Abstract
Epidermal keratinocyte-derived cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is the most common metastatic skin cancer, and its incidence is increasing worldwide. Solar UV radiation is an important risk factor for cSCC and leads to genetic and epigenetic changes both in epidermal keratinocytes and dermal cells. Tumor cells in cutaneous cSCCs typically harbor several driver gene mutations, but epidermal keratinocytes in sun-exposed normal skin also contain mutations in these same genes. Therefore, alterations in the microenvironment of premalignant lesions are evidently required for their progression to invasive and metastatic cSCC. For example, alterations in the composition of basement membrane and dermal extracellular matrix are early events in cSCC progression. The presence of microbial structures and the influx of inflammatory cells promote the secretion of proteases, which in turn regulate the availability of growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines and thus influence the growth and invasion of cSCC. Together, these observations emphasize the role of the tumor microenvironment in the progression of cSCC and identify it as a novel therapeutic target in cSCC and other malignant tumors.

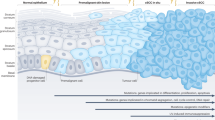
Tumor–stroma interactions in the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). Epidermal layer is separated by a well-organized basement membrane (BM) from the dermal layer. UV radiation, other environmental insults, and aging target both epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts and lead to genetic and epigenetic changes in these cells. In addition, epidermal keratinocytes in normal sun-exposed skin harbor several mutations in the cSCC driver genes. During transition to premalignant actinic keratosis (AK), the differentiation of keratinocytes is disturbed resulting in a neoplastic epithelium with hyperplastic cells. Expression of proteinases, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) by neoplastic cells and activated stromal fibroblasts and macrophages is induced in AK, and collagen XV and XVIII are lost from the dermal BM. Furthermore, inflammatory cells accumulate at the site of the hyperplastic epithelium. During a later stage of cSCC progression, the number of inflammatory cells increases, and the expression of complement components and inhibitors by tumor cells is induced (CFI complement factor I, CFH complement factor H, FHL-1 Factor H-like protein 1). In addition to MMPs, activated fibroblasts also produce growth factors and promote inflammation, growth, and invasion of tumor cells



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B (2009) Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res 15:425–430
Ahokas K, Skoog T, Suomela S, Jeskanen L, Impola U, Isaka K, Saarialho-Kere U (2005) Matrilysin-2 (matrix metalloproteinase-26) is upregulated in keratinocytes during wound repair and early skin carcinogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 124:849–856
Airola K, Johansson N, Kariniemi AL, Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere UK (1997) Human collagenase-3 is expressed in malignant squamous epithelium of the skin. J Invest Dermatol 109:225–231
Ala-aho R, Ahonen M, George SJ, Heikkilä J, Grenman R, Kallajoki M, Kähäri VM (2004) Targeted inhibition of human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) expression inhibits squamous cell carcinoma growth in vivo. Oncogene 23:5111–5123
Alam M, Ratner D (2001) Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 344:975–983
Berman B, Cockerell CJ (2013) Pathobiology of actinic keratosis: ultraviolet-dependent keratinocyte proliferation. J Am Acad Dermatol 68:S10–S19
Boukamp P (2005) Non-melanoma skin cancer: what drives tumor development and progression? Carcinogenesis 26:1657–1667
Cho MS, Vasquez HG, Rupaimoole R, Pradeep S, Wu S, Zand B, Han HD, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Bottsford-Miller J, Huang J, Miyake T, Choi HJ, Dalton HJ, Ivan C, Baggerly K, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Afshar-Kharghan V (2014) Autocrine effects of tumor-derived complement. Cell Rep 6:1085–1095
Córdoba SR de, Jorge EG de (2008) Translational mini-review series on complement factor H: genetics and disease associations of human complement factor H. Clin Exp Immunol 151:1–13
Corrales L, Ajona D, Rafail S, Lasarte JJ, Riezu-Boj JI, Lambris JD, Rouzaut A, Pajares MJ, Montuenga LM, Pio R (2012) Anaphylatoxin C5a creates a favorable microenvironment for lung cancer progression. J Immunol 189:4674–4683
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:9–34
Duk JM, Groenier KH, Bruijn HW de, Hollema H, Hoor KA ten, Zee AG van der, Aalders JG (1996) Pretreatment serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen: a newly identified prognostic factor in early-stage cervical carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 14:111–118
Durinck S, Ho C, Wang NJ, Liao W, Jakkula LR, Collisson EA, Pons J, Chan SW, Lam ET, Chu C, Park K, Hong SW, Hur JS, Huh N, Neuhaus IM, Yu SS, Grekin RC, Mauro TM, Cleaver JE, Kwok PY, LeBoit PE, Getz G, Cibulskis K, Aster JC, Huang H, Purdom E, Li J, Bolund L, Arron ST, Gray JW, Spellman PT, Cho RJ (2011) Temporal dissection of tumorigenesis in primary cancers. Cancer Discov 1:137–143
Farshchian M, Kivisaari A, Ala-Aho R, Riihilä P, Kallajoki M, Grénman R, Peltonen J, Pihlajaniemi T, Heljasvaara R, Kähäri VM (2011) Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade A member 1 (SerpinA1) is a novel biomarker for progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol 179:1110–1119
Farshchian M, Nissinen L, Siljamäki E, Riihilä P, Toriseva M, Kivisaari A, Ala-Aho R, Kallajoki M, Veräjänkorva E, Honkanen HK, Heljasvaara R, Pihlajaniemi T, Grénman R, Peltonen J, Peltonen S, Kähäri VM (2015) EphB2 promotes progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol 135:1882–1892
Fedarko NS, Jain A, Karadag A, Fisher LW (2004) Three small integrin binding ligand N-linked glycoproteins (SIBLINGs) bind and activate specific matrix metalloproteinases. FASEB J 18:734–736
Ferreira VP, Pangburn MK, Cortés C (2010) Complement control protein factor H: the good, the bad, and the inadequate. Mol Immunol 47:2187–2197
Forneris F, Wu J, Gros P (2012) The modular serine proteases of the complement cascade. Curr Opin Struct Biol 22:333–341
Genders RE, Mazlom H, Michel A, Plasmeijer EI, Quint KD, Pawlita M, Meijden E van der, Waterboer T, Fijter H de, Claas FH, Wolterbeek R, Feltkamp MC, Bouwes Bavinck JN (2015) The presence of betapapillomavirus antibodies around transplantation predicts the development of keratinocyte carcinoma in organ transplant recipients: a cohort study. J Invest Dermatol 135:1275–1282
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK (2011) Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J 278:16–27
Gkretsi V, Stylianou A, Papageorgis P, Polydorou C, Stylianopoulos T (2015) Remodeling components of the tumor microenvironment to enhance cancer therapy. Front Oncol 5:214
Gordon K, Kochkodan JJ, Blatt H, Lin SY, Kaplan N, Johnston A, Swindell WR, Hoover P, Schlosser BJ, Elder JT, Gudjonsson JE, Getsios S (2013) Alteration of the EphA2/Ephrin-A signaling axis in psoriatic epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 133:712–722
Gorter A, Meri S (1999) Immune evasion of tumor cells using membrane-bound complement regulatory proteins. Immunol Today 20:576–582
Graaf YG de, Rebel H, Elghalbzouri A, Cramers P, Nellen RG, Willemze R, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Gruijl FR de (2008) More epidermal p53 patches adjacent to skin carcinomas in renal transplant recipients than in immunocompetent patients: the role of azathioprine. Exp Dermatol 17:349–355
Greenwood J, Clark M, Waldmann H (1993) Structural motifs involved in human IgG antibody effector functions. Eur J Immunol 23:1098–1104
Gros P, Milder FJ, Janssen BJ (2008) Complement driven by conformational changes. Nat Rev Immunol 8:48–58
Guo H, Miao H, Gerber L, Singh J, Denning MF, Gilliam AC, Wang B (2006) Disruption of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase leads to increased susceptibility to carcinogenesis in mouse skin. Cancer Res 66:7050–7058
Hadler-Olsen E, Winberg JO, Uhlin-Hansen L (2013) Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: their value as diagnostic and prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Tumour Biol 34:2041–2051
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F, Hau P, Langmann T, Dietmaier W, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2004) Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem 50:490–499
Hafner C, Becker B, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2006) Expression profile of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in human skin and downregulation of EphA1 in nonmelanoma skin cancer. Mod Pathol 19:1369–1377
Hameetman L, Commandeur S, Bavinck JN, Wisgerhof HC, Gruijl FR de, Willemze R, Mullenders L, Tensen CP, Vrieling H (2013) Molecular profiling of cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas and actinic keratoses from organ transplant recipients. BMC Cancer 13:58
Hellwage J, Kuhn S, Zipfel PF (1997) The human complement regulatory factor-H-like protein 1, which represents a truncated form of factor H, displays cell-attachment activity. Biochem J 326:321–327
Hieta N, Impola U, López-Otín C, Saarialho-Kere U, Kähäri VM (2003) Matrix metalloproteinase-19 expression in dermal wounds and by fibroblasts in culture. J Invest Dermatol 121:997–1004
Hofbauer GF, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Euvrard S (2010) Organ transplantation and skin cancer: basic problems and new perspectives. Exp Dermatol 19:473–482
Hoste E, Arwert EN, Lal R, South AP, Salas-Alanis JC, Murrell DF, Donati G, Watt FM (2015) Innate sensing of microbial products promotes wound-induced skin cancer. Nat Commun 6:5932
Impola U, Toriseva M, Suomela S, Jeskanen L, Hieta N, Jahkola T, Grenman R, Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere U (2003) Matrix metalloproteinase-19 is expressed by proliferating epithelium but disappears with neoplastic dedifferentiation. Int J Cancer 103:709–716
Impola U, Jeskanen L, Ravanti L, Syrjänen S, Baldursson B, Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere U (2005) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-7 and MMP-13 and loss of MMP-19 and p16 are associated with malignant progression in chronic wounds. Br J Dermatol 152:720–726
Johansson N, Airola K, Grenman R, Kariniemi AL, Saarialho-Kere U, Kähäri VM (1997) Expression of collagenase-3 (matrix metalloproteinase-13) in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Am J Pathol 15:499–508
Johansson N, Vaalamo M, Grénman S, Hietanen S, Klemi P, Saarialho-Kere U, Kähäri VM (1999) Collagenase-3 (MMP-13) is expressed by tumor cells in invasive vulvar squamous cell carcinomas. Am J Pathol 154:469–480
Joshi N, Johnson LL, Wei WQ, Abnet CC, Dong ZW, Taylor PR, Limburg PJ, Dawsey SM, Hawk ET, Qiao YL, Kirsch IR (2006) Gene expression differences in normal esophageal mucosa associated with regression and progression of mild and moderate squamous dysplasia in a high-risk Chinese population. Cancer Res 66:6851–6860
Karppinen SM, Honkanen H-K, Heljasvaara R, Riihilä P, Autio-Harmainen H, Sormunen R, Harjunen V, Väisänen MR, Väisänen T, Hurskainen T, Tasanen K, Kähäri VM, Pihlajaniemi T (2016) Collagens XV and XVIII show different expression and localisation in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: type XV appears in tumor stroma while XVIII becomes upregulated in tumor cells and lost from microvessels. Exp Dermatol 25:348–354
Kerkelä E, Saarialho-Kere U (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor progression: focus on basal and squamous cell skin cancer. Exp Dermatol 12:109–125
Kerkelä E, Ala-Aho R, Jeskanen L, Rechardt O, Grenman R, Shapiro SD, Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere U (2000) Expression of human macrophage metalloelastase (MMP-12) by tumor cells in skin cancer. J Invest Dermatol 114:1113–1119
Kerkelä E, Ala-aho R, Lohi J, Grénman R, Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere U (2001) Differential patterns of stromelysin-2 (MMP-10) and MT1-MMP (MMP-14) expression in epithelial skin cancers. Br J Cancer 84:659–669
Kessenbrock K, Wang CY, Werb Z (2015) Matrix metalloproteinases in stem cell regulation and cancer. Matrix Biol 44–46:184–190
Kivisaari A, Kähäri VM (2013) Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: emerging need for novel biomarkers. World J Clin Oncol 4:85–90
Kivisaari AK, Kallajoki M, Mirtti T, McGrath JA, Bauer JW, Weber F, Konigova R, Sawamura D, Sato-Matsumura KC, Shimizu H, Csikos M, Sinemus K, Beckert W, Kähäri VM (2008) Transformation-specific matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-7 and MMP-13 are expressed by tumour cells in epidermolysis bullosa-associated squamous cell carcinomas. Br J Dermatol 158:778–785
Kivisaari AK, Kallajoki M, Ala-aho R, McGrath JA, Bauer JW, Königová R, Medvecz M, Beckert W, Grénman R, Kähäri VM (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase-7 activates heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol 163:726–735
Kloth JN, Gorter A, Fleuren GJ, Oosting J, Uljee S, Haar N ter, Dreef EJ, Kenter GG, Jordanova ES (2008) Elevated expression of SerpinA1 and SerpinA3 in HLA-positive cervical carcinoma. J Pathol 215:222–230
Law RH, Zhang Q, McGowan S, Buckle AM, Silverman GA, Wong W, Rosado CJ, Langendorf CG, Pike RN, Bird PI, Whisstock JC (2006) An overview of the serpin superfamily. Genome Biol 7:216
Lefort K, Mandinova A, Ostano P, Kolev V, Calpini V, Kolfschoten I, Devgan V, Lieb J, Raffoul W, Hohl D, Neel V, Garlick J, Chiorino G, Dotto GP (2007) Notch1 is a p53 target gene involved in human keratinocyte tumor suppression through negative regulation of ROCK1/2 and MRCKalpha kinases. Genes Dev 21:562–577
Li YY, Hanna GJ, Laga AC, Haddad RI, Lorch JH, Hammerman PS (2015) Genomic analysis of metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 21:1447–1456
Lim YZ, South AP (2014) Tumour-stroma crosstalk in the development of squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 53:450–458
Lin S, Gordon K, Kaplan N, Getsios S (2010) Ligand targeting of EphA2 enhances keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation via desmoglein 1. Mol Biol Cell 21:3902–3914
Lin S, Wang B, Getsios S (2012) Eph/ephrin signaling in epidermal differentiation and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 23:92–101
Lisle JE, Mertens-Walker I, Rutkowski R, Herington AC, Stephenson SA (2013) Eph receptors and their ligands: promising molecular biomarkers and therapeutic targets in prostate cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1835:243–257
Luukkaa M, Vihinen P, Kronqvist P, Vahlberg T, Pyrhönen S, Kähäri VM, Grénman R (2006) Association between high collagenase-3 expression levels and poor prognosis in patients with head and neck cancer. Head Neck 28:225–234
Madan V, Lear JT, Szeimies RM (2010) Non-melanoma skin cancer. Lancet 375:673–685
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454:436–444
Martincorena I, Roshan A, Gerstung M, Ellis P, Van Loo P, McLaren S, Wedge DC, Fullam A, Alexandrov LB, Tubio JM, Stebbings L, Menzies A, Widaa S, Stratton MR, Jones PH, Campbell PJ (2015) Tumor evolution. High burden and pervasive positive selection of somatic mutations in normal human skin. Science 348:880–886
Martins VL, Caley MP, Moore K, Szentpetery Z, Marsh ST, Murrell DF, Kim MH, Avari M, McGrath JA, Cerio R, Kivisaari A, Kähäri VM, Hodivala-Dilke K, Brennan CH, Chen M, Marshall JF, O’Toole EA (2016) Suppression of TGFβ and angiogenesis by Type VII Collagen in cutaneous SCC. J Natl Cancer Inst 108:djv293
Meyer S, Leusen JH, Boross P (2014) Regulation of complement and modulation of its activity in monoclonal antibody therapy of cancer. MAbs 6:1133–1144
Mittapalli VR, Madl J, Löffek S, Kiritsi D, Kern JS, Römer W, Nyström A, Bruckner-Tuderman L (2016) Injury-driven stiffening of the dermis expedites skin carcinoma progression. Cancer Res 76:940–951
Miura K, Nam JM, Kojima C, Mochizuki N, Sabe H (2009) EphA2 engages Git1 to suppress Arf6 activity modulating epithelial cell-cell contacts. Mol Biol Cell 20:1949–1959
Nilsson SC, Sim RB, Lea SM, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Blom AM (2011) Complement factor I in health and disease. Mol Immunol 48:1611–1620
Nissinen L, Kähäri VM (2014) Matrix metalloproteinases in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840:2571–2580
Okroj M, Holmquist E, Nilsson E, Anagnostaki L, Jirström K, Blom AM (2015) Local expression of complement factor I in breast cancer cells correlates with poor survival and recurrence. Cancer Immunol Immunother 64:467–478
Pasquale EB (2008) Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell 133:38–52
Pasquale EB (2010) Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 10:165–180
Perez White BE, Getsios S (2014) Eph receptor and ephrin function in breast, gut, and skin epithelia. Cell Adh Migr 8:327–338
Petrache I, Fijalkowska I, Medler TR, Skirball J, Cruz P, Zhen L, Petrache HI, Flotte TR, Tuder RM (2006) Alpha-1 antitrypsin inhibits caspase-3 activity, preventing lung endothelial cell apoptosis. Am J Pathol 169:1155–1166
Pickering CR, Zhou JH, Lee JJ, Drummond JA, Peng SA, Saade RE, Tsai KY, Curry JL, Tetzlaff MT, Lai SY, Yu J, Muzny DM, Doddapaneni H, Shinbrot E, Covington KR, Zhang J, Seth S, Caulin C, Clayman GL, El-Naggar AK, Gibbs RA, Weber RS, Myers JN, Wheeler DA, Frederick MJ (2014) Mutational landscape of aggressive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 20:6582–6592
Pio R, Corrales L, Lambris JD (2014) The role of complement in tumor growth. Adv Exp Med Biol 772:229–262
Ratushny V, Gober MD, Hick R, Ridky TW, Seykora JT (2012) From keratinocyte to cancer: the pathogenesis and modeling of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Invest 122:464–472
Ricklin D, Hajishengallis G, Yang K, Lambris JD (2010) Complement: a key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat Immunol 11:785–797
Riihilä PM, Nissinen LM, Ala-aho R, Kallajoki M, Grénman R, Meri S, Peltonen S, Peltonen J, Kähäri VM (2014) Complement factor H: a biomarker for progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol 134:498–506
Riihilä P, Nissinen L, Farshchian M, Kivisaari A, Ala-aho R, Kallajoki M, Grénman R, Meri S, Peltonen S, Peltonen J, Kähäri VM (2015) Complement factor I promotes progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol 135:579–588
Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Harris AR, Hinckley MR, Feldman SR, Fleischer AB, Coldiron BM (2010) Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States, 2006. Arch Dermatol 146:283–287
Rozanov DV, Savinov AY, Golubkov VS, Tomlinson S, Strongin AY (2006) Interference with the complement system by tumor cell membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase plays a significant role in promoting metastasis in mice. Cancer Res 66:6258–6263
Rutkowski MJ, Sughrue ME, Kane AJ, Ahn BJ, Fang S, Parsa AT (2010a) The complement cascade as a mediator of tissue growth and regeneration. Inflamm Res 59:897–905
Rutkowski MJ, Sughrue ME, Kane AJ, Mills SA, Parsa AT (2010b) Cancer and the complement cascade. Mol Cancer Res 8:1453–1465
Shaked Y (2016) Balancing efficacy of and host immune responses to cancer therapy: the yin and yang effects. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.57
Shirasuna K, Sugiyama M, Watatani K, Morioka S, Hayashido Y (1987) Serum alpha-1-antitrypsin in patients with malignant tumors occurring in the oral region. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 16:516–520
Silverman GA, Bird PI, Carrell RW, Church FC, Coughlin PB, Gettins PG, Irving JA, Lomas DA, Luke CJ, Moyer RW, Pemberton PA, Remold-O’Donnell E, Salvesen GS, Travis J, Whisstock JC (2001) The serpins are an expanding superfamily of structurally similar but functionally diverse proteins. Evolution, mechanism of inhibition, novel functions, and a revised nomenclature. J Biol Chem 276:33293–33296
Silverman GA, Whisstock JC, Askew DJ, Pak SC, Luke CJ, Cataltepe S, Irving JA, Bird PI (2004) Human clade B serpins (ov-serpins) belong to a cohort of evolutionarily dispersed intracellular proteinase inhibitor clades that protect cells from promiscuous proteolysis. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:301–325
Sim RB, Tsiftsoglou SA (2004) Proteases of the complement system.Biochem Soc Trans 32:21–27
South AP, Purdie KJ, Watt SA, Haldenby S, Breems NY den, Dimon M, Arron ST, Kluk MJ, Aster JC, McHugh A, Xue DJ, Dayal JH, Robinson KS, Rizvi SM, Proby CM, Harwood CA, Leigh IM (2014) NOTCH1 mutations occur early during cutaneous squamous cell carcinogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 134:2630–2638
Steward WP, Thomas AL (2000) Marimastat: the clinical development of a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9:2913–2922
Stokes A, Joutsa J, Ala-Aho R, Pitchers M, Pennington CJ, Martin C, Premachandra DJ, Okada Y, Peltonen J, Grenman R, James HA, Edwards DR, Kähäri VM (2010) Expression profiles and clinical correlations of degradome components in the tumor microenvironment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 16:2022–2035
Tessari G, Naldi L, Boschiero L, Nacchia F, Fior F, Forni A, Rugiu C, Faggian G, Sassi F, Gotti E, Fiocchi R, Talamini G, Girolomoni G (2010) Incidence and clinical predictors of a subsequent nonmelanoma skin cancer in solid organ transplant recipients with a first nonmelanoma skin cancer: a multicenter cohort study. Arch Dermatol 146:294–299
Tufaro AP, Chuang JC, Prasad N, Chuang A, Chuang TC, Fischer AC (2011) Molecular markers in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Surg Oncol 2011:231475
Vaalamo M, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Puolakkainen P, Kere J, Saarialho-Kere U (1998) Distinct expression profiles of stromelysin-2 (MMP-10), collagenase-3 (MMP-13), macrophage metalloelastase (MMP-12), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) in intestinal ulcerations. Am J Pathol 152:1005–1014
Vĕtvicka V, Reed W, Hoover ML, Ross GD (1993) Complement factors H and I synthesized by B cell lines function to generate a growth factor activity from C3. J Immunol 150:4052–4060
Vilen ST, Salo T, Sorsa T, Nyberg P (2013) Fluctuating roles of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. ScientificWorldJournal 2013:920595
Walsh R, Blumenberg M (2012) Eph-2B, acting as an extracellular ligand, induces differentiation markers in epidermal keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol 227:2330–2340
Wisgerhof HC, Boog PJ van der, Fijter JW de, Wolterbeek R, Haasnoot GW, Claas FH, Willemze R, Bouwes Bavinck JN (2009) Increased risk of squamous-cell carcinoma in simultaneous pancreas kidney transplant recipients compared with kidney transplant recipients. J Invest Dermatol 129:2886–2894
Zelvyte I, Stevens T, Westin U, Janciauskiene S (2004) Alpha1-antitrypsin and its C-terminal fragment attenuate effects of degranulated neutrophil-conditioned medium on lung cancer HCC cells, in vitro. Cancer Cell Int 4:7
Zipfel PF, Skerka C (1999) FHL-1/reconectin: a human complement and immune regulator with cell-adhesive function. Immunol Today 20:135–140
Zipfel PF, Skerka C (2009) Complement regulators and inhibitory proteins. Nat Rev Immunol 9:729–740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The original work of the authors was supported by the Finnish Cancer Research Foundation, Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, and Turku University Hospital VTR grant (project 13336) and by the Turku University Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nissinen, L., Farshchian, M., Riihilä, P. et al. New perspectives on role of tumor microenvironment in progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Tissue Res 365, 691–702 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2457-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2457-z