Abstract
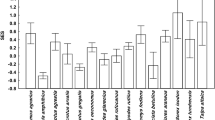
We studied the effect of host gender and body mass on species richness of flea infracommunities in nine rodent host species from three biomes (temperate zone of central Europe, desert of the Middle East and the tropics of East Africa). Using season- and species-specific generalized linear mixed models and controlling for year-to-year variation, spatial clustering of rodent sampling and over-dispersion of the data, we found inconsistent associations between host characteristics and flea species richness. We found strong support for male-biased flea parasitism, especially during the reproductive period (higher species richness in male hosts than in females) in all considered European rodents (Apodemus agrarius, Myodes glareolus and Microtus arvalis) and in one rodent species from the Middle East (Dipodillus dasyurus). In contrast, two of three African rodent species (Lophuromys kilonzoi and Praomys delectorum) demonstrated a trend of female-biased flea species richness. Positive associations between body mass and the number of flea species were detected mainly in males (five of nine species: A. agrarius, M. glareolus, M. arvalis, D. dasyurus and Mastomys natalensis) and not in females (except for M. natalensis). The results of this study support earlier reports that gender-biased, in general, and male-biased, in particular, infestation by ectoparasites is not a universal rule. This suggests that mechanisms of parasite acquisition by an individual host are species-specific and have evolved independently in different rodent host-flea systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RM, Gordon DM (1982) Processes influencing the distribution of parasite numbers within host populations with special emphasis on parasite-induced host mortality. Parasitology 85:373–398
Alzaga V, Vicente J, Villanua D, Acevedo P, Casas F, Gortazar C (2008) Body condition and parasite intensity correlates with escape capacity in Iberian hares (Lepus granatensis). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 62:769–775
Attuquayefio DK, Gorman ML, Wolton RJ (2009) Home rang sizes in the wood mouse Apodemus sylvaticus: habitat, sex and seasonal differences. J Zool 210:45–53
Bashenina NV (1962) Ecology of the common vole. Moscow Univ Press, Moscow, USSR (in Russian)
Bartón K (2013) Model selection and model averaging based on information criteria (AICc and alike). Available at: http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MuMIn/index.html
Bates D, Maechler M (2009) lme4: Linear mixed-effects models using S4 classes. R package, version. http://lme4.r-forge.r-project.org/
Bordes F, Blumstein DT, Morand S (2007) Rodent sociality and parasite diversity. Biol Letters 3:692–694
Bordes F, Morand S (2009) Parasite diversity: an overlooked metric of parasite pressures? Oikos 118:801–806
Bordes F, Ponlet N, Goüy de Bellocq J, Ribas A, Krasnov BR, Morand S (2012) Is there sex biased resistance and tolerance in Mediterranean wood mouse (Apodemus sylvaticus) populations facing multiple helminth infections? Oecologia 170:123–135
Borowski Z (2003) Habitat selection and home range size of field voles Microtus agrestis in Slowínski National Park, Poland. Acta Theriol 48:325–333
Boyer N, Réale D, Marmet J, Pisanu B, Chapuis J-L (2010) Personality, space use and tick load in an introduced population of Siberian chipmunks Tamias sibiricus. J Anim Ecol 79:538–547
Bronson FH (1989) Mammalian reproductive biology. University of Chicago Press, 325 pp
Bronson F, Desjardins C (1971) Steroid hormones and aggressive behaviour in mammals. p. 43-63 In B.E. Eleftheriou, JP Scott (eds) The physiology of aggression and defeat. Subject Strain Bibliography 1971. Paper 1041
Brunner JL, Ostfeld RS (2008) Multiple causes of variable tick burdens on small mammal hosts. Ecology 89:2259–2272
Buckling A, Rainey PB (2002) The role of parasites in sympatric and allopatric host diversification. Nature 6915:496–499
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information—theoretic approach, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Calabrese JM, Brunner JL, Ostfeld RS (2011) Partitioning the aggregation of parasites on hosts into intrinsic and extrinsic components via an extended Poisson-Gamma Mixture Model. PLoS ONE 6:e29215
Caruso C, Accardi G, Virruso C, Candore G (2013) Sex, gender and immunosenescence: a key to understand the different lifespan between men and women? Immun Ageing 10:20
Casto JM, Jr Nolan V, Ketterson ED (2001) Steroid hormones and immune function: experimental studies in wild and captive dark-eyed juncos (Junco hyemalis). Am Nat 157:408–420
Clay CA, Lehmer EM, Previtali A, St Jeor S, Dearing MD (2009) Contact heterogeneities in deer mice: implications for Sin Nombre virus transmission. Proc R Soc Lond B 276:1305–1312
Creel S, Creel N, Wildt DE, Monfort SL (1992) Behavioral and endocrine mechanisms of reproductive suppression in Serengeti dwarf mongooses. Anim Behav 43:231–245
Elston DA, Moss R, Boulinier T, Arrowsmith C, Lambin X (2001) Analysis of aggregation, a worked example: numbers of ticks on red grouse chicks. Parasitology 122:563–569
Erlinge S, Hoogenboom I, Agrell J, Nelson J, Sandell M (1990) Density-related home-range size and overlap in adult field voles (Microtus agrestis) in southern Sweden. J Mammal 71:597–603
Ferrari N, Cattadori IM, Nespereira J, Rizzoli A, Hudson PJ (2004) The role of host sex in parasite dynamics: field experiments on the yellow-necked mouse Apodemus flavicollis. Ecol Lett 7:88–94
Folstad I, Karter AJ (1992) Parasites, bright males, and the immunocompetence handicap. Amer Nat 139:603–622
Gelman A, Su Y-S, Yajima M, Hill J, Pittau MG, Kermann J, Zheng T (2013) arm: Data analysis using regression and multilevel/hierarchical models. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/arm/
Ginaldi L, Loreto MF, Corsi MP, Modesti M, de Martinis M (2001) Immunosenescence and infectious diseases. Microbes Infect 3:851–857
Gleason ED, Fuxjager MJ, Oyegbile TO, Marler CA (2009) Testosterone release and social context: when it occurs and why. Front Neuroendocrinol 30:460–469
Gliwicz J (1988) Seasonal dispersal in non-cyclic populations of Clethrionomys glareolus and Apodemus flavicollis. Acta Theriol 33:263–272
Goüy de Bellocq J, Charbonnel N, Morand S (2008) Coevolutionary relationship between helminth diversity and MHC class II polymorphism in rodents. J Evol Biol 21:1144–1150
Grueber CE, Nakagawa S, Laws RJ, Jamieson IG (2011) Multimodel inference in ecology and evolution: challenges and solutions. J Evol Biol 24:699–711
Harrison A, Scantlebury M, Montgomery W (2010) Body mass and sex-biased parasitism in wood mice Apodemus sylvaticus. Oikos 119:1099–1104
Hilbe JM (2011) Negative binomial regression. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge
Hillegass MA, Waterman JM, Roth JD (2008) The influence of sex and sociality on parasite loads in an African ground squirrel. Behav Ecol 19:1006–1011
Hirokawa K, Utsuyama M, Hayashi Y, Kitagawa M, Makinodan T, Fulop T (2013) Slower immune system aging in women versus men in the Japanese population. Immun Ageing 10:19
Ims RA (1987) Male spacing systems in microtine rodents. Am Nat 130:475–484
Jetz W, Carbone C, Fulford J, Brown JH (2004) The scaling of animal space use. Science 306:266–268
Khokhlova IS, Spinu M, Krasnov BR, Degen AA (2004) Immune responses to fleas in two rodent species differing in natural prevalence of infestation and diversity of flea assemblages. Parasitol Res 94:304–311
Khokhlova IS, Serobyan V, Krasnov BR, Degen AA (2009) Is the feeding and reproductive performance of the flea, Xenopsylla ramesis, affected by the gender of its rodent host, Meriones crassus? J Exp Biol 212:1429–1435
Khokhlova IS, Serobyan V, Degen AA, Krasnov BR (2010) Host gender and offspring quality in a flea parasitic on a rodent. J Exp Biol 213:3299–3304
Kiffner C, Lödige C, Alings M, Vor T, Rühe F (2011a) Body-mass or sex-biased tick parasitism in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus)? A GAMLSS approach. Med Vet Entomol 25:39–45
Kiffner C, Vor T, Hagedorn P, Niedrig M, Rühe F (2011b) Factors affecting patterns of tick parasitism on forest rodents in tick-borne encephalitis risk areas, Germany. Parasitol Res 108:323–35
Kiffner C, Stanko M, Morand S, Khoklova IS, Shenbrot I, Laudisoit A, Leirs H, Hawlena H, Krasnov B (2013) Sex-biased parasitism is not universal: evidence from rodent-flea associations from three biomes. Oecologia 173:1009–1022. doi:10.1007/s00442-013-2664-1
Klimpel S, Förster M, Schmahl G (2007) Parasites of two abundant sympatric rodent species in relation to host phylogeny and ecology. Parasitol Res 100:867–875
Korallo NP, Vinarsky MV, Krasnov BR, Shenbrot GI, Mouillot D, Poulin R (2007) Are there general rules governing parasite diversity? Small mammalian hosts and gamasid mite assemblages. Divers Distrib 13:353–360
Koshev Y, Atanassov N, Kocheva M (2005) Relation between body mass and home range size of small mammals. In Proceedings of the Balkan Scientific Conference of Biology. Eds B. Gruev, M. Nikolov, A. Donev, p 437-444
Krasnov BR, Hastriter M, Medvedev SG, Shenbrot GI, Khokhlova IS, Vaschenok VS (1999) Additional records of fleas (Siphonaptera) on wild rodents in the southern part of Israel. Israel J Zool 45:333–340
Krasnov BR, Kokhlova IS (2002) The effect of behavioural interactions on the exchange of flea (Siphonaptera) between two rodent species. J Vector Ecol 26:181–190
Krasnov BR, Matthee S (2010) Spatial variation in gender-biased parasitism: host-related, parasite-related and environment-related effects. Parasitology 137:1527–1536
Krasnov BR, Shenbrot GI, Medvedev SG, Vatschenok VS, Khokhlova IS (1997) Host-habitat relations as an important determinant of spatial distribution of flea assemblages (Siphonaptera) on rodents in the Negev Desert. Parasitology 114:159–173
Krasnov BR, Burdelova NV, Shenbrot GI, Khokhlova IS (2002) Annual cycles of four flea species (Siphonaptera) in the central Negev desert. Med Vet Entomol 16:266–276
Krasnov BR, Shenbrot GI, Khokhlova IS, Degen AA (2004) Flea species richness and parameters of host body, host geography and host “milieu”. J Anim Ecol 73:1121–1128
Krasnov BR, Morand S, Hawlena H, Khokhlova IS, Shenbrot GI (2005) Sex-biased parasitism, seasonality and sexual size dimorphism in desert rodents. Oecologia 146:209–217
Krasnov BR, Shenbrot GI, Khokhlova IS, Hawlena H, DEGEN AA (2006a) Temporal variation in parasite infestations of a host individual: does a parasite-free host remain uninfested permanently? Parasitol Res 99:541–545
Krasnov BR, Stanko M, Miklisova D, Morand S (2006b) Habitat variation in species composition of flea assemblages on small mammals in central Europe. Ecol Res 21:460–469
Krasnov BR, Stanko M, Matthee S, Laudisot A, Leirs H, Khokhlova IS, Korallo-Vinarskaya NP, Vinarski MV, Morand S (2011) Male hosts drive infracommunity structure of ectoparasites. Oecologia 166:1099–1010
Krasnov BR, Bordes F, Khokhlova IS, Morand S (2012) Gender-biased parasitism in small mammals: patterns, mechanisms, consequences. Mammalia 76:1–13
Laudisoit A, Leirs H, Makundi RH, Krasnov BR (2009) Seasonal and habitat dependence of species composition of flea assemblages parasitic on small mammals in Tanzania. Integr Zool 4:196–212
Leirs H (1992) Population ecology of Mastomys natalensis (SMITH, 1834) multimammate rats: possible implications for rodent control in Africa. 273 pp. UIA, Department of Biology, Antwerp.
Leirs H, Verheyen W, Michiels M, Verhagen R, Stuyck J (1989) The relation between rainfall and breeding season of Mastomys natalensis (Smith 1834) in Morogoro, Tanzania. Ann soc R zool Belg 119:59–64
Lindenfors P, Nunn CL, Jones KE, Cunnungham AA, Sechrest W, Gittleman JL (2007) Parasite species richness in carnivores: effects of host body mass, latitude, geographical range and population density. Global Ecol Biogeograph 16:496–509
Lott DF (1991) Intraspecific variation in the social systems of wild vertebrates. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge
Luong LT, Perkins SE, Grear DA, Rizzoli A, Hudson PJ (2010) The relative importance of host characteristics and co-infection in generating variation in Heligmosomoides polygyrus fecundity. Parasitology 137:1003–1012
Makundi RH, Massawe AW, Mulungu LS (2007) Reproduction and population dynamics of Mastomys natalensis Smith, 1834 in an agricultural landscape in the Western Usambara. Integr Zool 2:233–238
Matthee S, McGeoch MA, Krasnov BR (2010) Gender-biased ectoparasite infections: species-specific variation and the extent of male-biased parasitism. Parasitology 137:651–660
Matthysen E (2005) Density-dependent dispersal in birds and mammals. Ecography 28:403–416
Moller AP, Rosza L (2005) Parasite biodiversity and host defenses: chewing lice and immune response of their avian hosts. Oecologia 142:169–176
Moore SL, Wilson K (2002) Parasites as a viability cost of sexual selection in natural populations of mammals. Science 297:2015–2018
Morand S, Harvey PH (2000) Mammalian metabolism, longevity and parasite species richness. Proc Biol Sci 267:1999–2003
Morand S, De Bellocq JG, Stanko M, Miklisova D (2004) Is sex-biased ectoparasitism related to size dimorphism in small mammals of Central Europe? Parasitology 129:505–510
Navarro-Gonzalez N, Verheyden H, Hoste H, Cargnelutti B, Lourtet B, Merlet J, Daufresne T, Lavín S, Hewison AJM, Morand S, Serrano E (2011) Diet quality and immunocompetence influence parasite load of roe deer in a fragmented landscape. Eur J Wildlife Res 57:639–645
Nunn CL, Altizer S, Sechrest W, Jones KE, Barton RA, Gittleman JL (2004) Parasites and the evolutionary diversification of primate clades. Am Nat 164:S90–103
Ostfeld RS (1985) Limiting resources and territoriality in microtine rodents. Am Nat 126:1–15
Perkins SE, Cattadori IM, Tagliapietra V, Rizzoli AP, Hudson PJ (2003) Empirical evidence for key hosts in persistence of a tick-borne disease. Int J Parasitol 33:909–917
Poulin R (1996) Sexual inequalities in helminth infections: a cost of being male? Am Nat 147:289–295
Poulin R, George-Nascimento M (2007) The scaling of total parasite biomass with host body mass. Int J Parasitol 37:359–364
Previtali MA, Lehmer EM, Pearce-Duvet JMC, Jones JD, Clay CA, Wood BA, Ely PW, Laverty SM, Dearing MD (2010) Roles of human disturbance, precipitation, and a pathogen on the survival and reproductive probabilities of deer mice. Ecology 91:582–592
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.project.org
Råberg L, Sim D, Read AF (2007) Disentangling genetic variation for resistance and tolerance to infectious diseases in animals. Science 318:812–814
Råberg L, Graham AL, Read AF (2009) Decomposing health: tolerance and resistance to parasites in animals. Phil Trans R Soc B 364:37–49
Razzoli M, Cushing BS, Carter CS, Valsecchi P (2003) Hormonal regulation of agonistic and affiliative behaviour in female Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). Horm Behav 43:549–553
Rolff J (2002) Bateman’s principle and immunity. Proc R Soc Lond B 269:867–872
Rueesch S, Lemoine M, Richner H (2012) Ectoparasite performance when host condition varies. Parasitol Res 111:1193–1203
Schalk G, Forbes MR (1997) Male biases in parasitism of mammals: effects of study type, host age, and parasite taxon. Oikos 78:67–74
Schmid-Hempel P (2003) Variation in immune defence as a question of evolutionary ecology. Proc R Soc Lond B 270:357–366
Schwarzenberger T, Klingel H (1994) Telemetrische Untersuchungen zur Raumnutzung und Aktivitätsrhytmik freilebender Gelbhalsmäuse, Apodemus flavicollis Melchior, 1834. Z Säugetierkunde 60:33–40
Sheldon BC, Verhulst S (1996) Ecological immunology: costly parasite defenses and trade offs in evolutionary ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 11:317–321
Šimková A, Lafond T, Ondrackova M, Jurajda P, Ottova E, Morand S (2008) Parasitism, life history traits and immune defence in cyprinid fish from Central Europe. BMC Evol Biol 8:29. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-29
Stanko M, Miklisova D, Gouy de Bellocq J, Morand S (2002) Mammal density and patterns of ectoparasite species richness and abundance. Oecologia 131:289–295
Stenseth NC, Lidicker WZ (eds) (1992) Animal dispersal: small mammals as a model. Chapman & Hall, London, p 240
van Hooft P, Cosson JF, Vibe-Peteresen S, Leirs H (2008) Dispersal in Mastomys natalensis mice: use of fine-scale genetic analyses for pest management. Hereditas 145:262–273
Vázquez L, Panadero R, Dacal V, Pato FJ, López C, Díaz P, Arias MS, Fernández G, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P (2011) Tick infestation (Acari: Ixodidae) in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) from northwestern Spain: population dynamics and risk stratification. Exp Appl Acarol 53:399–409
Viljoen H, Bennet NC, Ueckermann EA, Luterman H (2011) The role of host traits, season and group size on parasite burdens in a cooperative mammal. PLoS ONE 6:e27003
Vor T, Kiffner C, Hagedorn P, Niedrig M, Rühe F (2010) Tick burden on European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus). Exp Appl Acarol 51:405–417
Waterman J (2007) Male mating strategies in rodents. In: Wolff JO, Sherman PW (eds) Rodent societies. An ecological & evolutionary perspective. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 27–41
Wolff JO (1993) Why are female small mammals territorial? Oikos 68:364–370
Zahn A, Rupp D (2004) Ectoparasite load in European vespertilionid bats. J Zool 262:383–391
Zuk M (1996) Disease, endocrine-immune interactions, and sexual selection. Ecology 77:1037–1042
Zuk M, McKean KA (1996) Sex differences in parasite infections: patterns and processes. Int J Parasitol 26:1009–1024
Acknowledgments
Allan Degen read the earlier version of the manuscript and made helpful comments, and Kiri Brenner edited the English. Studies in Israel were partly supported by Israel Science Foundation (grant 26/12 to ISK and BRK). Studies in Slovakia were conducted under the licenses of the Ministry of Environment of the Slovak Republic No. 297/108/06-3.1 and No. 6743/2008-2.1 and partly supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency (grant APVV 0267-10 to MS). Studies in Tanzania were supported by the Belgian Fund for the Research in Industry and Agro-alimentary, the Fund for Scientific Research—Flanders for scientific research, the University of Antwerp and the Sokoine University of Agriculture (Tanzania). This is publication no. 834 of the Mitrani Department of Desert Ecology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 40 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiffner, C., Stanko, M., Morand, S. et al. Variable effects of host characteristics on species richness of flea infracommunities in rodents from three continents. Parasitol Res 113, 2777–2788 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3937-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3937-2