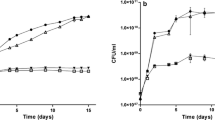
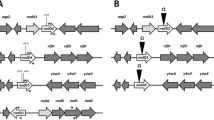
Abstract
We show that an unusual transcriptional regulator, called IrrA, regulates many genes in the symbiotic N2-fixing bacterium Rhizobium leguminosarum in response to iron availability. Several operons in R. leguminosarum are expressed at lower levels in cells grown in Fe-depleted compared to Fe-replete medium. These include hemA1, which encodes the haem biosynthesis enzyme amino-levulinic acid synthase; sufS2BCDS1XA, which specify enzymes for FeS cluster synthesis; rirA, a global, Fe-responsive transcriptional repressor; RL0400, which likely encodes an unusual FeS cluster scaffold; and the possible ferri-siderophore ABC transporter rrp1. Reduced expression in Fe-depleted medium was effected by IrrA, a member of the Fur super-family, which in Bradyrhizobium, the symbiont of soybeans, and in the mammalian pathogen Brucella, is unstable in Fe-replete conditions, due to an interaction with haem. The R. leguminosarum IrrA likely interacts with ICE (iron-control element) motifs, conserved sequences near the promoters of its target genes. The rirA, sufS2BCDS1XA and rrp1 genes are also known to be regulated by RirA, which represses their expression in Fe-replete medium. We present a possible model for iron-responsive gene regulation in Rhizobium, in which the IrrA and RirA regulators, working in parallel, respond to the intracellular availability of haem and, possibly, of FeS clusters respectively. Thus, these regulators may sense the physiological consequences of extraneous Fe concentrations, rather than the concentration of Fe per se, as happens in those bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli) in which the ferric uptake regulator Fur is the global Fe-responsive gene regulator.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agar JN, Yuvaniyama P, Jack RF, Cash VL, Smith AD, Dean DR, Johnson MK (2000) Modular organization and identification of a mononuclear iron-binding site within the NifU protein. J Biol Inorg Chem 5:167–177
Andrews SC, Robinson A., Rodriguez-Quinones F (2003) Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 27:215–237
Bateman A, Birney E, Cerruti L, Durbin R, Etwiller L et al (2002) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 30:276–280
Beaumont HJ, Lens SI, Reijnders WN, Westerhoff HV, van Spanning RJ (2004) Expression of nitrite reductase in Nitrosomonas europaea involves NsrR, a novel nitrite-sensitive transcription repressor. Mol Microbiol 54:148–158
Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Wheeler DL (2005) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D34–D38
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Carter RA, Worsley PS, Sawers G, Challis GL, Dilworth MJ, Carson KC, Lawrence JA, Wexler M, Johnston AWB, Yeoman KH (2002) The vbs genes that direct synthesis of the siderophore vicibactin in Rhizobium leguminosarum: their expression in other genera requires ECF σ factor RpoI. Mol Microbiol 44:1153–1166
Chao TC, Becker A, Buhrmester J, Pühler A, Weidner S (2004) The Sinorhizobium meliloti fur gene regulates, with dependence on Mn(II), transcription of the sitABCD operon, encoding a metal-type transporter. J Bacteriol 86:3609–3620
Chao TC, Buhrmester J, Hansmeier N, Puhler A, Weidner S (2005) The role of the regulatory gene rirA for the transcriptional response of Sinorhizobium meliloti to iron limitation. Appl Env Microbiol 71:5969–5982
Delany I, Rappuoli R, Scarlato V (2004) Fur functions as an activator and as a repressor of putative virulence genes in Neisseria meningitides. Mol Microbiol 52:1081–1090
de Peredo AG, Saint-Pierre C, Latour JM, Michaud-Soret I, Forest E (2001) Conformational changes of the ferric uptake regulation protein upon metal activation DNA binding; first evidence of structural homologies with the diphtheria toxin repressor. J Mol Biol 310:83–91
Díaz -Mireles E, Wexler M, Sawers G, Bellini D, Todd JD, Johnston AWB (2004) The Fur-like protein Mur of Rhizobium leguminosarum is a Mn(2+)-responsive transcriptional regulator. Microbiol 150:1447–1456
Díaz-Mireles E, Wexler M, Todd JD, Bellini D, Johnston AWB, Sawers RG (2005) The manganese-responsive repressor Mur of Rhizobium leguminosarum is a member of the fur-superfamily that recognises an unusual operator sequence. Microbiol 151:4071–4078
Durham KA, Porta D, McKay RM, Bullerjahn GS (2003) Expression of the iron-responsive irpA gene from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp strain PCC 7942. Arch Microbiol 179:131–134
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Figurski DH, Helinski DR (1979) Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1648–1652
Fuangthong M, Helmann JD (2003) Recognition of DNA by three ferric uptake regulator (Fur) homologs in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 185:6348–6357
Hamza I, Chauhan S, Hassett R, O’Brian MR (1998) The bacterial irr protein is required for coordination of heme biosynthesis with iron availability. J Biol Chem 273:21669–21674
Hamza I, Qi Z, King ND, O’Brian MR. (2000) Fur-independent regulation of iron metabolism by Irr in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Microbiol 146:669–676
Gelfand MS, Koonin EV, Mironov AA (2000) Prediction of transcription regulatory sites in Archaea by a comparative genomic approach. Nucleic Acids Res 28:695–705
Gottesman S (2004) The small RNA regulators of Escherichia coli: roles and mechanisms. Ann Rev Microbiol 58:303–328
Johnston AWB (2004) Mechanisms and regulation of iron uptake in the rhizobia. In: Crosa JH, Payne SM (eds) Iron transport in bacteria: molecular genetics, biochemistry, microbial pathogenesis and ecology. ASM Press, pp 469–488
Keon RG, Fu RD, Voordouw G (1997) Deletion of two downstream genes alters expression of the hmc operon of Desulfovibrio vulgaris subsp vulgaris Hildenborough. Arch Microbiol 167:376–383
Lee JH, Yeo WS, Roe JH (2004) Induction of the sufA operon encoding Fe–S assembly proteins by superoxide generators hydrogen peroxide: involvement of OxyR, IHF and an unidentified oxidant-responsive factor. Mol Microbiol 51:1745–1755
Leong SA, Ditta GS, Helinski DR (1982) Heme biosynthesis in Rhizobium. Identification of a cloned gene coding for delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase from Rhizobium meliloti. J Biol Chem 257:8724–8730
Lorain S, Lecluse Y, Scamps C, Mattei MG, Lipinski M (2001) Identification of human and mouse HIRA-interacting protein-5 (HIRIP5), two mammalian representatives in a family of phylogenetically conserved proteins with a role in the biogenesis of Fe/S proteins. Biochem Biophys Acta 1517:376–383
Martínez M, Ugalde RA, Almirón M (2005) Dimeric Brucella abortus Irr protein controls its own expression and binds haem. Microbiol 151:3427–3433
McGinnis S, Madden TL (2004) BLAST: at the core of a powerful and diverse set of sequence analysis tools. Nucl Acid Res 32(Web Server issue):W20–W25
Nienaber A, Hennecke H, Fischer HM (2001) Discovery of a haem acquisition system in the soil bacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Micriobiol 41:787–800
Mironov AA, Koonin EV, Roytberg MA, Gelfand MS (1999) Computer analysis of transcription regulatory patterns in completely sequenced bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 27:2981–2989
Mironov AA, Vinokurova NP, Gelfand MS (2000) GenomeExplorer: software for analysis of complete bacterial genomes. Mol Biol (Moscow) 34:222–231
Neidle E L, Kaplan S (1993) Expression of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides hemA and hemT genes, encoding two 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase isozymes. J Bacteriol 175:2292–2303
Outten FW, Djaman O, Storz G (2004) A suf operon requirement for Fe–S cluster assembly during iron starvation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 52:861–872
Page KM, Connolly EL, Guerinot ML (1994) Effect of iron availability on expression of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum hemA gene. J Bacteriol 176:1535–1538
Page KM, Guerinot ML (1995) Oxygen control of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum hemA gene. J Bacteriol 177:3979–3984
Panina EM, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS (2001) Comparative analysis of FUR regulons in gamma-proteobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 29:5195–5206
Platero R, Peixoto L, O’Brian MR, Fabiano E (2004) Fur is involved in manganese-dependent regulation of mntA (sitA) expression in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4349–4355
Qi Z, O’Brian MR (2002) Interaction between the bacterial iron response regulator and ferrochelatase mediates genetic control of heme biosynthesis. Mol Cell 9:155–162
Qian Y, Lee JH, Holmes RK (2002) Identification of a DtxR-regulated operon that is essential for siderophore-dependent iron uptake in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol 184:4846–4856
Rodionov DA, Dubchak I, Arkin A, Alm E, Gelfand MS (2004) Reconstruction of regulatory and metabolic pathways in metal-reducing delta-proteobacteria. Genome Biol 5:R90
Rossen L, Shearman CA, Johnston AWB, Downie JA (1985) The nodD gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum is autoregulatory and in the presence of plant root exudate induces the nodABC genes. EMBO J 4:3369–3374
Rudolph G, Semini G, Hauser F, Lindemann A, Friburg M, Hennecke H, Fischer HM (2006) The iron control element (ICE), acting in positive and negative control of iron-regulated Bradyrhizobium japonicum genes, is a target for the Irr protein. J Bacteriol 188:733–744
Sawers G, Böck A (1989) Novel transcriptional control of the pyruvate formate-lyase gene: upstream regulatory sequences and multiple promoters regulate anaerobic expression. J Bacteriol 171:2485–2498
Schwartz CJ, Giel JL, Patschkowski T, Luther C, Ruzicka FJ, Beinert H, Kiley PJ (2001) IscR, an Fe–S cluster-containing transcription factor, represses expression of Escherichia coli genes encoding Fe–S cluster assembly proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 18:14895–14900
Spaink HP, Okker RJH, Wijffelman CA, Pees E, Lugtenberg BJJ (1987) Promoters in the nodulation region of the Rhizobium leguminosarum symbiotic plasmid pRL1JI. Plant Mol Biol 9:27–39
Stevens JB, Carter RA, Hussain H, Carson KC, Dilworth MJ, Johnston AWB (1999) The fhu genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum specifying siderophore uptake proteins: fhuCDB are adjacent to a pseudogene version of fhuA. Microbiol 145:593–601
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Todd JD, Sawers G, Johnston AWB (2005) Proteomic analysis reveals the wide-ranging effects of the novel, iron-responsive regulator RirA in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv viciae. Mol Gen Genom 273:197–206
Todd JD, Wexler M, Sawers G, Yeoman KH, Poole PS, Johnston AWB. (2002) RirA, an iron-responsive regulator in the symbiotic bacterium Rhizobium leguminosarum. Microbiol 148:4059–4071
Viguier C, Cuiv P, Clarke P, O’Connell M (2005) RirA is the iron response regulator of the rhizobactin 1021 biosynthesis and transport genes in Sinorhizobium meliloti 2011. FEMS Microbiol Lett 15:235–242
Wexler M, Yeoman KH, Stevens JB, de Luca NG, Sawers G, Johnston AWB (2001) The Rhizobium leguminosarum tonB gene is required for the uptake of siderophore and haem as sources of iron. Mol Microbiol 41:801–816
Wexler M, Todd JD, Kolade O, Bellini D, Hemmings AM, Sawers G, Johnston AWB (2003) Fur is not the global regulator of iron uptake genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum. Microbiol 149:1357–1365
Wood WB (1966) Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli; bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol 16:118–133
Yang J, Ishimori K, O’Brian M R (2005) Two heme binding sites are involved in the regulated degradation of the bacterial iron response regulator (Irr) protein. J Biol Chem 280:7671–7676
Yeoman KH, Curson ARJ, Todd JD, Sawers G, Johnston AWB (2004) Evidence that the Rhizobium regulatory protein RirA binds to cis-acting iron-responsive operators (IROs) at promoters of some Fe-regulated genes. Microbiol 150:4065–4074
Yeoman KH, Wisniewski-Dye F, Timony C, Stevens JB, deLuca NG, Downie JA, Johnston AWB (2000) Analysis of the Rhizobium leguminosarum siderophore-uptake gene fhuA: differential expression in free-living bacteria and nitrogen-fixing bacteroids and distribution of an fhuA pseudogene in different strains. Microbiol 146:829–837
Zhang L, Guarente L (1995) Heme binds to a short sequence that serves a regulatory function in diverse proteins. EMBO J 16:313–320
Acknowledgements
Our thanks go to Nick le Brun and Jason Crack for useful discussions and to the BBSRC for funding. D.R. was supported by the Russian Fund of Basic Research (04-04-49361) and the Russian Academy of Sciences (Program “Molecular and Cellular Biology”). We are grateful to Gesine Rudolph and Hans-Martin Fischer for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Kondorosi
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todd, J.D., Sawers, G., Rodionov, D.A. et al. The Rhizobium leguminosarum regulator IrrA affects the transcription of a wide range of genes in response to Fe availability. Mol Genet Genomics 275, 564–577 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0115-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0115-y