Abstract
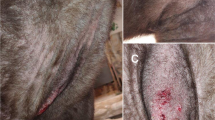
Sarcoptes scabiei infestation was diagnosed in four freshly dead and three net-captured gazelle while ranging freely. The captured animals presented with an alopecic pruritic skin disease with signs of crusted skin lesions, numerous small nodules which first appeared on the lips or nostrils and then it also extended towards the eyelids, around the ears, and, in some cases, over entire face, neck, trunk, and legs. Skin over the affected area gradually became bald, thick and hard, being dry and doughy to the touch, and serous fluid or sometimes blood oozes from the lesions which had a severe malodor. Skin scrapings confirmed the presence of the mite S. scabiei. Histopathology of lesions demonstrated marked acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and parakeratosis. Microscopical examination also revealed all stages of S. scabiei, which were located mainly in the stratum corneum and also in the stratum granulosum. During the capture and sampling of the animals, four persons ranging in age from 25 to 62 years were exposed to scabies. Two relatives of one of them have been also affected by familiar contact. Clinical signs appeared within 9 days of exposure. They developed several pruretic erythematous papules with intense itching.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlian LG, Vyszencki-Moher L, Pole M J (1989) Survival of adults and development stages of Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis when off the host. Exp Appl Acarol 6:181–187
Burgess L (1994) Sarcoptes scabiei and scabies. Adv Parasitol 33:236–292
Eslami A, Nikbine S, Rahbari S (1979) Lungworms infestation of wild sheep (ovis Ammon Orientalis) and gazelle (Gazella subguturosa) in Iran. Journal of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine University of Tehran, 3, 4(35):11–16
Eslami A, Rahbari S, Meydani M (1981) Cestods and trematods of wild sheep, Ovis Ammon Orientalis and Goitered gazelle, Gazella subguturosa, in Iran. Vet Parasitol 8:99–100
Fitzgerald S, Cooley TM, Murphy A, Cosgrove MK, King BA (2004) Sarcoptic Mange in Raccoons in Michigan, J Wildl Dis 40:347–350
Fletcher KC (1978) Notoedric mange in a litter of snow leopards. J Am Vet Med Assoc 173:1231–1232
Foley RH (1991) A notoedric mange epizootic in an island’s cat population. Feline Practice 19:8–10
Gonzalez-Candela M, Leon-Vizcaino L, Cubero-Pablo MJ (2004) Population effects of sarcoptic mange in Barbary sheep (Ammotragus Lervia) from Sierra Espuna regional park, Spain. J Wildl Dis 40(3):456–465
Gonzalez-Candela M, Cubero-Pablo MJ, Martin-Atance P, Leon-Vizcaino L (2006) Potential pathogens carried by Spanish ibex (Capra pyrenaica hispanica) in southern Spain. J Wildl Dis 42(2):325–334
Harwood RF, James M (1976) Mites and mites borne diseases. In Entomology in human and animal health. Washington State University, Pulmann, pp 342–370
Ibrahim KEE, ABU-Samra MT (1987) Experimental transmission of a goat strain of Sarcoptes sabiei to desert sheep and its treatment with Ivermectin. Vet Parasitol 26:157–164
Jubb KVF, Kennedy PC, Palmer N (1993) Pathology of Domestic Animals. 4th ed. Academic Press San Diago, Vol1. 681–682
Kral F, Schowartzman (1964) Veterinary and comparative dermatology. J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, PA, pp 343–368
Leon-Vizcaino L (1990) Patologia de la saran en la Cabra monte en Cazorla. Quercus 50:22
Leon-Vizcaino L, Ruiz de Ybanez MR, Cubero MJ, Ortiz JM, Espinosa J, Perez L, Simon MA, Alonso F (1999) Sarcoptic mange in Spanish ibex from Spain, J Wildl Dis 35:647–659
Maehr DS, Greiner EC, Lanier JE, Murphy D (1995) Notoedric mange in the Florida panther (Felis concolor coryi). J Wildl Dis 31:251–254
Menzano A, Rambozi L, Rossi L (2004) Outbreak of scabieis in human beings, acquired from chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra). Vet Rec, 30, 155:568
Mitra M, Mahanta SK, Sen S, Ghosh C, Hati AK (1995) Transmission of Sarcoptes scabiei from animal to man and its control. J Indian Med Assoc 93:142–143
Nadalian M, Najafzadeh A, Rahbari S, Nourozian I (1989) Epidemiological syrvey on sheep mite infestation in Tehran and central provinces. J Vet Fac Univ Iran 44(4):1–22
Ninomiya H, Ogata M (2002) Notoedric mange in two free-ranging North American raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Japan. Vet Dermatol 13:119–121
Pence DBF, Matthews D, Windberg LA (1982). Notoedric mange in the bobcat, Felis rufus, from South Texas. J Wildl Dis 18:47–50
Pence DB, Windberg LA, Pence BC, Sprowls R (1983) The epizootiology and pathology of sarcoptic mange in coyotes, Canis latrans, from south Texas. J Parasitol 69:1100–1115
Pence DBF (1984) Disease of laboratory animals. In: Nuffing WB (ed) Mammalian diseases and arachnids. CRC press, Bosca Raton, Florida, pp 129–187
Rafyi A, Alavi nainy A, Rak H (1966) Les speces do mites rencontres en Iran— J. Vet.Fac.Univ. of Iran. Revue de la Faculte Veterinaire, Universite de Tehran 23(1):38–45
Rambozzi L, Menzano A, Lavin S, Rossi L (2004) Biotin-avidin amplified ELISA for detection of antibodies to Sarcoptes scabiei in chamois (Rupicapra spp.). Vet Res 35(6):701–708
Uzal FA, Houston RS, Riley SPD, Poppenga R, Odani J, Boyce W(2007) Notoedric mange in two free-ranging mountain lions (Puma concolor), J Wildl Dis 43:274–278
Valenzuela D, Ceballos G, Garcia A (2000) Mange epizootic in white-nosed coatis in western Mexico. J Wildl Dis 36:56–63
Yeruham I, Rosen S, Hadani A, Nyska (1996) Sarcoptic mange in wild ruminants in zoological gardens in Israel. J Wildlife Dis 32(1):57–61
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank the staff of Environmental Organization in Khark for their collaboration in this work. Appreciation is also given for the assistant of Dr. P.Seifori from Veterinary Organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bazargani, T.T., Hallan, J.A., Nabian, S. et al. Sarcoptic mange of gazelle (Gazella subguttarosa) and its medical importance in Iran. Parasitol Res 101, 1517–1520 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0669-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0669-6