Abstract
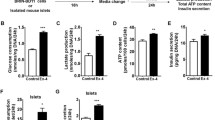
We have examined the expression and activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and the activity of neuronal constitutive NOS (ncNOS) in isolated rat pancreatic islets, stimulated by a “hyperglycaemic” concentration of glucose, and whether the NOS activities could be modulated by activation of the cyclic AMP/protein kinase A (cyclic AMP/PKA) system in relation to the insulin secretory process. Here, we show that glucose stimulation (20 mmol/l) induces iNOS and increases ncNOS activity. No iNOS is detectable at basal glucose levels (3.3 mmol/l). The addition of glucagon-like-peptide 1 (GLP-1) or dibutyryl-cAMP to islets incubated with 20 mmol/l glucose results in a marked suppression of iNOS expression and activity, a reduction in ncNOS activity and increased insulin release. The GLP-1-induced suppression of glucose-stimulated iNOS activity and expression and its stimulation of insulin release is, at least in part, PKA dependent, since the PKA inhibitor H-89 reverses the effects of GLP-1. These observations have been confirmed by confocal microscopy showing the glucose-stimulated expression of iNOS, its suppression by GLP-1 and its reversion by H-89 in β-cells. We have also found that the NO scavenger cPTIO and the NOS inhibitor L-NAME potentiate the insulin response to glucose, again suggesting that NO is a negative modulator of glucose-stimulated insulin release. We conclude that the induction of iNOS and the increase in ncNOS activity caused by glucose in rat islets is suppressed by the cyclic AMP/PKA system. The inhibition of iNOS expression by the GLP-1/cyclic AMP/PKA pathway might possibly be of therapeutic potential in NO-mediated β-cell dysfunction and destruction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akesson B, Henningsson R, Salehi A, Lundquist I (1999) Islet constitutive nitric oxide synthase and glucose regulation of insulin release in mice. J Endocrinol 163:39–48
Alm P, Ekstrom P, Henningsson R, Lundquist I (1999) Morphological evidence for the existence of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide pathways in the rat islets of Langerhans: an immunocytochemical and confocal microscopical study. Diabetologia 42:978–986
Belin VD, Mabley JG, James RF, Swift SM, Clayton HA, Titheradge MA, Green IC (1999) Glucagon decreases cytokine induction of nitric oxide synthase and action on insulin secretion in RIN5F cells and rat and human islets of Langerhans. Cytokine 11:585–592
Beshay E, Prud’homme GJ (2001) Inhibitors of phosphodiesterase isoforms III or IV suppress islet-cell nitric oxide production. Lab Invest 81:1109–1117
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Ceriello A, Quagliaro L, D’Amico M, DiFilippo C, Marfella R, Nappo F, Berrino L, Rossi F, Giugliano D (2002) Acute hyperglycemia induces nitrotyrosine formation and apoptosis in perfused heart from rat. Diabetes 51:1076–1082
Christopherson KS, Bredt DS (1997) Nitric oxide in excitable tissues: physiological roles and disease. J Clin Invest 100:2424–2429
Corbett JA, McDaniel ML (1992) Does nitric oxide mediate autoimmune destruction of beta-cells? Possible therapeutic interventions in IDDM. Diabetes 41:897–903
Drucker DJ (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 and the islet beta-cell: augmentation of cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. Endocrinology 144:5145–5148
Dunger A, Cunningham JM, Delaney CA, Lowe JE, Green MH, Bone AJ, Green IC (1996) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma inhibit insulin secretion and cause DNA damage in unweaned-rat islets. Extent of nitric oxide involvement. Diabetes 45:183–189
Eizirik DL, Korbutt GS, Hellerstrom C (1992) Prolonged exposure of human pancreatic islets to high glucose concentrations in vitro impairs the beta-cell function. J Clin Invest 90:1263–1268
Eizirik DL, Flodstrom M, Karlsen AE, Welsh N (1996) The harmony of the spheres: inducible nitric oxide synthase and related genes in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 39:875–890
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, Grodsky GM (2003) Are oxidative stress-activated signaling pathways mediators of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction? Diabetes 52:1–8
Flodstrom M, Tyrberg B, Eizirik DL, Sandler S (1999) Reduced sensitivity of inducible nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice to multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetes 48:706–713
Gotoh M, Maki T, Kiyoizumi T, Satomi S, Monaco AP (1985) An improved method for isolation of mouse pancreatic islets. Transplantation 40:437–438
Gross R, Roye M, Manteghetti M, Broca C, Hillaire-Buys D, Masiello P, Ribes G (1997) Mechanisms involved in the effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on l-arginine-induced insulin secretion. Br J Pharmacol 120:495–501
Guo L, Zhang Z, Green K, Stanton RC (2002) Suppression of interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production in RINm5F cells by inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 41:14726–14733
Hadjivassiliou V, Green MH, James RF, Swift SM, Clayton HA, Green IC (1998) Insulin secretion, DNA damage, and apoptosis in human and rat islets of Langerhans following exposure to nitric oxide, peroxynitrite, and cytokines. Nitric Oxide 2:429–441
Harbrecht BG, Wirant EM, Kim YM, Billiar TR (1996) Glucagon inhibits hepatocyte nitric oxide synthesis. Arch Surg 131:1266–1272
Henningsson R, Lundquist I (1998) Arginine-induced insulin release is decreased and glucagon increased in parallel with islet NO production. Am J Physiol 275:E500–E506
Henningsson R, Alm P, Lindstrom E, Lundquist I (2000) Chronic blockade of NO synthase paradoxically increases islet NO production and modulates islet hormone release. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E95–E107
Henningsson R, Alm P, Lundquist I (2001) Evaluation of islet heme oxygenase-CO and nitric oxide synthase-NO pathways during acute endotoxemia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C1242–C1254
Henningsson R, Salehi A, Lundquist I (2002) Role of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in glucose-stimulated insulin release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C296–C304
Jaffrey SR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Ferris CD, Tempst P, Snyder SH (2001) Protein S-nitrosylation: a physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat Cell Biol 3:193–197
Knowles RG, Moncada S (1994) Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J 298:249–258
Lajoix AD, Reggio H, Chardes T, Peraldi-Roux S, Tribillac F, Roye M, Dietz S, Broca C, Manteghetti M, Ribes G, Wollheim CB, Gross R (2001) A neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase expressed in pancreatic beta-cells controls insulin secretion. Diabetes 50:1311–1323
Lakey JR, Suarez-Pinzon WL, Strynadka K, Korbutt GS, Rajotte RV, Mabley JG, Szabo C, Rabinovitch A (2001) Peroxynitrite is a mediator of cytokine-induced destruction of human pancreatic islet beta cells. Lab Invest 81:1683–1692
Mandrup-Poulsen T (1996) The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetologia 39:1005–1029
Marshak S, Leibowitz G, Bertuzzi F, Socci C, Kaiser N, Gross DJ, Cerasi E, Melloul D (1999) Impaired beta-cell functions induced by chronic exposure of cultured human pancreatic islets to high glucose. Diabetes 48:1230–1236
Panagiotidis G, Alm P, Lundquist I (1992) Inhibition of islet nitric oxide synthase increases arginine-induced insulin release. Eur J Pharmacol 229:277–278
Panagiotidis G, Akesson B, Rydell EL, Lundquist I (1995) Influence of nitric oxide synthase inhibition, nitric oxide and hydroperoxide on insulin release induced by various secretagogues. Br J Pharmacol 114:289–296
Prentki M, Matschinsky FM (1987) Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev 67:1185–1248
Renstrom E, Eliasson L, Rorsman P (1997) Protein kinase A-dependent and -independent stimulation of exocytosis by cAMP in mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol (Lond) 502:105–118
Robertson RP, Harmon J, Tran PO, Tanaka Y, Takahashi H (2003) Glucose toxicity in beta-cells: type 2 diabetes, good radicals gone bad, and the glutathione connection. Diabetes 52:581–587
Rossetti L, Giaccari A, DeFronzo RA (1990) Glucose toxicity. Diabetes Care 13:610–630
Salehi A, Carlberg M, Henningson R, Lundquist I (1996) Islet constitutive nitric oxide synthase: biochemical determination and regulatory function. Am J Physiol 270:C1634–C1641
Salehi A, Parandeh F, Lundquist I (1998) Signal transduction in islet hormone release: interaction of nitric oxide with basal and nutrient-induced hormone responses. Cell Signal 10:645–651
Salehi A, Ekelund M, Henningsson R, Lundquist I (2001) Total parenteral nutrition modulates hormone release by stimulating expression and activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrine 16:97–104
Salehi A, Ekelund M, Lundquist I (2003) Total parenteral nutrition-stimulated activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat pancreatic islets is suppressed by glucagon-like peptide-1. Horm Metab Res 35:48–54
Schmidt HH, Warner TD, Ishii K, Sheng H, Murad F (1992) Insulin secretion from pancreatic B cells caused by l-arginine-derived nitrogen oxides. Science 255:721–723
Smukler SR, Tang L, Wheeler MB, Salapatek AM (2002) Exogenous nitric oxide and endogenous glucose-stimulated beta-cell nitric oxide augment insulin release. Diabetes 51:3450–3460
Takamura T, Kato I, Kimura N, Nakazawa T, Yonekura H, Takasawa S, Okamoto H (1998) Transgenic mice overexpressing type 2 nitric-oxide synthase in pancreatic beta cells develop insulin-dependent diabetes without insulitis. J Biol Chem 273:2493–2496
Zawalich WS, Rasmussen H (1990) Control of insulin secretion: a model involving Ca2+, cAMP and diacylglycerol. Mol Cell Endocrinol 70:119–137
Zawalich WS, Tesz GJ, Zawalich KC (2002) Inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase amplify insulin release from islets of lean but not obese mice. J Endocrinol 174:247–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jimenez-Feltstrom, J., Lundquist, I. & Salehi, A. Glucose stimulates the expression and activities of nitric oxide synthases in incubated rat islets: an effect counteracted by GLP-1 through the cyclic AMP/PKA pathway. Cell Tissue Res 319, 221–230 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-1013-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-1013-4