Abstract
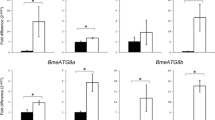
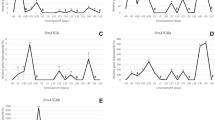
Autophagy is the intracellular protein degradation process which is induced by starvation. Ticks have a unique tolerance for starvation, and it is possible that this tolerance is associated with their longevity. Previously, we isolated the homologues of four autophagy-related (ATG) genes in the hard tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis, suggesting that autophagy appeared to play an important role in tolerance for starvation as well as the development of ticks. In this study, the homologue of ATG6 was isolated from H. longicornis (HlATG6). HlATG6 mRNA expression was higher in the egg and unfed larval stages than in other stages and upregulated in ovaries during the blood-feeding period. Moreover, HlATG6-knockdowned ticks laid a few and poorly developed eggs that were white brown in color and not well surface-coated with wax. However, the expression of vitellogenin (Vg)-2, HlVg-2, in the fat body of HlATG6-knockdowned ticks was significantly upregulated. In addition, hemolymph had a deep brown color in HlATG6-knockdowned ticks on day 21 after engorgement and drop-off, indicating that the Vgs synthesized by the fat body and midgut are retained and accumulated in the hemolymph of HlATG6-knockdowned ticks, probably due to the downregulation of the Vg uptake capability of oocytes. Interestingly, HlATG6 knockdown provided non-significant influences on the expression of the Vg receptor (HlVgR) at oocytes, suggesting a non-significant depression of VgR-mediated endocytosis in the oocytes of HlATG6-knockdowned ticks. Therefore, it was interpreted that the repression of Vg uptake in the oocytes of HlATG6-knockdowned ticks may be involved in endocytic processes other than the receptor recognition of Vgs in oocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boldbaatar D, Battsetseg B, Matsuo T, Hatta T, Umemiya-Shirafuji R, Xuan X, Fujisaki K (2008) Tick vitellogenin receptor reveals critical role in oocyte development and transovarial transmission of Babesia parasite. Biochem Cell Biol 86:331–333
Boldbaatar D, Umemiya-Shirafuji R, Liao M, Tanaka T, Xuan X, Fujisaki K (2010) Multiple vitellogenins from the Haemaphysalis longicornis tick are crucial for ovarian development. J Insect Physiol 56:1587–1598
Cao Y, Klionsky DJ (2007) Physiological functions of Atg6/Beclin 1: a unique autophagy-related protein. Cell Res 17:839–849
de la Fuente J, Kocan KM, Almazán C, Blouin EF (2007) RNA interference for the study and genetic manipulation of ticks. Trends Parasitol 23:427–433
Di Bartolomeo S, Nazio F, Cecconi F (2010) The role of autophagy during development in higher eukaryotes. Traffic 11:1280–1289
Fujisaki K (1978) Development of acquired resistance and precipitating antibody in rabbits experimentally infested with females of Haemaphysalis longicornis (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae). Natl Inst Anim Health Q Tokyo 18:27–38
Gao J, Luo J, Li Y, Fan R, Zhao H, Guan G, Liu J, Wiske B, Sugimoto C, Yin H (2007) Cloning and characterization of a ribosomal protein L23a from Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis eggs by immuno screening of a cDNA expression library. Exp Appl Acarol 41:289–303
Gong H, Liao M, Zhou J, Hatta T, Huang P, Zhang G, Kanuka H, Nishikawa Y, Xuan X, Fujisaki K (2008) Gene silencing of ribosomal protein P0 is lethal to the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Vet Parasitol 151:268–278
Gupta GD, Swetha MG, Kumari S, Lakshminarayan R, Dey G, Mayor S (2009) Analysis of endocytic pathways in Drosophila cells reveals a conserved role of GBF1 in internalization via GEECs. PLoS ONE 4:e6768
Hatta T, Tsuji N, Miyoshi T, Alim MA, Islam MK, Fujisaki K (2009) Leucine aminopeptidase in the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis longicornis: endogenous expression profiles in midgut. J Vet Med Sci 71:589–594
Hatta T, Tsuji N, Miyoshi T, Islam MK, Alim MA, Yamaji K, Anisuzzaman FK (2010) Leucine aminopeptidase, HlLAP, from the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis longicornis, plays vital roles in the development of oocytes. Parasitol Int 59:286–289
Horigane M, Shinoda T, Honda H, Taylor D (2010) Characterization of a vitellogenin gene reveals two phase regulation of vitellogenesis by engorgement and mating in the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata (Acari: Argasidae). Insect Mol Biol 19:501–515
Juhász G, Hill JH, Yan Y, Sass M, Baehrecke EH, Backer JM, Neufeld TP (2008) The class III PI(3)K Vps34 promotes autophagy and endocytosis but not TOR signaling in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 181:655–666
Kametaka S, Okano T, Ohsumi M, Ohsumi Y (1998) Apg14p and Apg6/Vps30p form a protein complex essential for autophagy in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 273:22284–22291
Kato S, Ohtoko K, Ohtake H, Kimura T (2005) Vector-capping: a simple method for preparing high-quality full-length cDNA library. DNA Res 12:53–62
Kihara A, Kabeya Y, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori T (2001) Beclin-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex functions at the trans-Golgi network. EMBO Rep 2:330–335
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J, Murata S, Tanida I, Ezaki J, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Uchiyama Y, Kominami E, Tanaka K, Chiba T (2005) Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 169:425–434
Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y, Tokuhisa T, Mizushima N (2004) The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature 432:1032–1036
Meléndez A, Tallóczy Z, Seaman M, Eskelinen EL, Hall DH, Levine B (2003) Autophagy genes are essential for Dauer debelopment and life-span extension in C. elegans. Science 301:1387-1391
Miyoshi T, Tsuji N, Islam MK, Kamio T, Fujisaki K (2004) Gene silencing of a cubilin-related serine proteinase from the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis by RNA interference. J Vet Med Sci 66:1471–1473
Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori T (2002) Autophagosome formation in mammalian cells. Cell Struct Funct 27:421–429
Roggo L, Bernard V, Kovacs AL, Rose AM, Savoy F, Zetka M, Wymann MP, Müller F (2002) Membrane transport in Caenorhabditis elegans: an essential role for VPS34 at the nuclear membrane. EMBO J 21:1673–1683
Seaman MN, Marcusson EG, Cereghino JL, Emr SD (1997) Endosome to Golgi retrieval of the vacuolar protein sorting receptor, Vps10p, requires the function of the VPS29, VPS30, and VPS35 gene products. J Cell Biol 137:79–92
Sonenshine DE (1991) Biology of ticks. Oxford University Press, New York
Takacs-Vellai K, Vellai T, Puoti A, Passannante M, Wicky C, Streit A, Kovacs AL, Müller F (2005) Inactivation of the autophagy gene bec-1 triggers apoptotic cell death in C. elegans. Curr Biol 15:1513–1517
Tsukada M, Ohsumi Y (1993) Isolation and characterization of autophagy-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 333:169–174
Tufail M, Takeda M (2008) Molecular characteristics of insect vitellogenins. J Insect Physiol 54:1447–1458
Umemiya R, Matsuo T, Hatta T, Sakakibara S, Boldbaatar D, Fujisaki K (2007) Cloning and characterization of an autophagy-related gene, ATG12, from the three-host tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:975–984
Umemiya-Shirafuji R, Matsuo T, Fujisaki K (2008) Autophagy in ticks. Meth Enzymol 451:621–638
Umemiya-Shirafuji R, Matsuo T, Liao M, Boldbaatar D, Battur B, Suzuki H, Fujisaki K (2010) Increased expression of ATG genes during nonfeeding periods in the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Autophagy 6:473–481
Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N (2003) Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:15077–15082
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS). R. U-S. was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for a Research Activity Start-up from the JSPS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Primers used in this study. (DOC 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawano, S., Umemiya-Shirafuji, R., Boldbaatar, D. et al. Cloning and characterization of the autophagy-related gene 6 from the hard tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis . Parasitol Res 109, 1341–1349 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2429-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2429-x