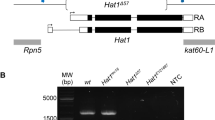
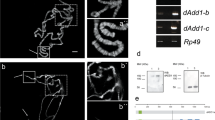
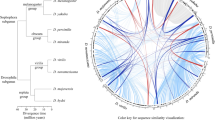
Abstract
Organization of chromatin structure and regulation of gene transcription are contingent on histone tail modifications. Regions of the genome packaged with nucleosomes that contain methyl histone H3 at lysine 9 (Me K9H3) strongly correlate with regions that are silenced for transcription. To date Su(var)3-9 is the only K9H3 specific enzyme characterized in Drosophila melanogaster. In this study, we describe the identification of three additional Drosophila genes that potentially encode K9H3 specific methyltransferases (HMTase) with homology to known mammalian proteins. By several criteria, including sequence alignments, phylogenic analyses, and enzyme activity of the protein, one of these is a homologue of the human G9a and hence, we name it dG9a. dG9a catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups to full-length histone H3 and to N-terminal H3 peptides that contain lysine 9, suggesting that the major target for dG9a is K9H3. Chromatin extracts prepared from a P-element insert mutation in dG9a display an altered K9H3 methylation profile. In addition, the dG9a mutant is a dominant suppressor of position-effect variegation (PEV), a heterochromatin-associated gene silencing phenomenon. Su(var)3-9 also suppresses PEV. The combined Su(var)3-9 and dG9a mutations have severe developmental defects suggesting an overlapping role for dG9a and Su(var)3-9 in the packaging of heterochromatin and gene silencing via a K9H3 methylation pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Si-Ali S, Guasconi V, Fritsch L, Yahi H, Sekhri R, Naguibneva I, Robin P, Cabon F, Polesskaya A, Harel-Bellan A (2004) A Suv39h-dependent mechanism for silencing S-phase genes in differentiating but not in cycling cells. EMBO J 23:605–615
Appel LF, Prout M, Abu-Shumays R, Hammonds A, Garbe JC, Fristrom D, Fristrom J (1993) The Drosophila stubble-stubbloid gene encodes an apparent transmembrane serine protease required for epithelial morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4937–4941
Beisel C, Imhof A, Greene J, Kremmer E, Sauer F (2002) Histone methylation by the Drosophila epigenetic transcriptional regulator Ash1. Nature 419:857–862
Czvitkovich S, Sauer S, Peters AH, Deiner E, Wolf A, Laible G, Opravil S, Beug H, Jenuwein T (2001) Over-expression of the SUV39H1 histone methyltransferase induces altered proliferation and differentiation in transgenic mice. Mech Dev 107:141–153
Dorigo B, Schalch T, Kulangara A, Duda S, Schroeder RR, Richmond TJ (2004) Nucleosome arrays reveal the two-start organization of the chromatin fiber. Science 306:1571–1573
Efron B, Tibshirani RJ (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman and Hall, New York
Esteve PO, Patnaik D, Chin HG, Benner J, Teitell MA, Pradhan S (2005) Functional analysis of the N- and C-terminus of mammalian G9a histone H3 methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res 33:3211–3223
Finch JT, Lutter LC, Rhodes D, Brown RS, Rushton B, Levitt M, Klug A (1977) Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature 269:29–36
Fischle W, Wang Y, Allis CD (2003) Histone and chromatin cross-talk. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:172–183
Greil F, van der Kraan I, Delrow J, Smothers JF, de Wit E, Bussemaker HJ, van Driel R, Henikoff S, van Steensel B (2003) Distinct HP1 and Su(var)3-9 complexes bind to sets of developmentally coexpressed genes depending on chromosomal location. Genes Dev 17:2825–2838
Grigliatti T (1991) Position-effect variegation—an assay for nonhistone chromosomal proteins and chromatin assembly and modifying factors. Methods Cell Biol 35:587–627
Gyory I, Wu J, Fejer G, Seto E, Wright KL (2004) PRDI-BF1 recruits the histone H3 methyltransferase G9a in transcriptional silencing. Nat Immunol 5:299–308
Huang S (2002) Histone methyltransferases, diet nutrients and tumour suppressors. Nat Rev Cancer 2:469–476
Huang S, Shao G, Liu L (1998) The PR domain of the Rb-binding zinc finger protein RIZ1 is a protein binding interface and is related to the SET domain functioning in chromatin-mediated gene expression. J Biol Chem 273:15933–15939
Jenuwein T, Allis CD (2001) Translating the histone code. Science 293:1074–1080
Jenuwein T, Laible G, Dorn R, Reuter G (1998) SET domain proteins modulate chromatin domains in eu- and heterochromatin. Cell Mol Life Sci 54:80–93
Kim KC, Geng L, Huang S (2003) Inactivation of a histone methyltransferase by mutations in human cancers. Cancer Res 63:7619–7623
Klug A, Rhodes D, Smith J, Finch JT, Thomas JO (1980) A low resolution structure for the histone core of the nucleosome. Nature 287:509–516
Lachner M, O’Sullivan RJ, Jenuwein T (2003) An epigenetic road map for histone lysine methylation. J Cell Sci 116:2117–2124
Lehnertz B, Ueda Y, Derijck AA, Braunschweig U, Perez-Burgos L, Kubicek S, Chen T, Li E, Jenuwein T, Peters AH (2003) Suv39h-mediated histone H3 lysine 9 methylation directs DNA methylation to major satellite repeats at pericentric heterochromatin. Curr Biol 13:1192–1200
Lewis EB (1950) The phenomenon of position effect. Adv Genet 3:73–115
Min J, Zhang X, Cheng X, Grewal SI, Xu RM (2002) Structure of the SET domain histone lysine methyltransferase Clr4. Nat Struct Biol 9:828–832
Muller HJ (1930) Types of visible variations induced by X-rays in Drosophila. J Genet 22:299–334
Mushegian AR, Bassett DE Jr, Boguski MS, Bork P, Koonin EV (1997) Positionally cloned human disease genes: patterns of evolutionary conservation and functional motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5831–5836
Nakayama J, Rice JC, Strahl BD, Allis CD, Grewal SI (2001) Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly. Science 292:110–113
Ner SS, Harrington MJ, Grigliatti TA (2002) A role for the Drosophila SU(VAR)3-9 protein in chromatin organization at the histone gene cluster and in suppression of position-effect variegation. Genetics 162:1763–1774
Nishio H, Walsh MJ (2004) CCAAT displacement protein/cut homolog recruits G9a histone lysine methyltransferase to repress transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11257–11262
O’Carroll D, Scherthan H, Peters AH, Opravil S, Haynes AR, Laible G, Rea S, Schmid M, Lebersorger A, Jerratsch M, Sattler L, Mattei MG, Denny P, Brown SD, Schweizer D, Jenuwein T (2000) Isolation and characterization of Suv39h2, a second histone H3 methyltransferase gene that displays testis-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol 20:9423-9433
Peters AH, O’Carroll D, Scherthan H, Mechtler K, Sauer S, Schofer C, Weipoltshammer K, Pagani M, Lachner M, Kohlmaier A, Opravil S, Doyle M, Sibilia M, Jenuwein T (2001) Loss of the Suv39h histone methyltransferases impairs mammalian heterochromatin and genome stability. Cell 107:323–337
Peters AH, Kubicek S, Mechtler K, O’Sullivan RJ, Derijck AA, Perez-Burgos L, Kohlmaier A, Opravil S, Tachibana M, Shinkai Y, Martens JH, Jenuwein T (2003) Partitioning and plasticity of repressive histone methylation states in mammalian chromatin. Mol Cell 12:1577–1589
Ponting CP (1997) Tudor domains in proteins that interact with RNA. Trends Biochem Sci 22:51–52
Rea S, Eisenhaber F, O’Carroll D, Strahl BD, Sun ZW, Schmid M, Opravil S, Mechtler K, Ponting CP, Allis CD, Jenuwein T (2000) Regulation of chromatin structure by site-specific histone H3 methyltransferases. Nature 406:593–599
Rice JC, Briggs SD, Ueberheide B, Barber CM, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Shinkai Y, Allis CD (2003) Histone methyltransferases direct different degrees of methylation to define distinct chromatin domains. Mol Cell 12:1591–1598
Roopra A, Qazi R, Schoenike B, Daley TJ, Morrison JF (2004) Localized domains of G9a-mediated histone methylation are required for silencing of neuronal genes. Mol Cell 14:727–738
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sauve DM, Anderson HJ, Ray JM, James WM, Roberge M (1999) Phosphorylation-induced rearrangement of the histone H3 NH2-terminal domain during mitotic chromosome condensation. J Cell Biol 145:225–235
Schotta G, Ebert A, Krauss V, Fischer A, Hoffmann J, Rea S, Jenuwein T, Dorn R, Reuter G (2002) Central role of Drosophila SU(VAR)3-9 in histone H3-K9 methylation and heterochromatic gene silencing. EMBO J 21:1121–1131
Schotta G, Lachner M, Sarma K, Ebert A, Sengupta R, Reuter G, Reinberg D, Jenuwein T (2004) A silencing pathway to induce H3-K9 and H4-K20 trimethylation at constitutive heterochromatin. Genes Dev 18:1251–1262
Schultz DC, Ayyanathan K, Negorev D, Maul GG, Rauscher FJ 3rd (2002) SETDB1: a novel KAP-1-associated histone H3, lysine 9-specific methyltransferase that contributes to HP1-mediated silencing of euchromatic genes by KRAB zinc-finger proteins. Genes Dev 16:919–932
Shi Y, Sawada J, Sui G, Affar el B, Whetstine JR, Lan F, Ogawa H, Luke MP, Nakatani Y (2003) Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature 422:735–738
Sinclair DAR, Mottus RC, Grigliatti TA (1983) Genes which suppress position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster are clustered. Mol Gen Genet 191:326–333
Strahl BD, Allis CD (2000) The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403:41–45
Strahl BD, Ohba R, Cook RG, Allis CD (1999) Methylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 is highly conserved and correlates with transcriptionally active nuclei in Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14967–14972
Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Fukushima T, Shinkai Y (2001) Set domain-containing protein, G9a, is a novel lysine-preferring mammalian histone methyltransferase with hyperactivity and specific selectivity to lysines 9 and 27 of histone H3. J Biol Chem 276:25309–25317
Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Nozaki M, Ueda J, Ohta T, Ohki M, Fukuda M, Takeda N, Niida H, Kato H, Shinkai Y (2002) G9a histone methyltransferase plays a dominant role in euchromatic histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and is essential for early embryogenesis. Genes Dev 16:1779–1791
Talbot K, Miguel-Aliaga I, Mohaghegh P, Ponting CP, Davies KE (1998) Characterization of a gene encoding survival motor neuron (SMN)-related protein, a constituent of the spliceosome complex. Hum Mol Genet 7:2149–2156
Tamaru H, Selker EU (2001) A histone H3 methyltransferase controls DNA methylation in Neurospora crassa. Nature 414:277–283
Thoma F, Koller T, Klug A (1979) Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol 83:403–427
Trievel RC, Beach BM, Dirk LM, Houtz RL, Hurley JH (2002) Structure and catalytic mechanism of a SET domain protein methyltransferase. Cell 111:91–103
Tschiersch B, Hofmann A, Krauss V, Dorn R, Korge G, Reuter G (1994) The protein encoded by the Drosophila position-effect variegation suppressor gene Su(var)3-9 combines domains of antagonistic regulators of homeotic gene complexes. EMBO J 13:3822–3831
Vaquero A, Loyola A, Reinberg D (2003) The constantly changing face of chromatin. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ 2003:RE4
Wilson J, Jing C, Walker P, Martin S, Howell S, Blackburn G, Gamblin S, Xiao B (2002) Crystal structure and functional analysis of the histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Cell 111:105
Wolffe AP (1998) Packaging principle: how DNA methylation and histone acetylation control the transcriptional activity of chromatin. J Exp Zool 282:239–244
Xiao B, Jing C, Wilson V, Walker PA, Vasisht N, Kelly G, Howell S, Taylor IA, Blackburn V, Gamblin SJ (2003a) Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Nature 421:652–656
Xiao B, Wilson JR, Gamblin SJ (2003b) SET domains and histone methylation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 13:699–705
Zhang X, Tamaru H, Khan SI, Horton JR, Keefe LJ, Selker EU, Cheng X (2002) Structure of the Neurospora SET domain protein DIM-5, a histone H3 lysine methyltransferase. Cell 111:117–127
Zhang X, Yang Z, Khan SI, Horton JR, Tamaru H, Selker EU, Cheng X (2003) Structural basis for the product specificity of histone lysine methyltransferases. Mol Cell 12:177–185
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a research grant from the NCIC (#013378) to T.A.G. We thank Hugh Brock, and Louis Lefebvre for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Aguilera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mis, J., Ner, S.S. & Grigliatti, T.A. Identification of three histone methyltransferases in Drosophila: dG9a is a suppressor of PEV and is required for gene silencing. Mol Genet Genomics 275, 513–526 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0116-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0116-x