Abstract
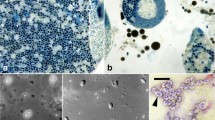
The life cycle, ultrastructure, and molecular phylogeny of a new microsporidium Crispospora chironomi g.n. sp.n., a parasite of the midge Chironomus plumosus, are described. The parasite infects the gut epithelium of the host larvae and possesses sporogonies of two types, polysporoblastic and disporoblastic, respectively, proceeding within the same host cell. In the sporogonial sequence of the first type, dozens of spherical monokaryotic spores within a thick-walled capsule are formed. The spores are 1.5–2.0 μm in diameter; the exospore possesses two to three bundles of tubular protrusions. In the sporogonial sequence of the second type, diplokaryotic oval spores, 2.5 × 1.5 μm in size, are formed within a compartment, partially surrounded with multilayered membranes. Spores of both types are similar in respect to inner structure, possessing a well-developed extrusion apparatus with (a) the anterior vesicular part of the polaroplast covering the lamellar posterior one and (b) isofilar polar filament with several coils in one row. Small subunit ribosomal DNA phylogeny showed position of the new microsporidium in a cluster uniting microsporidia of terrestrial origin infecting diverse hosts, nested within Clade IV, corresponding to Class Terresporidia sensu Vossbrinck and Debrunner-Vossbrinck (Folia Parasitol 52:131–142, 2005).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrianov AV, Rybakov AV (1991) Kinorhynchospora japonica gen. n., sp. n. (Microsporidia) from the intestine epithelium of Kinorhynchus yushini (Homalorhagida, Pycnophyidae) from the Sea of Japan. Zoologicheskiy Zh 70:5–11 (In Russian with English summary)
Baker MD, Vossbrinck CR, Didier ES, Maddox JV, Shadduck JA (1995) Small subunit ribosomal DNA phylogeny of various microsporidia with emphasis on AIDS related forms. J Eukaryot Microbiol 42:564–570
Baker MD, Vossbrinck CR, Becnel JJ, Maddox JV (1997) Phylogenetic position of Amblyospora Hazard and Oldacre (Microspora, Amblyosporidae) based on small subunit rRNA data and its implication for the evolution of the Microsporidia. J Eukaryot Microbiol 44:220–225
Codreanu-Bãlcescu D, Codreanu R (1980) Parazitarea masivã a populatiilor crustaceului Artemia salina si chironomidului Halliella noctivaga dominante în biocenoza lacului Techirghiol. “Pontus Euxinus” Stud Sercetari 1:305–314
Debaisieux P (1928) Etudes cytologiques sur quelques Microsporidies. Cellule 38:389–450
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp 41:95–98
Issi IV (1986) Microsporidia as a phylum of parasitic protozoa. Protozoology. Leningrad. Nauka 10:1–136
Issi IV, Tokarev YS, Voronin VN, Seliverstova EV, Pavlova OA, Dolgikh VV (2010) Ultrastructure and molecular phylogeny of Mrazekia macrocyclopis sp.n. (Microsporidia, Mrazekiidae), a microsporidian parasite of Macrocyclops albidus (Jur.) (Crustacea, Copepoda). Acta Protozool 49:75–84
Fokin SI, di Guiseppe D, Erra F, Dini F (2008) Euplotespora binucleata n. gen., n. sp. (Protozoa: Microsporidia), a parasite infecting the hypotrichous ciliate Euplotes woodruffi, with observations on microsporidian infections in Ciliophora. J Eukaryot Microbiol 55:214–228
Kyei-Poku G, Gauthier D, Van Frankenhuyzen K (2008) Molecular data and phylogeny of Nosema infecting Lepidoptera forest defoliators in the genera Choristoneura and Malacosoma. J Eukaryot Microbiol 55:51–58
Kudo R (1924) A biologic and taxonomic study of the Microsporidia. Illin Biol Monogr 9:1–268
Posada D (2008) jModeltest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256
Refardt D, Decaestecker E, Johnson PTJ, Vávra J (2008) Morphology, molecular phylogeny, and ecology of Binucleata daphniae n. g., n. sp. (Fungi: Microsporidia), a parasite of Daphnia magna Straus, 1820 (Crustacea: Branchiopoda). J Eukaryot Microbiol 55:393–408
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Simakova AV, Pankova TF, Tokarev YS, Issi IV (2005) New genus of microsporidia Senoma gen. n. with type species Senoma globulifera comb. n. (syn. Issia globulifera Issi, Pankova,1983) from malaria mosquito Anopheles messae Fall. Protistology 4:134–145
Sokolova YY, Lange CE, Mariottini Y, Fuxa JR (2009) Morphology and taxonomy of the microsporidium Liebermannia covasacrae n. sp. from the grasshopper Covasacris pallidinota (Orthoptera, Acrididae). J Invertebr Pathol 101:34–42
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Tokarev YS, Voronin VN, Seliverstova EV, Dolgikh VV, Pavlova OA, Ignatieva AN, Issi IV (2010) Ultrastructure and molecular phylogeny of Anisofilariata chironomi sp.n. g.n. (Microsporidia: Terresporidia), a microsporidian parasite of Chironomus plumosus L. (Diptera: Chironomidae). Parasitol Res 107:39–46
Voronin VN (1999) The microsporidia of freshwater invertebrates and fish of Russia. The thesis of doctoral dissertation. Saint-Petersburg, 45pp (In Russian)
Vossbrinck CR, Debrunner-Vossbrinck BA (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the Microsporidia: ecological, ultrastructural and taxonomic considerations. Folia Parasitol 52:131–142
Weiser J (1961) Die Mikrosporidien als Parasiten der Insekten. Monogr Angew Entomol 17:5–149
Weiss LM, Vossbrinck CR (1999) Molecular biology, molecular phylogeny, and molecular diagnostic approaches to the Microsporidia. The Microsporidia and Microsporidiosis. Washington, ASM Press, pp 129–171
Weiss LM, Zhu X, Cali A, Tanowitz HB, Wittner M (1994) Utility of microsporidian rRNA in diagnosis and phylogeny: a review. Folia Parasitol 41:81–90
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Anastasiya Ignatieva and Igor Senderskiy for the help with cloning and sequencing the PCR products. The research is supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (no. 10-04-00284) and Rosnauka (no. MK-3419.2009.4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokarev, Y.S., Voronin, V.N., Seliverstova, E.V. et al. Life cycle, ultrastructure, and molecular phylogeny of Crispospora chironomi g.n. sp.n. (Microsporidia: Terresporidia), a parasite of Chironomus plumosus L. (Diptera: Chironomidae). Parasitol Res 107, 1381–1389 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2012-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2012-x