Abstract
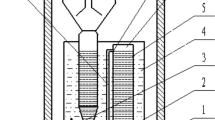
This study aims at comparing the sulfur-based autotrophic and mixotrophic denitrification performances in fixed-bed bioreactors to reveal the impact of alkalinity source, methanol supplementation and use of thiosulfate as electron source. Three different columns were operated. Reactor 1 was packed with elemental sulfur (3–5 mm) and limestone (1–3 mm). The second reactor (reactor 2) was packed with elemental sulfur (3–5 mm) and bicarbonate was used as alkalinity source. In the third reactor (reactor 3), thiosulfate and bicarbonate were used as electron and alkalinity sources, respectively. Nearly complete autotrophic denitrification was attained at loading rates of 0.1, 0.36, and 0.1 g NO3 −-N/(L day) in reactors 1, 2 and 3, respectively. Sulfate generated in autotrophic denitrification processes was nearly stoichiometric. Stimulating simultaneous heterotrophic and autotrophic denitrification by dozing methanol increased denitrification rate up to 0.72 g NO3 −-N/(L day), decreased alkalinity requirement, and reduced sulfate generation.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Liu H, Jiang W, Wan D, Qu J (2009) Study of a combined heterotrophic and sulfur autotrophic denitrification technology for removal of nitrate in water. J Hazard Mater 169:23–28
Yesilnacar MI, Sahinkaya E, Naz M, Ozkaya B (2008) Neural network prediction of nitrate in groundwater of Harran Plain, Turkey. Environ Geol 56:19–25
Lee KC, Rittmann BE (2002) Applying a novel autotrophic hollow-fiber membrane biofilm reactor for denitrification of drinking water. J Hazard Mater 36:2040–2052
Sierra-Alvarez R, Beristan-Cardoso R, Salazar M, Gomez J, Razo-Flores E, Field JA (2007) Chemolithotrophic denitrification with elemental sulfur for groundwater treatment. Water Res 41:1253–1262
Moon HS, Shin DY, Nam K, Kim JY (2008) A long-term performance test on an autotrophic denitrification column for application as a permeable reactive barrier. Chemosphere 73:723–728
Sahinkaya E, Dursun N, Kilic A, Demirel S, Uyanik S, Cinar O (2011) Simultaneous heterotrophic and sulfur-oxidizing autotrophic denitrification process for drinking water treatment: control of sulfate production. Water Res 45:6661–6667
Zhao Y, Feng C, Wang Q, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Sugiura N (2011) Nitrate removal from groundwater by cooperating heterotrophic with autotrophic denitrification in a biofilm-electrode reactor. J Hazard Mater 192:1033–1039
Sahinkaya E, Dursun N (2012) Sulfur-oxidizing autotrophic and mixotrophic denitrification processes for drinking water treatment: elimination of excess sulfate production and alkalinity requirement. Chemosphere 89:144–149
Boles AR, Conneely T, McKeever R, Nixon P, Nüsslein KR, Ergas SJ (2012) Performance of a pilot-scale packed bed reactor for perchlorate reduction using a sulfur oxidizing bacterial consortium. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:637–646
Park JH, Shin HS, Lee IS, Bae JH (2002) Denitrification of high NO3-N containing wastewater using elemental sulfur; nitrogen loading rate and N2O production. Environ Technol 23:53–65
Liu LH, Koenig A (2002) Use of limestone for pH control in autotrophic denitrification: batch experiments. Process Biochem 37:885–893
Ju X, Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R, Salazar M, Bentley H, Bentley R (2007) Chemolithotrophic perchlorate reduction linked to the oxidation of elemental sulfur. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:1073–1082
Park S, Yu J, Byun I, Cho S, Park T, Lee T (2011) Microbial community structure and dynamics in a mixotrophic nitrogen removal process using recycled spent caustic under different loading conditions. Bioresource Technol 102:7265–7271
Oh SE, Yoo YB, Young JC, Kim IS (2001) Effect of organics on sulfur-utilizing autotrophic denitrification under mixotrophic conditions. J Biotechnol 92:1–8
Cord-Ruwisch R (1985) A quick method for the determination of dissolved and precipitated sulfides in cultures of sulfate reducing bacteria. J Microbiol Meth 4:33–36
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Soares MIM (2002) Denitrification of groundwater with elemental sulfur. Water Res 36:1392–1395
Lee DU, Lee IS, Choi YD, Bae JH (2001) Effect of external carbon source and empty bed contact time on simultaneous heterotrophic and sulfur-utilizing autotrophic denitrification. Process Biochem 36:1215–1224
McAdam EJ, Judd SJ (2007) Denitrification from drinking water using a membrane bioreactor: chemical and biochemical feasibility. Water Res 41:4242–4250
Luna-Velasco A, Sierra-Alvarez R, Castro B, Field JA (2010) Removal of nitrate and hexavalent uranium from groundwater by sequential treatment in bioreactor packed with elemental sulfur and zero-valent iron. Biotechnol Bioeng 107:933–942
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK Project No: 110Y256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahinkaya, E., Dursun, N. Use of elemental sulfur and thiosulfate as electron sources for water denitrification. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38, 531–541 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1293-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1293-3