic digester liquor of swine wastewater (ADLSW) in a continuous-flow biofilm reactor. Water Environ J 34:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12568
Shao M-F, Zhang T, Fang HH-P (2010) Sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification: diversity, biochemistry, and engineering applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:1027–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2847-1
Nesbø CL, Charchuk R, Pollo SMJ, Budwill K, Kublanov IV, Haverkamp THA, Foght J (2019) Genomic analysis of the mesophilic Thermotogae genus Mesotoga reveals phylogeographic structure and genomic determinants of its distinct metabolism. Environ Microbiol 21:456–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14477
Kong Z, Zhou Y, Fu Z, Zhang Y, Yan R (2022) Mechanism of stable power generation and nitrogen removal in the ANAMMOX-MFC treating low C/N wastewater. Chemosphere 296:133937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133937
Xing W, Li J, Li D, Hu J, Deng S, Cui Y, Yao H (2018) Stable-Isotope probing reveals the activity and function of autotrophic and heterotrophic denitrifiers in nitrate removal from organic-limited wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 52:7867–7875. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01993
Liu S, Xin X, Yang W, Yan X, Dai Y, Hu J (2023) Influence mechanisms of BC filters of different pyrolysis temperatures on BAFs treating aquaculture wastewater. China Environ Sci 43:1131–1141. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2023.0037
Zhang J, Miao Y, Zhang Q, Sun Y, Wu L, Peng Y (2020) Mechanism of stable sewage nitrogen removal in a partial nitrification-anammox biofilm system at low temperatures: microbial community and EPS analysis. Bioresour Technol 297:122459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122459
Peng Z, Lei Y, Liu Y, Wan X, Yang B, Pan X (2022) Fast start-up and reactivation of anammox process using polyurethane sponge. Biochem Eng J 177:108249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.108249
Funding
This work was funded by National Natural Science Founda-tion of China (Grant No. 42377083); Open Project Program of Engineering Research Center of Groundwater Pollution Control and Remediation, Ministry of Education (No. GW202211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL: methodology, investigation, data curation, data analysis, writing-original draft. XX: conceptualization, writing-review and editing, data curation, funding acquisition. WY: writing—review and editing, validation, data curation. XZ: investigation, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Xin, X., Yang, W. et al. Effect mechanism of micron-scale zero-valent iron enhanced pyrite-driven denitrification biofilter for nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 46, 1847–1860 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02941-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02941-x