Abstract.
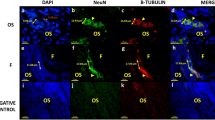
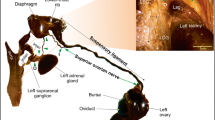
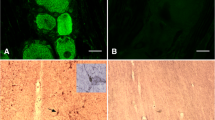
Mammalian ovarian function is regulated by both hormonal inputs and direct neural influences. Recent studies have shown that, in addition to the extrinsic innervation, the ovaries of nonhuman primates and a strain of rats contain a discrete population of intrinsic neurons. In the present study, we used histological and immunohistochemical approaches to identify the presence of neuronal cell bodies in the fetal and neonatal human ovary. Neurons containing neurofilament immunoreactivity were detected in the hilum and medulla of the ovary at all ages studied, ranging from 24 weeks of gestation to 10 months of postnatal age. Most of them coexpressed the low affinity neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR), and some were catecholaminergic, as determined by their content of immunoreactive tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine biosynthesis. The presence of intrinsic neurons in the human ovary, similar to those previously found in other species, indicates that they may be engaged in regulating common, phylogenetically conserved, ovarian functions. It also raises the possibility that their dysfunction may contribute to the manifestation of particular ovarian pathologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anesetti, G., Lombide, P., D'Albora, H. et al. Intrinsic neurons in the human ovary. Cell Tissue Res 306, 231–237 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410100451
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410100451