Abstract
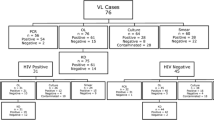
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is one of the neglected tropical diseases that require a global policy for integrated control programs. The disease is fatal if untreated, affects ∼500,000 persons/year, and is most prevalent in poor countries. Treatment is expensive and carries a risk of toxicity. Therefore, sensitive and specific diagnosis of VL is crucial to avoid under- or overdiagnosis. Selecting an appropriate serological diagnostic test is an issue of controversy and depends on geographic location. The study aimed to evaluate the performance of two serological techniques: recombinant antigen K39 (rK39)-immunochromatographic (IC) lateral flow assay (InBios, USA) that uses a recombinant Leishmania antigen K39 and the specific IgG detection by direct agglutination test (DAT, for the diagnosis of imported VL in non-endemic region (Saudi Arabia). The diagnostic accuracy of the two assays was assessed using bone marrow aspiration, direct microscopic examination, and culture on NNN agar as the “gold standard”. The bone marrow specimens from Indian, Sudanese, and Bengali patients (n = 98) with suspected VL features were cultured. Thirty-five specimens were positive (36%). The sensitivity and specificity of rK39-IC test were 89% (95% CI 78–99) and 92% (95% CI 85–99), respectively. DAT (with cutoff ≥1:1,600) showed comparable results (sensitivity 94%; 95% CI 87–101 and specificity 95%; 95% CI 90–100). To conclude, the performance of rK39-IC test and DAT is comparable. Both tests are moderately sensitive and specific and could be used to facilitate the global drive to eliminate this disease. The rK39-IC test is a rapid, easy-to-perform test and can be used as a point-of-care diagnostic method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badar’o R, Benson D, Eul’alio MC, Freire M, Cunha S, Netto EM, Pedral-Sampio D, Madureira C, Burns JM, Houghton RL, David JR, Reed SG (1996) rK39: a cloned antigen for Leishmania chagasi that predicts active visceral leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis 173:758–761
Boelaert M, Rijal S, Regmi S, Singh R, Karki B, Jacquet D, Chappuis F, Campino L, Desjeux P, Le Ray D, Koirala S, Van der Stuyft P (2004) A comparative study of the effectiveness of diagnostic tests for visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 70:72–77
Boelaert M, El-Safi S, Hailu A, Mukhtar M, Rijal S, Sundar S, Wasunna M, Aseffa A, Mbui J, Menten J, Desjeux P, Peeling RW (2008) Diagnostic tests for kala-azar: a multi-centre study of the freeze-dried DAT, rK39 strip test and KAtex in East Africa and the Indian subcontinent. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 102:32–40
Carvalho SF, Lemos EM, Corey R, Dietze R (2003) Performance of recombinant K39 antigen in the diagnosis of Brazilian visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 68:321–324
Chappuis F, Rijal S, Singh R, Acharya P, Karki BM, Das ML, Bovier PA, Desjeux P, Le Ray D, Koirala S, Loutan L (2003) Prospective evaluation and comparison of the direct agglutination test and an rK39-antigen-based dipstick test for the diagnosis of suspected kala-azar in Nepal. Trop Med Int Health 8:277–285
Chappuis F, Rijal S, Soto A, Menten J, Boelaert M (2006) A meta-analysis of the diagnostic performance of the direct agglutination test and rK39 dipstick for visceral leishmaniasis. Br Med J 333:723
Chowdhury MS, Al Masum A, Al Karim E, Semiáo-Santos S, Rahman KM, Ar-Rashid H, El Harith A (1993) Applicability of direct agglutination test (DAT) at a rural health setting in Bangladesh and feasibility of local antigen production. Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis 70:333–344
Desjeux P (1996) Leishmaniasis. Public health aspects and control. Clin Dermatol 14:417–23
El Amin ER, Wright EP, Abdel Rahman AM, Kolk A, Laarman JJ, Pondman KW (1986) Serodiagnosis of Sudanese visceral and mucosal leishmaniasis: comparison of ELISA–immunofluorescence and indirect haemagglutination. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 80:271–274
El Harith A, Kolk AH, Kager PA, Leeuwenburg J, Muigai R, Kiugu S, Kiugu S, Laarman JJ (1986) A simple and economical direct agglutination test for serodiagnosis and sero-epidemiological studies of visceral leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 80:583–587
Hyun BH, Gulati GL, Ashton JK (1988) Bone marrow examination: techniques and interpretation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2(4):513–523
Jacquet D, Boelaert M, Seaman J, Rijal S, Sundar S, Menten J, Magnus E (2006) Comparative evaluation of freeze-dried and liquid antigens in the direct agglutination test for serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis (ITMA-DAT/VL). Trop Med Int Health 11:1777–1784
Kar K (1995) Serodiagnosis of leishmaniasis. Crit Rev Microbiol 21:123–152
Kumar R, Pai K, Pathak K, Sundar S (2001) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for recombinant K39 antigen in diagnosis and prognosis of Indian visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 8:1220–1224
Marsden PD, Jones TC (1985) Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis. In: Chang KP, Bray RS (eds) Leishmaniasis. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 183–198
Maurya R, Singh RK, Kumar B, Salotra P, Rai M, Sundar S (2005) Evaluation of PCR for diagnosis of Indian kala-azar and assessment of cure. J Clin Microbiol 43:3038–3041
Meredith SE, Kroon NC, Sondorp E, Seaman J, Goris MG, van Ingen CW, Oosting H, Schoone GJ, Terpstra WJ, Oskam L (1995) Leish-KIT, a stable direct agglutination test based on freeze dried antigen for serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. J Clin Microbiol 33:1742–1745
Ozerdem D, Eroglu F, Genc A, Demirkazik M, Koltas IS (2009) Comparison of microscopic examination, rK39, and PCR for visceral leishmaniasis diagnosis in Turkey. Parasitol Res 106:197–200
Pedra MJ, Viana LG, Oliveira EJ, Rabello A (2008) Comparative evaluation of direct agglutination test, rK39 and soluble antigen ELISA and IFAT for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 102:172–178
Ritmeijer K, Melaku Y, Mueller M, Kipngetich S, O'keeffe C, Davidson RN (2006) Evaluation of a new recombinant K39 rapid diagnostic test for Sudanese visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 74:76–80
Schallig HD, Schoone GJ, Hailu A, Beijer EG, Kroon CC, Hommers M, Ozbel Y, Ozensoy S, da Silva ES, Cardoso LM, da Silva ED (2002) Development of a fast agglutination screening test (FAST) for the detection of anti-Leishmania antibodies in dogs. Vet Parasitol 109:1–8
Schur LF, Jacobson RL (1987) Parasitological techniques. In: Peters W, Killick-Kendrick R (eds) Leishmaniasis in biology and medicine. Academic, New York, pp 500–541
Shyam S, Reed G, Singh VP, Kumar PC, Murray HW (1998) Rapid accurate field diagnosis of Indian visceral leishmaniasis. Lancet 351:563–565
Siddig M, Ghalib HW, Shillington DC, Petersen EA (1988) Visceral leishmaniasis in the Sudan: comparative parasitological methods of diagnosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 82:66–68
Singh S, Gilman-Sachs A, Chang KP, Reed SG (1995) Diagnostic and prognostic value of K39 recombinant antigen in Indian leishmaniasis. J Parasitol 81:1000–1003
Sinha R, Sehgal S (1994) Comparative evaluation of serological tests in Indian kala-azar. J Trop Med Hyg 97:333–340
Sundar S, Reed SG, Singh VP, Kumar PC, Murray HW (1998) Rapid accurate field diagnosis of Indian visceral leishmaniasis. Lancet 351:563–565
Sundar S, Maurya R, Singh RK, Bharti K, Chakravarty J, Parekh A, Rai M, Kumar K, Murray HW (2006) Rapid, noninvasive diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in India: comparison of two immunochromatographic strip tests for detection of anti-K39 antibody. J Clin Microbiol 44:251–253
WHO (1990) Control of the Leishmaniasis. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organization Technical Report Series no. 793, Geneva
WHO (1996) Manual on visceral leishmaniasis control [www.who.int] World Health Organization, Geneva
World Health Organization (1998) Leishmania and HIV in gridlock. WHO/CTD/Leish/98.9 add. 1, UNAIDS/98.23. World Health Organization, Geneva
Zijlstra EE, Ali MS, El-Hassan AM, El-Toum IA, Satti M, Ghalib HW, Kager PA (1992) Kala-azar: a comparative study of parasitological methods and the direct agglutination test in diagnosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 86:505–507
Zijlstra EE, Nur Y, Desjeux P, Khalil EA, El Hassan AM, Groen J (2001) Diagnosing visceral leishmaniasis with the recombinant K39 strip test: experience from the Sudan. Trop Med Int Health 6:108–113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Moamly, A., El-Sweify, M. & Hafeez, M. Performance of rK39 immunochromatography and freeze-dried direct agglutination tests in the diagnosis of imported visceral leishmaniasis. Parasitol Res 110, 349–354 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2499-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2499-9