Abstract
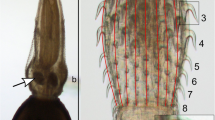
The morphology, ultrastructure, genetics, and morphometrics of a species of Diplostomum von Nordmann 1832 (Digenea: Diplostomidae), isolated from the European flounder (Platichthys flesus (L.)) caught off the northwest coast of Portugal, are characterized. The metacercarial stage was found unencysted in the lens capsule of the eye. Light microscopical observations revealed the existence of some variability in specimen shape and size, with two morphotypes, referred to as “round” and “long”, being apparent. Scanning electron microscopy revealed a smooth, unarmed tegument, with the lappet region being the most irregular and porose. Both the oral and ventral suckers were provided with a series of papillae, which presented very distinctive ultrastructural features and were particularly conspicuous in the case of the ventral sucker. The two morphotypes detected were found to have 100% genetic correspondence in the 18S + ITS1 + 5.8S region of the rDNA. Since the genetic data for this metacercaria differed from those of the species of Diplostomum available in GenBank, a description of a new genotype (accession number GQ370809) is provided. The molecular phylogenetic analyses, in conjunction with principal components and cluster analyses based on morphometric data, revealed the existence of consistent differences between the Diplostomum sp. metacercariae from flounder compared with Diplostomum spathaceum, Diplostomum mergi, Diplostomum pseudospathaceum, and Diplostomum paracaudum. The latter of these species was found to be the most similar to the present material. Our results do not support an evolutionary separation of the European and North American species of Diplostomum.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brucko-Stempkowski R (1970) Parasites of the flounder—Platichthys flesus (L.) from the brackish water of Kamieński Bay. Acta Ichthyol Piscat 1:97–102
Chappell LH (1995) The biology of diplostomatid eyeflukes of fishes. J Helminthol 69:97–101
Chibani M, Rokicki J (2004) Seasonal occurrence of parasites of flounder Platichthys flesus (L.) from the Gulf of Gdańsk. Oceanol Hydrobiol St 33:17–30
Chibwana FD, Nkwengulila G (2009) Variation in the morphometrics of diplostomid metacercariae (Digenea: Trematoda) infecting the catfish, Clarias gariepinus in Tanzania. J Helminthol 21:1–10
Conneely JJ, McCarthy TK (1984) The metazoan parasites of freshwater fishes in the Corrib catchment area, Ireland. J Fish Biol 24:363–375
Dorovskikh GN (1997) Results of the study of fishes' parasites in river basins of the north-east of the European part of Russia. Trematodes (Trematoda). Parazitologiya 21:551–564 (in Russian)
Dwyer WP, Smith CE (1989) Metacercariae of Diplostomum spathaceum in the eyes of fishes from Yellowstone Lake, Wyoming. J Wildlife Dis 25:126–129
Engelbrecht H (1958) Untersuchungen über den parasitenbefall der Nutzfische in Greifswalder Bodden und Kleinen Haff. Z Fischkd 7:481–511
Felgenhaeur BE (1987) Techniques for preparing crustaceans for scanning electron microscopy. J Crust Biol 7:71–76
Field JS, Irwin SWB (1995) Life-cycle description and comparison of Diplostomum spathaceum (Rudolphi, 1819) and D. pseudobaeri (Razmaskin & Andrejak, 1978) from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) maintained in identical hosts. Parasitol Res 81:505–517
Field JS, McKeown CA, Irwin SWB (1994) A proposed standard method for the maintenance of Diplostomum spp. (Digenea: Diplostomatidae) in the laboratory. Parasitol Res 80:253–254
Galazzo DE, Dayanandan S, Marcogliese DJ, McLaughlin JD (2002) Molecular systematics of some North American species of Diplostomum (Digenea) based on rDNA-sequence data and comparisons with European congeners. Can J Zool 80:2207–2217
Gibson DI (1996) Trematoda. In: Margolis L, Kabata Z (eds) Guide to the parasites of fishes of Canada. Part IV. Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences No. 124. NRC Press, Ottawa
Gibson DI, Jones A, Bray RA (2002) Keys to the Trematoda, volume I. CABI Publishing, Wallingford
Graczyk T (1991) Variability of metacercariae of Diplostomum spathaceum (Rudolphi, 1819) (Trematoda, Diplostomidae). Acta Parasitol Pol 36:135–139
Graczyk T (1992) Variability of metacercariae of Diplostomum pseudospathaceum Niewiadomska, 1984 (Trematoda, Diplostomidae). Acta Parasitol 37:5–9
Höglund J, Thulin J (1992) Identification of Diplostomum spp. in the retina of perch Perca fluviatilis and the lens of roach Rutilus rutilus from the Baltic Sea—an experimental study. Syst Parasitol 21:1–19
Hughes RC (1929) Studies on the trematode family Strigeidae (Holostomidae) no. XIV. Two new species of Diplostomula. Occas Pap Mus Zool Univ Mich 202:1–29
Inchausty VH, Foutz M, Heckmann RA, Ruas C, Ruas P (1997) Diplostomiasis in native and introduced fishes from Yellowstone Lake, Wyoming. Great Basin Nat 57:178–183
Kennedy CR, Burrough RJ (1978) Parasites of trout and perch in Malham Tarn. Field Stud 4:617–629
Kennedy CR, Nie P, Kaspers J, Paulisse J (1992) Are eels (Anguilla anguilla L.) planktonic feeders? Evidence from parasite communities. J Fish Biol 41:567–580
Køie M (1999) Metazoan parasites of flounder Platichthys flesus (L.) along a transect from the southwestern to the northeastern Baltic Sea. ICES J Mar Sci 56:157–163
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) ClustalW and ClustalX version 2. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Locke SA, McLaughlin JD, Dayanandan S, Marcogliese DJ (2010) Diversity and specificity in Diplostomum spp. metacercariae in freshwater fishes revealed by cytochrome c oxidase I and internal transcribed spacer sequences. Int J Parasitol 40:333–343
Lucas M, Baras E (2001) Migration of freshwater fishes. Blackwell Science Ltd., Oxford
Lüthen K (1988) Zur parasitierung der flunder, Platichthys flesus (L.), an der Ostseeküste der DDR. Wiss Z Pädagog Hochsch Güstrow 1:49–62
McKeown C, Irwin S (1995) The life cycle of three Diplostomum species maintained in the laboratory. Int J Parasitol 25:897–906
Moravec F (2003) Observations on the metazoan parasites of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) after its reintroduction into the Elbe River basin in the Czech Republic. Folia Parasit 50:298–304
Niewiadomska K (1996) The genus Diplostomum—taxonomy, morphology and biology. Acta Parasitol 41:55–66
Niewiadomska K (2002) Superfamily Diplostomoidea Poirier, 1886. In: Gibson DI, Jones A, Bray RA (eds) Keys to the Trematoda. CABI Publishing, Oxon
Niewiadomska K, Laskowski, Z (2002) Systematic relationships among six species of Diplostomum Nordmann, 1832 (Digenea) based on morphological and molecular data. Acta Parasitol 47:1230–1237
Niewiadomska K, Niewiadomska-Bugaj M (1995) Optimal identification procedure for Diplostomum paracaudum (Iles, 1959) and D. pseudospathaceum Niewiadomska, 1984 metacercariae (Digenea) based on morphological characters. Syst Parasitol 30:165–171
Niewiadomska K, Niewiadomska-Bugaj M (1998) Morphometric separation of Diplostomum spathaceum (Rud.) and D. mergi (Dubois) metacercariae (Digenea). Acta Parasitol 43:209–213
Niewiadomska K, Szymański S (1991) Host-induced variability of Diplostomum paracaudum (Iles, 1959) metacercariae (Digenea). Acta Parasitol Pol 36:11–17
Niewiadomska K, Szymański S (1992) Host-induced variability of Diplostomum pseudospathaceum Niewiadomska, 1984 metacercariae (Digenea). Acta Parasitol 37:11–17
Palm HW, Klimpel S, Bucher C (1999) Checklist of metazoan fish parasites of German coastal waters. Ber Inst Meereskd Kiel 307:1–148
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Saldanha I, Leung TLF, Poulin R (2009) Causes of intraspecific variation in body size among trematode metacercariae. J Helminthol 83:289–293
Shigin AA (1976) Metacercariae of the genus Diplostomum in the fauna of the USSR. Parazitologiya 10:346–351 (in Russian)
Shigin AA (1986) Trematodes of the USSR. Genus Diplostomum metacercariae. Nauka
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA 4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Valtonen ET, Gibson DI (1997) Aspects of the biology of diplostomid metacercarial (Digenea) populations occurring in fishes in different localities of northern Finland. Ann Zool Fenn 34:47–59
Violante-González J, García-Varela M, Rojas-Herrera A, Guerrero SG (2009) Diplostomiasis in cultured and wild tilapia Oreochromis niloticus in Guerrero State, Mexico. Parasitol Res 105:803–807
Whitehead PJP, Bauchot M-L, Hureau J-C, Nielsen J, Tortonese E (eds) (1986) Fishes of the North-eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean: volume III. United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris, pp 1016–1473
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Council of Rectors of the Portuguese Universities and the British Council—Treaty of Winsor—UR58 (U13[05/06]), CIMAR—CIIMAR Pluriannual Program, the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology and the European Social Fund (grants SFRH/BM/23063/2005; SFRH/BD/65258/2009 [F.I. Cavaleiro] SFRH/BD/31767/2006 [S. Pina]) for funding, Professor Vítor Silva from the Rector’s Office of Porto University for his help with the images, and Dr. Alex Ball from the Natural History Museum of London for his help with the scanning electron microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavaleiro, F.I., Pina, S., Russell-Pinto, F. et al. Morphology, ultrastructure, genetics, and morphometrics of Diplostomum sp. (Digenea: Diplostomidae) metacercariae infecting the European flounder, Platichthys flesus (L.) (Teleostei: Pleuronectidae), off the northwest coast of Portugal. Parasitol Res 110, 81–93 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2453-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2453-x