Abstract
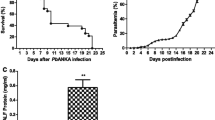
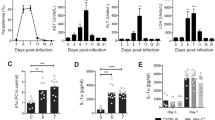
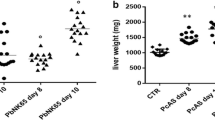
Malaria has been one of the most devastating tropical parasite infectious diseases popular around the world. Severe malaria is characterized by multiple organ dysfunctions, especially liver damage. However, the mechanisms of malarial liver injury remain to be better clarified. In this study, Kunming mice inoculated intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 106 Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbANKA)-infected red blood cells (iRBCs) were investigated at days 5, 10, 15, and 20 post-infection (p.i.) to elucidate the profiles of T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (Tim-3) and its ligand galecin-9 (Gal-9) in the development of liver injury. The histopathology of livers and spleens from PbANKA-infected mice were observed, the parasite burdens of the livers and spleens using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), Tim-3- and Gal-9-positive cells in the livers and spleens using immunohistochemical staining, and the mRNA levels of Tim-3, Gal-9, and cytokines in both the livers and spleens using qRT-PCR were examined. Our results showed that parasite burdens in the livers and spleens were significantly increased with time after PbANKA infection. Histological scores of both the liver and spleen tissues were significantly increased with time; the numbers of Tim-3- and Gal-9-positive cells were significantly increased in both the livers and spleens using immunohistochemical staining, and the mRNA levels of Tim-3 and Gal-9 in the livers and spleens were also significantly increased after infection. Our data suggests that the increase of Tim-3/Gal-9 expressions may play an important role in the liver damage during P. berghei infection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Tsutsui H, Kashiwamura SI, Seki E, Nakano H, Takeuchi O, Takeda K, Okumura K, Van Kaer L, Okamura H, Akira S, Nakanishi K (2001) Plasmodium berghei infection in mice induces liver injury by an IL-12- and Toll-like receptor/myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 167(10):5928–5934
Adachi K, Tsutsui H, Seki E, Nakano H, Takeda K, Okumura K, Van Kaer L, Nakanishi K (2004) Contribution of CD1d-unrestricted hepatic DX5+ NKT cells to liver injury in Plasmodium berghei-parasitized erythrocyte-injected mice. Int Immunol 16(6):787–798
Anand AC, Puri P (2005) Jaundice in malaria. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20(9):1322–1332
Anderson AC, Anderson DE (2006) TIM-3 in autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol 18(6):665–669
Anderson AC, Anderson DE, Bregoli L, Hastings WD, Kassam N, Lei C, Chandwaskar R, Karman J, Su EW, Hirashima M, Bruce JN, Kane LP, Kuchroo VK, Hafler DA (2007) Promotion of tissue inflammation by the immune receptor Tim-3 expressed on innate immune cells. Science 318(5853):1141–1143
Bacigalupo ML, Manzi M, Rabinovich GA, Troncoso MF (2013) Hierarchical and selective roles of galectins in hepatocarcinogenesis, liver fibrosis and inflammation of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 19(47):8831–8849
Berrocal Almanza LC, Muñoz M, Kühl AA, Kamradt T, Heimesaat MM, Liesenfeld O (2013) Tim-3 is differently expressed in genetically susceptible C57BL/6 and resistant BALB/c mice during oral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp) 3(3):211–221
Engwerda C, Belnoue E, Grüner AC, Rénia L (2005) Experimental models of cerebral malaria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 297:103–143
Fazalul Rahiman SS, Basir R, Talib H, Tie TH, Chuah YK, Jabbarzare M, Chong WC, Mohd Yusoff MA, Nordin N, Yam MF, Abdullah WO, Abdul Majid R (2013) Interleukin-27 exhibited anti-inflammatory activity during Plasmodium berghei infection in mice. Trop Biomed 30(4):663–680
Findlay EG, Greig R, Stumhofer JS, Hafalla JC, de Souza JB, Saris CJ, Hunter CA, Riley EM, Couper KN (2010) Essential role for IL-27 receptor signaling in prevention of Th1-mediated immunopathology during malaria infection. J Immunol 185(4):2482–2492
Geng H, Zhang GM, Li D, Zhang H, Yuan Y, Zhu HG, Xiao H, Han LF, Feng ZH (2006) Soluble form of T cell Ig mucin 3 is an inhibitory molecule in T cell-mediated immune response. J Immunol 176(3):1411–1420
Good MF, Xu H, Wykes M, Engwerda CR (2005) Development and regulation of cell-mediated immune responses to the blood stages of malaria: implications for vaccine research. Annu Rev Immunol 23:69–99
Haque A, Best SE, Amante FH, Ammerdorffer A, de Labastida F, Pereira T, Ramm GA, Engwerda CR (2011) High parasite burdens cause liver damage in mice following Plasmodium berghei ANKA infection independently of CD8(+) T cell-mediated immune pathology. Infect Immun 79(5):1882–1888
Helegbe GK, Yanagi T, Senba M, Huy NT, Shuaibu MN, Yamazaki A, Kikuchi M, Yasunami M, Hirayama K (2011) Histopathological studies in two strains of semi-immune mice infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA after chronic exposure. Parasitol Res 108(4):807–814
Jash A, Kwon HK, Sahoo A, Lee CG, So JS, Kim J, Oh YK, Kim YB, Im SH (2011) Topical application of porcine placenta extract inhibits the progression of experimental contact hypersensitivity. J Ethnopharmacol 133(2):654–662
Jennings VM, Actor JK, Lal AA, Hunter RL (1997) Cytokine profile suggesting that murine cerebral malaria is encephalitis. Infect Immun 65(11):4883–4887
Jones LA, Roberts F, Nickdel MB, Brombacher F, McKenzie AN, Henriquez FL, Alexander J, Roberts CW (2010) IL-33 receptor (T1/ST2) signaling is necessary to prevent the development of encephalitis in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Eur J Immunol 40(2):426–436
Klibi J, Niki T, Riedel A, Pioche-Durieu C, Souquere S, Rubinstein E, Le Moulec S, Guigay J, Hirashima M, Guemira F, Adhikary D, Mautner J, Busson P (2009) Blood diffusion and Th1-suppressive effects of galectin-9-containing exosomes released by Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Blood 113(9):1957–1966
Li H, Wu K, Tao K, Chen L, Zheng Q, Lu X, Liu J, Shi L, Liu C, Wang G, Zou W (2012) Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 56(4):1342–1351
Li Z, Ju Z, Frieri M (2013) The T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain (Tim) gene family in asthma, allergy, and autoimmunity. Allergy Asthma Proc 34(1):e21–e26
Mengshol JA, Golden-Mason L, Arikawa T, Smith M, Niki T, McWilliams R, Randall JA, McMahan R, Zimmerman MA, Rangachari M, Dobrinskikh E, Busson P, Polyak SJ, Hirashima M, Rosen HR (2010) A crucial role for Kupffer cell-derived galectin-9 in regulation of T cell immunity in hepatitis C infection. PLoS One 5(3):e9504
Mimche PN, Brady LM, Bray CF, Mimche SM, Thapa M, King TP, Quicke K, McDermott CD, Lee CM, Grakoui A, Morgan ET, Lamb TJ (2015) The receptor tyrosine kinase EphB2 promotes hepatic fibrosis in mice. Hepatology Mar 17
Murthy GL, Sahay RK, Sreenivas DV, Sundaram C, Shantaram V (1998) Hepatitis in falciparum malaria. Trop Gastroenterol 19(4):152–154
Reddy PB, Sehrawat S, Suryawanshi A, Rajasagi NK, Mulik S, Hirashima M, Rouse BT (2011) Influence of galectin-9/Tim-3 interaction on herpes simplex virus-1 latency. J Immunol 187(11):5745–5755
Rodríguez-Acosta A, Finol HJ, Pulido-Méndez M, Márquez A, Andrade G, González N, Aguilar I, Girón ME, Pinto A (1998) Liver ultrastructural pathology in mice infected with Plasmodium berghei. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 30(2):299–307
Rosen HR (2008) Transplantation immunology: what the clinician needs to know for immunotherapy. Gastroenterology 134(6):1789–1801
Saita N, Goto E, Yamamoto T, Cho I, Tsumori K, Kohrogi H, Maruo K, Ono T, Takeya M, Kashio Y, Nakamura K, Hirashima M (2002) Association of galectin-9 with eosinophil apoptosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 128:42–50
Sánchez-Fueyo A, Tian J, Picarella D, Domenig C, Zheng XX, Sabatos CA, Manlongat N, Bender O, Kamradt T, Kuchroo VK, Gutiérrez-Ramos JC, Coyle AJ, Strom TB (2003) Tim-3 inhibits T helper type 1-mediated auto- and alloimmune responses and promotes immunological tolerance. Nat Immunol 4(11):1093–1101
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C (T) method. Nat Protoc 3(6):1101–1108
Singh R, Kashiwamura S, Rao P, Okamura H, Mukherjee A, Chauhan V (2002) The role of IL-18 in blood-stage immunity against murine malaria Plasmodium yoelii 265 and Plasmodium berghei ANKA. J Immunol 168(9):4674–4681
Tang ZH, Liang S, Potter J, Jiang X, Mao HQ, Li Z (2013) Tim-3/galectin-9 regulate the homeostasis of hepatic NKT cells in a murine model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Immunol 190(4):1788–1796
Uchida Y, Ke B, Freitas MC, Yagita H, Akiba H, Busuttil RW, Najafian N, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2010) T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 determines severity of liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice in a TLR4-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 139:2195–2206
Uri-Belapolsky S, Shaish A, Eliyahu E, Grossman H, Levi M, Chuderland D, Ninio-Many L, Hasky N, Shashar D, Almog T, Kandel-Kfir M, Harats D, Shalgi R, Kamari Y (2014) Interleukin-1 deficiency prolongs ovarian lifespan in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(34):12492–12497
Viriyavejakul P, Khachonsaksumet V, Punsawad C (2014) Liver changes in severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria: histopathology, apoptosis and nuclear factor kappa B expression. Malar J 13:106
Vollmar B, Menger MD (2009) The hepatic microcirculation: mechanistic contributions and therapeutic targets in liver injury and repair. Physiol Rev 89(4):1269–1339
Wada J, Kanwar YS (1997) Identification and characterization of galectin-9, a novel beta-galactoside-binding mammalian lectin. J Biol Chem 272(9):6078–6086
Whitten R, Milner DA Jr, Yeh MM, Kamiza S, Molyneux ME, Taylor TE (2011) Liver pathology in Malawian children with fatal encephalopathy. Hum Pathol 42(9):1230–1239
WHO (2010) Guideline for the treatment of malaria, 2nd ed
Yoshida H, Imaizumi T, Kumagai M, Kimura K, Satoh C, Hanada N, Fujimoto K, Nishi N, Tanji K, Matsumiya T, Mori F, Cui XF, Tamo W, Shibata T, Takanashi S, Okumura K, Nakamura T, Wakabayashi K, Hirashima M, Sato Y, Satoh K (2001) Interleukin-1beta stimulates galectin-9 expression in human astrocytes. Neuroreport 12:3755–3758
Zhao J, Endoh I, Hsu K, Tedla N, Endoh Y, Geczy CL (2011) S100A8 modulates mast cell function and suppresses eosinophil migration in acute asthma. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(9):1589–1600
Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong H, Imitola J, Khoury SJ, Zheng XX, Strom TB, Kuchroo VK (2005) The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat Immunol 6(12):1245–1252
Zhu C, Anderson AC, Kuchroo VK (2011) TIM-3 and its regulatory role in immune responses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 350:1–15
Acknowledgments
Research reported in this publication was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China to F.L. (nos. 81271854 and 81471973), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China to F.L. (no. S2013010016736), and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (nos. 2014A020212108, 2013B021800043, and 2014A020212212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, S., Liu, J., Huang, S. et al. Increased Gal-9 and Tim-3 expressions during liver damage in a murine malarial model. Parasitol Res 115, 663–672 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4784-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4784-5