Abstract
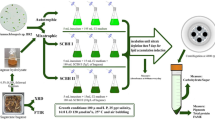
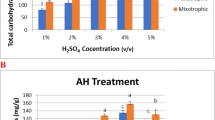
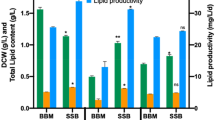
Microalgal lipid production by Chlorella protothecoides using sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate was investigated in this study. First, maximum glucose and reducing sugar concentrations of 15.2 and 27.0 g/L were obtained in sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate (SCBH), and the effects of different percentages of glucose and xylose on algal cultivation were investigated. Afterwards, SCBH was used as a carbon source for the cultivation of C. protothecoides and higher biomass concentration of 10.7 g/L was achieved. Additionally, a large amount of fatty acids, accounting up to 16.8% of dry weight, were accumulated in C. protothecoides in the nitrogen-limited (0.1–1 mmol/L) culture. Although SCBH inhibited fatty acid accumulation to a certain degree and the inhibition was aggravated by nitrogen starvation, SCBH favored microalgal cell growth and fatty acid production. The present study is of significance for the integration of cost-effective feedstocks production for biodiesel with low-cost SCBH as well as environmentally friendly disposal of lignocellulosic wastes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schenk PM, Thomas-Hall SR, Stephens E, Marx UC, Mussgnug JH, Posten C, Kruse O, Hankamer B (2008) Second generation biofuels: high-efficiency microalgae for biodiesel production. Bioenerg Res 1:20–43
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:217–232
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
Damiani D, Litynski JT, McIlvried HG, Vikara DM, Srivastava RD (2012) The US Department of Energy’s R&D program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through beneficial uses of carbon dioxide. Greenhouse Gas Sci Technol 2:9–19
Wahlen BD, Morgan MR, Mccurdy AT, Willis RM, Morgan MD, Dye DJ, Bugbee B, Wood BD, Seefeldt LC (2013) Biodiesel from microalgae, yeast, and bacteria: engine performance and exhaust emissions. Energ Fuel 27:220–228
Singh A, Nigam PS, Murphy JD (2011) Renewable fuels from algae: an answer to debatable land based fuels. Bioresour Technol 102:10–16
Jin M, Slininger PJ, Dien BS, Waghmode S, Moser BR, Orjuela A, Sousal LdC, Balan V (2015) Microbial lipid-based lignocellulosic biorefinery: feasibility and challenges. Trends Biotechnol 33:43–54
Ratledge C, Cohen Z (2008) Microbial and algal oils: do they have a future for biodiesel or as commodity oils? Lipid Technol 20:155–160
Demirbas MF (2011) Biofuels from algae for sustainable development. Appl Energy 88:3473–3480
Miao XL, Wu QY (2006) Biodiesel production from heterotrophic microalgal oil. Bioresour Technol 97:841–846
Perez-Garcia O, Escalante FME, de-Bashan LE, Bashan Y (2011) Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: metabolism and potential products. Water Res 45:11–36
Rawat I, Ranjith Kumar R, Mutanda T, Bux F (2013) Biodiesel from microalgae: a critical evaluation from laboratory to large scale production. Appl Energ 103:444–467
Ahmad AL, Yasin NHM, Derek CJC, Lim JK (2011) Microalgae as a sustainable energy source for biodiesel production: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 15:584–593
Singh J, Gu S (2010) Commercialization potential of microalgae for biofuels production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:2596–2610
Huang C, Chen X-f, Xiong L, Chen X-d, Ma L-l, Chen Y (2013) Single cell oil production from low-cost substrates: the possibility and potential of its industrialization. Biotechnol Adv 31:129–139
Baeyens J, Kang Q, Appels L, Dewil R, Lv Y, Tan T (2015) Challenges and opportunities in improving the production of bio-ethanol. Prog Energ Combust 47:60–88
Reno MLG, Olmo OAD, Palacio JCE, Lora EES, Venturini OJ (2014) Sugarcane biorefineries: case studies applied to the Brazilian sugar-alcohol industry. Energy Convers Manage 86:981–991
Loh YR, Sujan D, Rahman ME, Das CA (2013) Sugarcane bagasse—the future composite material: a literature review. Resour Conserv Recy 75:14–22
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Xia Y, Fang HH, Zhang T (2013) Recent studies on thermophilic anaerobic bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. RSC Adv 3:15528–15542
Arevalo-Gallegos A, Ahmad Z, Asgher M, Parra-Saldivar R, Iqbal HMN (2017) Lignocellulose: a sustainable material to produce value-added products with a zero waste approach—a review. Int J Biol Macromol 99:308–318
Slade R, Bauen A (2013) Micro-algae cultivation for biofuels: cost, energy balance, environmental impacts and future prospects. Biomass Bioenerg 53:29–38
Huang C, Wu H, Li R-f, Zong M-h (2012) Improving lipid production from bagasse hydrolysate with Trichosporon fermentans by response surface methodology. New Biotechnol 29:372–378
Mondala A, Hernandez R, French T, Green M, McFarland L, Ingram L (2015) Enhanced microbial oil production by activated sludge microorganisms from sugarcane bagasse hydrolyzate. Renew Energy 78:114–118
Mu J, Li s, Chen D, Xu H, Han F, Feng B, Li Y (2015) Enhanced biomass and oil production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate (SBH) by heterotrophic oleaginous microalga Chlorella protothecoides. Bioresour Technol 185:99–105
Tsigie YA, Wang C-Y, Chi-Thanh T, Ju Y-H (2011) Lipid production from Yarrowia lipolytica Po1g grown in sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Bioresour Technol 102:9216–9222
Rabelo SC, Andrade RR, Maciel Filho R, Costa AC (2014) Alkaline hydrogen peroxide pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of sugarcane bagasse to ethanol. Fuel 136:349–357
Francisco Castanon-Rodriguez J, Manuel Dominguez-Gonzalez J, Ortiz-Muniz B, Torrestiana-Sanchez B, Alberto Ramirez de Leon J, Guadalupe Aguilar-Uscanga M (2015) Continuous multistep versus fed-batch production of ethanol and xylitol in a simulated medium of sugarcane bagasse hydrolyzates. Eng Life Sci 15:96–107
Mesquita JF, Ferraz A, Aguiar A (2016) Alkaline-sulfite pretreatment and use of surfactants during enzymatic hydrolysis to enhance ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 39:441–448
Su H, Liu G, He M, Tan F (2015) A biorefining process: sequential, combinational lignocellulose pretreatment procedure for improving biobutanol production from sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour Technol 187:149–160
Jonglertjunya W, Makkhanon W, Siwanta T, Prayoonyong P (2014) Dilute acid hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse for butanol fermentation. Chiang Mai J Sci 41:60–70
Chen J, Liu X, Wei D, Chen G (2015) High yields of fatty acid and neutral lipid production from cassava bagasse hydrolysate (CBH) by heterotrophic Chlorella protothecoides. Bioresour Technol 191:281–290
Shi X-M, Chen F, Yuan J-P, Chen H (1997) Heterotrophic production of lutein by selected Chlorella strains. J Appl Phycol 9:445–450
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Huang G-H, Chen G, Chen F (2009) Rapid screening method for lipid production in alga based on Nile red fluorescence. Biomass Bioenerg 33:1386–1392
Wei A, Zhang X, Wei D, Chen G, Wu Q, Yang S-T (2009) Effects of cassava starch hydrolysate on cell growth and lipid accumulation of the heterotrophic microalgae Chlorella protothecoides. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1383–1389
Pino MS, Rodríguez-Jasso RM, Michelin M, Flores-Gallegos AC, Morales-Rodriguez R, Teixeira JA, Ruiz HA (2018) Bioreactor design for enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass under the biorefinery concept. Chem Eng J 347:119–136
Neil C, Ian T, Lye GJ (2015) Creation of an ultra scale-down bioreactor mimic for rapid development of lignocellulosic enzymatic hydrolysis processes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:1983–1990
Kumar R, Wyman CE (2014) Strong cellulase inhibition by Mannan polysaccharides in cellulose conversion to sugars. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:1341–1353
Alvira P, Tomas-Pejo E, Ballesteros M, Negro MJ (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4851–4861
Yang S, Liu G, Meng Y, Wang P, Zhou S, Shang H (2014) Utilization of xylose as a carbon source for mixotrophic growth of Scenedesmus obliquus. Bioresour Technol 172:180–185
Sharma NK, Behera S, Arora R, Kumar S (2016) Enhancement in xylose utilization using Kluyveromyces marxianus NIRE-K1 through evolutionary adaptation approach. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 39:835–843
Kumar S, Dheeran P, Singh SP, Mishra IM, Adhikari DK (2015) Bioprocessing of bagasse hydrolysate for ethanol and xylitol production using thermotolerant yeast. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 38:39–47
Liu L, Zhang L, Tang W, Gu Y, Hua Q, Yang S, Jiang W, Yang C (2012) Phosphoketolase pathway for xylose catabolism in Clostridium acetobutylicum revealed by 13C metabolic flux analysis. J Bacteriol 194:5413
Belle HV, Goossens F (2011) Lipids of oleaginous yeasts. Part I: Biochemistry of single cell oil production. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 113:1031–1051
Hawkins RL (1999) Utilization of xylose for growth by the eukaryotic alga, Chlorella. Curr Microbiol 38:360–363
Ghazali WNMW, Mamat R, Masjuki HH, Najafi G (2015) Effects of biodiesel from different feedstocks on engine performance and emissions: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 51:585–602
Xu H, Miao X, Wu Q (2006) High quality biodiesel production from a microalga Chlorella protothecoides by heterotrophic growth in fermenters. J Biotechnol 126:499–507
Gopinath A, Puhan S, Nagarajan G (2009) Relating the cetane number of biodiesel fuels to their fatty acid composition: a critical study. Proc Inst Mech Eng Pt D J Automobile Eng 223:565–583
Chao H, Hong W, Liu ZJ, Cai J, Lou WY, Zong MH (2012) Effect of organic acids on the growth and lipid accumulation of oleaginous yeast Trichosporon fermentans. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:4
Jonsson LJ, Alriksson B, Nilvebrant NO (2013) Bioconversion of lignocellulose: inhibitors and detoxification. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:16–16
Zhang GC, Liu JJ, Ding WT (2012) Decreased xylitol formation during xylose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae due to overexpression of water-forming NADH oxidase. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1081–1086
Chandel AK, da Silva SS, Singh OV (2013) Detoxification of lignocellulose hydrolysates: biochemical and metabolic engineering toward white biotechnology. Bioenerg Res 6:388–401
Almeida JRM, Modig T, Petersson A, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Liden G, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) Increased tolerance and conversion of inhibitors in lignocellulosic hydrolysates by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82:340–349
Liu H, Jiang S, Wang J, Yang C, Guo H, Wang X, Han S (2015) Fatty acid esters: a potential cetane number improver for diesel from direct coal liquefaction. Fuel 153:78–84
Pandey A, Soccol CR, Nigam P, Soccol VT, Vandenberghe LPS, Mohan R (2000) Biotechnological potential of agro-industrial residues. II: Cassava bagasse. Bioresour Technol 74:81–87
Bonturi N, Crucello A, Viana AJC, Miranda EA (2017) Microbial oil production in sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic hydrolysate without nutrient supplementation by a Rhodosporidium toruloides adapted strain. Process Biochem 57:16–25
Kitahara Y, Yin T, Zhao X, Wachi M, Du W, Liu D (2014) Isolation of oleaginous yeast (Rhodosporidium toruloides) mutants tolerant of sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 78:336–342
Abd-Alla MH, Bagy MMK, Morsy FM, Hassan EA (2014) Enhancement of biodiesel, hydrogen and methane generation from molasses by Cunninghamella echinulata and anaerobic bacteria through sequential three-stage fermentation. Energy 78:543–554
Bagy MMK, Abd-Alla MH, Morsy FM, Hassan EA (2014) Two stage biodiesel and hydrogen production from molasses by oleaginous fungi and Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Int J Hydrogen Energ 39:3185–3197
Kamat S, Khot M, Zinjarde S, RayiKumar A, Gade WN (2013) Coupled production of single cell oil as biodiesel feedstock, xylitol and xylanase from sugarcane bagasse in a biorefinery concept using fungi from the tropical mangrove wetlands. Bioresour Technol 135:246–253
Zhao X, Peng F, Du W, Liu C, Liu D (2012) Effects of some inhibitors on the growth and lipid accumulation of oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides and preparation of biodiesel by enzymatic transesterification of the lipid. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 35:993–1004
Delrue F, Seiter PA, Sahut C, Cournac L, Roubaud A, Peltier G, Froment AK (2012) An economic, sustainability, and energetic model of biodiesel production from microalgae. Bioresour Technol 111:191–200
Xin CH, Addy MM, Zhao JY, Cheng YL, Cheng SB, Mu DY, Liu YH, Ding RJ, Chen P, Ruan R (2016) Comprehensive techno-economic analysis of wastewater-based algal biofuel production: a case study. Bioresour Technol 211:584–593
Orfield ND, Keoleian GA, Love NG (2014) A GIS based national assessment of algal bio-oil production potential through flue gas and wastewater co-utilization. Biomass Bioenerg 63:76–85
Sun A, Davis R, Starbuck M, Ben-Amotz A, Pate R, Pienkos PT (2011) Comparative cost analysis of algal oil production for biofuels. Energy 36:5169–5179
Moncada J, Tamayo JA, Cardona CA (2014) Integrating first, second, and third generation biorefineries: incorporating microalgae into the sugarcane biorefinery. ChEnS 118:126–140
Parsaeimehr A, Mancera-Andrade EI, Robledo-Padilla F, Iqbal HMN, Parra-Saldivar R (2017) A chemical approach to manipulate the algal growth, lipid content and high-value alpha-linolenic acid for biodiesel production. Algal Res 26:312–322
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the program of Science and Technology of Guangzhou (Grant no. 201704030084) and the SinoPec Technology Development Program (218017-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Jh., Liu, L., Lim, PE. et al. Effects of sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate (SCBH) on cell growth and fatty acid accumulation of heterotrophic Chlorella protothecoides. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42, 1129–1142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02110-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02110-z