Abstract
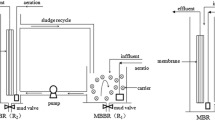
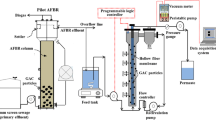
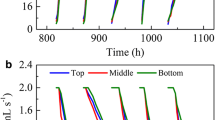
Non-woven fabric filter- (NWFF) and microfilter-MBR modules were made using 100 μm polypropylene and 0.25 μm polyethylene materials, respectively. The performances and mechanisms of the two processes were investigated, including additional batch filtration tests to find the function of the dynamic gel layer on the membrane surface. The HRT of both MBRs was 9 h and the operating permeate flux was 13 L/m2/h. The two MBRs consisted of an anoxic and aerobic reactor. The NWFF or microfilter (MF) was submerged in each of the aerobic reactors. The two MBRs showed similar performances for the removal of organic matters, suspended solids and nitrogen. Cake formation on the NWFF contributed to major resistance, while the gel layer on the microfilter or internal fouling of the pores played a key role in the fouling of the membrane surface. The amount of soluble extracellular polymer substances (EPS) (13 mg/L) of the attached sludge on the NWFF surface was larger than that (11 mg/L) of that suspended sludge. Consequently, the functional gel layer for the coarse and microfilter is established based on the relationship among the EPS, transmembrane pressure and MLSS.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiso Y, Jung YJ, Ichinari T, Park M, Kitao T, Nishimura K, Min KS (2000) Wastewater treatment performance of a filtration bio-reactor equipped with a mesh as a filter material. Water Res 34:4143–4150
Chang IS, Gander M, Jefferson B, Judd SJ (2001) Low-cost membranes for use in a submerged MBR. Trans IChemE 79:183–188
Chang MC, Horng RY, Shao H, Hu YJ (2006) Performance and filtration characteristics of non-woven membranes used in a submerged membrane bioreactor for synthetic wastewater treatment. Desalination 191:8–15
Chang WK, Hu AYJ, Horng RY, Tzou WY (2007) Membrane bioreactor with nonwoven fabrics as solid-liquid separation media for wastewater treatment. Desalination 202:122–128
Iversen V, Drews A, Schmidt T (2007) Textile filter medium for the use in membrane vistalization plant. Chem Ing Technol 79:1945–1950
Seo GT, Moon BH, Park YM, Kim SH (2007) Filtration characteristics of immersed coarse pore filters in an activated sludge system for domestic wastewater reclamation. Water Sci Technol 55:51–58
Satyawali Y, Balakrishnan M (2008) Treatment of distillery effluent in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) equipped with mesh filter. Sep Purif Technol 63:278–286
Meng F, Chae SR, Drews A, Kraume M, Shin HS, Yang F (2009) Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res 43:1489–1512
Chang IS, Clech PL, Jefferson B, Judd S (2002) Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment. J Environ Eng 128:1018–1029
Le-Clech P, Chen V, Fane TAG (2006) Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J Membr Sci 248:17–53
Moghaddam MRA, Guan Y, Satoh H, Mino T (2006) Filter clogging in coarse pore filtration activated sludge process under high MLSS concentration. Water Sci Technol 54:55–66
Fan B, Huang X (2002) Characteristics of a self-forming dynamic membrane coupled with a bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 36:5245–5251
Zhou XH, Shi HC, Cai Q, He M, Wu YX (2008) Function of self-forming dynamic membrane and biokinetic parameters determination by microelectrode. Water Res 42:2369–2376
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Dominguez L, Rodriguez M, Prats D (2010) Effect of different extraction methods on bound EPS from MBR sludge. Part Ι: influence of extraction methods over three-dimensional EEM fluorescence spectroscopy fingerprint. Desalination 261:19–26
Lee J, Ahn WY, Lee CH (2011) Comparison of the filtration characteristics between attached and suspended growth microorganisms in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res 35:2435–2445
Ognier S, Wisniewski C, Grasmick A (2004) Membrane bioreactor fouling in sub-critical filtration conditions: a local critical flux concept. J Membr Sci 229:171–177
Wu YX, Huang X, Wen XH, Chen FT (2005) Function of dynamic membrane in self-forming dynamic membrane coupled bioreactor. Water Sci Technol 51:107–114
Jeong TY, Cha GC, Yoo IK, Kim DJ (2007) Characteristics of bio-fouling in a submerged MBR. Desalination 207:107–113
Barker DJ, Stuckey DC (1999) A review of soluble microbial products (SMP) in wastewater treatment system. Water Res 33:3063–3082
Bouhabila EH, Ben AR, Buisson H (1998) Microfiltration of activated sludge using submerged membrane with air bubbling (application to wastewater treatment). Desalination 118:315–322
Wisniewski C, Grasmick A (1998) Floc size distribution in a membrane bioreactor and consequences for membrane fouling. Colloids Surf 138:403–411
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (1999) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances-characterization, structure and function. Springer, Berlin
Hocaoglu SM, Orhon D (2010) Fate of soluble residual organics in membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 364:65–74
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology and the Korea Ministry of Environment as Program for Promoting Commercialization of Promising Environmental Technologies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JY., Choi, BK., Ahn, KH. et al. Characteristics of flux and gel layer on microfilter and non-woven fabric filter surface based on anoxic–aerobic MBRs. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35, 1389–1398 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0727-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0727-z