Abstract
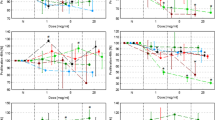
In this study, we present in vitro cytotoxicity of iron oxide (Fe3O4) and manganese oxide (MnO) using live/dead cell assay, lactate dehydrogenase assay, and reactive oxygen species detection with variation of the concentration of nanoparticles (5–500 μg/ml), incubation time (18–96 h), and different human cell lines (lung adenocarcinoma, breast cancer cells, and glioblastoma cells). The surface of nanoparticles is modified with polyethyleneglycol-derivatized phospholipid to enhance the biocompatibility, water-solubility, and stability under an aqueous media. While the cytotoxic effect was negligible for 18 h incubation even at highest concentration of 500 μg/ml, MnO nanoparticle represented higher level of toxicity than those of Fe3O4 and the commercial medical contrast reagent, Feridex after 2 and 4 day incubation time. However, the cytotoxicity of Fe3O4 is equivalent or better than Feridex based on the live/dead cell viability assay. The engineered MnO and Fe3O4 exhibited excellent stability compared with Feridex for a prolonged incubation time.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lynch I, Dawson KA, Linse S (2006) Detecting cryptic epitopes created by nanoparticles. Sci STKE 327:pe14
Colvin VL (2003) The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol 21:1166–1170
Warheit DB (2004) Nanoparticles: health impacts. Mater Today 7:32–35
Adams LK, Lyon DY, Alvarez PJJ (2006) Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res 40:3527–3532
Kagan VE, Bayir H, Shvedova AA (2005) Nanomedicine and nanotoxicology: two sides of the same coin. Nanomedicine 1:313–316
Fischer HC, Chan WCW (2007) Nanotoxicity: the growing need for in vivo study. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:565–571
Linkov I, Satterstrom FK, Corey LM (2008) Nanotoxicology and nanomedicine: making hard decisions. Nanomedicine 4:167–171
Lewinski N, Colvin V, Drezek R (2008) Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small 4:26–49
Na HB, Lee JH, An K, Park YI, Park M, Lee IS, Nam D-H, Kim ST, Kim S-H, Sim S-W, Lim K-H, Kim K-S, Kim S-O, Hyeon T (2007) Development of a T1 contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging using MnO nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:5397–5401
Yin M, Brien SO (2003) Synthesis of monodisperse nanocrystals of manganese oxides. J Am Chem Soc 125:10180–10181
Sun S, Zeng H (2002) Size controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124:8204–8205
Park J, An K, Hwang Y, Park J-G, Noh H-J, Kim J-Y, Park J-H, Hwang N-M, Hyeon T (2004) Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat Mater 3:891–895
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mat 4:435–446
Bruchez M Jr, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281:2013–2016
Wu H, Zhu H, Zhuang J, Yang S, Liu C, Cao YC (2008) Water soluble nanocrystals through dual interaction ligands. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:3730–3734
White MA, Johnson JA, Koberstein JT, Turro NJ (2006) Towards the syntheses of universal ligands for metal oxide surfaces: controlling surface functionality through click chemistry. J Am Chem Soc 128:11356S–11357S
Selvan ST, Patra PK, Ang CY, Ying JY (2007) Synthesis of silica coated semiconductor and magnetic quantum dots and their use in the imaging of live cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:2448–2452
Kim BS, Qiu JM, Wang JP, Taton TA (2005) Magnetomicelles: composite nanostructures from magnetic nanoparticles and cross-linked amphiphilic block copolymers. Nano Lett 5:1987–1991
Dubertret B, Skourides P, Norris DJ, Noireaux V, Brivanlou AH, Libchaber A (2002) In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phospholipid micelles. Science 298:1759–1762
Hayes AW (1994) Principles and methods of toxicology, 3rd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 1231–1258
Papadopoulos NG, Dedoussis GVZ, Spanakos G, Gritzapis AD, Constantin N, Papamichail M (1994) An improved fluorescence assay for the determination of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity using flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 177:101–111
Kaneshiro ES (1993) Reliability of calcein acetoxy methyl ester and ethidium homodimer or propidium iodide for viability assessment of microbes. J Microbiol Methods 17:1–16
Pisanic TR, Blackwell JD, Shubayev VI, Finones RR, Jin S (2007) Nanotoxicity of iron oxide nanoparticle internalization in growing neurons. Biomaterials 28:2572–2581
Hussain SM, Hess KL, Gearhart JM, Geiss KT, Schlager JJ (2005) In vitro toxicity of nanoparticle in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicology In Vitro 19:975–983
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Cytotoxicity suppression and cellular uptake enhancement of surface modified magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 26:1565–1573
Gupta AK, Wells S (2004) Surface-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: preparation, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 3:66–73
Muller K, Skepper JN, Posfai M, Trivedi R, Howarth S, Corot C, Lancelot E, Thompson PW, Brown AP, Gillard JH (2007) Effect of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Ferumoxtran-10) on human monocyte-macrophages in vitro. Biomaterials 28:1629–1642
Yu WW, Chang E, Sayes CM, Drezek R, Colvin VL (2006) Aqueous dispersion of monodisperse magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals through phase transfer. Nanotechnology 17:4483–4487
Chen JY, Tsao GC, Zhao Q, Zheng W (2001) Differential cytotoxicity of Mn(II) and Mn(III): special reference to mitochondrial [Fe-S] containing enzymes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 175:160–168
Hu F, Neoh KG, Cen L, Kang ET (2006) Cellular response to magnetic nanoparticles “PEGylated” via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Biomacromolecules 7:809–816
Nordberg J, Arner ESJ (2001) Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free Radic Biol Med 31:1287–1312
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Korzeniewski C, Callewaert DM (1983) An enzyme-release assay for natural cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods 64:313–320
Arechabala B, Coiffard C, Rivalland P, Coiffard LJM, Roeck-Holtzhauer YD (1999) Comparison of cytotoxicity of various surfactants tested on normal human fibroblast cultures using the neutral red test, MTT assay and LDH release. J Appl Toxicol 19:163–165
Roehn NW, Rodgers GH, Hatfield SM, Glasebrook AL (1991) An improved colorimetric assay for cell proliferation and viability utilizing the tetrazolium salt XTT. J Immunol Methods 142:257–265
Legrand C, Bour JM, Jacob C, Capiaumont J, Martial A, Marc A, Wudtke M, Kretzmer G, Demangel C, Duval D, Hache J (1992) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity of the number of dead cells in the medium of cultured eukaryotic cells as marker. J Biotechnol 25:231–243
Marzin D (1999) New approaches to estimating the mutagenic potential of chemicals. Cell Biol Toxicol 15:359–365
Maurer BJ, Metelitsa LS, Seeger RC, Cabot MC, Reynolds CP (1999) Increase of ceramide and induction of mixed apoptosis/necrosis by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide in neuroblastoma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1138–1146
Konorev EA, Zhang H, Joseph J, Kennedy MC, Kalyanaraman B (2000) Bicarbonate exacerbates oxidative injury induced by antitumor antibiotic doxorubicin in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol 279:H2424–H2430
Lin W, Huang YW, Zhou XD, Ma Y (2006) Toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells. Int J Toxicol 25:451–457
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. R11-2001-089-10002-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.Y., Lee, S.H., Na, H.B. et al. In vitro cytotoxicity screening of water-dispersible metal oxide nanoparticles in human cell lines. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33, 21–30 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-009-0354-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-009-0354-5