Abstract
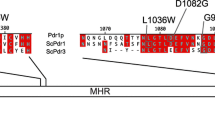
In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutations in the genes encoding the transcription factors Pdr1p and Pdr3p are known to be associated with pleiotropic drug resistance mediated by the overexpression of the efflux pumps Pdr5p, Snq2p, and Yor1p. Mutagenesis of PDR3 was used to induce multidrug resistance phenotypes and independent pdr3 mutants were isolated and characterized. DNA sequence analysis revealed seven different pdr3 alleles with mutations in the N-terminal region of PDR3. The pdr3 mutants were semidominant and conferred different drug resistance patterns on host strains deleted either for PDR3 or for PDR3 and PDR1. Transactivation experiments proved that the mutated forms of Pdr3p induced increased activation of the PDR3, PDR5, and SNQ2 promoters. The amino acid changes encoded by five pdr3 mutant alleles were found to occur in a short protein segment (amino acids 252–280), thus revealing a regulatory domain. This region may play an important role in protein–DNA or protein–protein interactions during activation by Pdr3p. Moreover, this hot spot for gain-of-function mutations overlaps two structural motifs, MI and MII, recently proposed to be conserved in the large family of Zn2Cys6 transcription factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 February 1997 / Accepted: 20 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nourani, A., Papajova, D., Delahodde, A. et al. Clustered amino acid substitutions in the yeast transcription regulator Pdr3p increase pleiotropic drug resistance and identify a new central regulatory domain. Mol Gen Genet 256, 397–405 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050583
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050583