Abstract
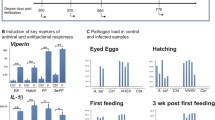
Expression of immune-regulatory genes that code for cyclooxigenase-2 (COX-2), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), and two isoforms of interleukin-1beta (IL-1β1 and IL-1β2) was studied in susceptible and non-susceptible rainbow trout strains for 200 days after exposure to Myxobolus cerebralis. Expression of COX-2, IL-1β1, and IL-1β2 increased 5 min post exposure (p.e.) and was always more elevated in the susceptible strain than in the non-susceptible strain. In both strains, expression of COX-2 returned to the control level within a few hours p.e. Expression of IL-1β1 and IL-1β2 showed two elevated waves in both strains until 4 days p.e. Expression of TGF-β in the non-susceptible strain was elevated at nearly all sampling points, but was decreased in the susceptible strain until up-regulation between 4 and 20 days p.e.; TGF-β was the only gene where the expression in the non-susceptible strain was more elevated than in the susceptible strain. Rainbow trout of the non-susceptible strain appeared to resist infection by M. cerebralis with only minor transcriptional regulation of the genes investigated. Increased transcriptions of genes in the susceptible strain may be the result of an inability to antagonize the infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benus GFJD, Wierenga ATJ, de Gorter DJJ, Schuringa JJ, van Bennekum AM, Drenth-Diephuis L, Vellenga E, Eggen BJL (2005) Inhibition of the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) pathway by interleukin-1β is mediated through TGFβ-activated kinase 1 phosphorylation of SMAD3. Mol Biol Cell 16:3501–3510
Bridle AR, Morrison RN, Nowak BF (2006) The expression of immune-regulatory genes in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, during amoebic gill disease (AGD). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:346–364
Buchmann K (1999) Immune mechanisms in fish skin against monogenean infections—a model. Folia Parasitol 46:1–9
Davis JM, Clay H, Lewis JL, Ghori N, Herbomel P, Ramakrishnan L (2002) Real-time visualisation of mycobacterium–macrophage interactions leading to initiation of granuloma formation in zebrafish embryos. Immunity 17:693–702
El-Matbouli M, Hoffmann RW (1998) Light and electron microscopic study on the chronological development of Myxobolus cerebralis in Tubifex tubifex to the actinosporean stage triactinomyxon. Int J Parasitol 28:195–217
El-Matbouli M, Fischer-Scherl Th, Hoffmann RW (1992) Present knowledge on life cycle, taxonomy, pathology and therapy of some Myxosporea spp. important for freshwater fish—a review. Annu Rev Fish Dis 2:367–402
El-Matbouli M, Hoffmann RW, Mandok C (1995) Light and electron microscopic observations on the route of the triactinomyxon-sporoplasm of Myxobolus cerebralis from epidermis into rainbow trout (O. mykiss) cartilage. J Fish Biol 46:919–935
El-Matbouli M, Meixner M, Mattes M (2003) Susceptibility of Hofer strain of rainbow trout to Myxobolus cerebralis, Yersinia ruckeri, Tetracapsula bryosalmonae and VHS virus. Field and laboratory studies. In: Proceedings of the 9th Annual Whirling Disease Symposium, pp 39–40
Fast MD, Ross NW, Craft CA, Locke SJ, MacKinnon SL, Johnson SC (2004) Lepeophtheirus salmonis: characterisation of prostaglandin E2 in secretory products of the salmon louse by RP-HPLC and mass spectrometry. Exp Parasitol 107(1–2):5–13
Fast MD, Ross NW, Johnson SC (2005) Prostaglandin E2 modulation of gene expression in an Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) macrophage-like cell-line (SHK-1). Dev Comp Immunol 29(11):951–963
Fast MD, Muise DM, Easy RE, Ross NW, Johnson SC (2006) The effects of Lepeophtheirus salmonis infections on the stress response and immunological status of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol 21:228–241
Grayson TH, Cooper LF, Wrathmell AB, Roper J, Evenden AJ, Gilpin ML (2002) Host responses to Renibacterium salmoninarum and specific components of the pathogen reveal the mechanisms of immune suppression and activation. Immunology 106:273–283
Harms CA, Kennedy-Stoskopf S, Horne WA, Fuller FJ, Tompkins WAF (2000) Cloning and sequencing hybrid striped bass (Morone saxatilis x M. chrysops) transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), and development of a reverse transcription quantitative competitive polymerase chain reaction (RT-qcPCR) assay to measure TGF-β mRNA of teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 10:61–85
Harms CA, Howard KE, Wolf JC, Smith SA, Kennedy-Stoskopf S (2003) Transforming growth factor-β response to mycobacterial infection in striped bass Morone saxatilis and hybrid tilapia Oreochromis spp. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 95:155–163
Harris SG, Padilla J, Koumas L, Ray D, Phipps RP (2002) Prostaglandins as modulators of immunity. Trends Immunol 23:144–150
Hedrick RP, El-Matbouli M, Adkison MA, MacConnell E (1998) Whirling disease: re-emergence among wild trout. Immunol Rev 166:365–376
Hedrick RP, McDowell TS, Gay M, Marty GD, Georgiadis MP, MacConnell E (1999a) Comparative susceptibility of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and brown trout Salmo trutta to Myxobolus cerebralis, the cause of salmonid Whirling disease. Dis Aquat Org 37(3):173–183
Hedrick RP, Mc Dowell TS, Mukkatira K, Georgiadis MP, MacConnell E (1999b) Susceptibility of selected inland salmonids to experimentally induced infections with Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of Whirling disease. J Aquat Anim Health 11:330–339
Hedrick RP, McDowell TS, Mukkatira K, Georgiadis MP (2001) Susceptibility of three species of anadromous salmonids to experimentally induced infections with Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of Whirling disease. J Aquat Anim Health 13:43–50
Hedrick RP, McDowell TS, Marty GD, Fosgate GT, Mukkatira K, Myklebust K, El-Matbouli M (2003) Susceptibility of two strains of rainbow trout (one with suspected resistance to Whirling disease) to Myxobolus cerebralis infection. Dis Aquat Org 55(1):37–44
Herbomel P, Thisse B, Thisse C (1999) Ontogeny and behaviour of early macrophages in the zebrafish embryo. Development 126:3735–3745
Hofer B (1903) Über die Drehkrankheit der Regenbogenforelle. Allg Fleisch Ztg 28:7–8
Holland JW, Gould CRW, Jones CS, Noble LR, Secombes CJ (2003) The expression of immune-regulatory genes in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, during a natural outbreak of proliferative kidney disease (PKD). Parasitology 126:95–102
Hong S, Zou J, Crampe M, Peddie S, Scapigliati G, Bols N, Cunninghamj C, Secombes CJ (2001) The production and bioactivity of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) recombinant IL-1β. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 81(1–2):1–14
Hong S, Peddie S, Campos-Pérez JJ, Zou J, Secombes CJ (2003) The effect of intraperitoneally administered recombinant IL-1β on immune parameters and resistance to Aeromonas salmonicida in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dev Comp Immunol 27(9):801–812
Ingram GA (1980) Substances involved in the natural resistance of fish infection—a review. J Fish Biol 16:23–60
Jang SI, Hardie LJ, Secombes CJ (1994) Effects of transforming growth factor-β1 on rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss macrophage respiratory burst activity. Dev Comp Immunol 18(4):315–323
Jyung RW, Mustoe TA (1993) Role of cytokines in wound repair. In: Oppenheim JJ, Rossio JL, Gearing AJH (eds) Clinical applications of cytokines: role in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Oxford University Press, pp 307–311
Knight J, Rowley AF (1995) Immunoregulatory activities of eicosanoids in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunology 85:389–393
Lindenstrøm T, Buchmann K, Secombes CJ (2003) Gyrodactylus derjavini infection elicits IL-1ß expression in rainbow trout skin. Fish Shellfish Immunol 15:107–115
Lindenstrøm T, Secombes CJ, Buchmann K (2004) Expression of immune response genes in rainbow trout skin induced by Gyrodactylus derjavini infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 97:137–148
Lindenstrøm T, Sigh J, Dalgaard MB, Buchmann K (2006) Skin-expression of IL-1β in East Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., highly susceptible to Gyrodactylus salaris infection is enhanced compared to a low susceptibility Baltic stock. J Fish Dis 29:123–128
MacConnell E, Vincent ER (2002) The effects of Myxobolus cerebralis on the salmonid host. In: Bartholomew J, Wilson C (eds) Whirling disease: reviews and current topics. America Fisheries Society Symposium no. 29, Bethesda, MD, pp 95–108
Markiw ME (1992) Salmonid Whirling disease. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Fish and Wildlife Leaflet 17, pp 1–11
McCartney-Francis NL, Wahl SM (1994) Transforming growth factor-β: a matter of life and death. J Leukoc Biol 55:401–409
Nehring RB, Walker PG (1996) Whirling disease in the wild: the new reality in the intermountain west. Fisheries (Bethesda) 21:28–32
O’Grodnick J (1979) Susceptibility of various salmonids to Whirling disease (Myxosoma cerebralis). Trans Am Fish Soc 108:187–190
Pelegrín P, Chaves-Pozo E, Mulero V, Meseguer J (2004) Production and mechanism of secretion of interleukin-1β from the marine fish gilthead seabream. Dev Comp Immunol 28(3):229–237
Pleguezuelos O, Zou J, Cunningham C, Secombes CJ (2000) Cloning, sequencing, and analysis of expression of a second IL-1β gene in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunogenetics 51:1002–1011
Pressley ME, Phelan III PE, Witten PE, Mellon MT, Kim CH (2005) Pathogenesis and inflammatory response to Edwardsiella tarda infection in the zebrafish. Dev Comp Immunol 29(6):501–513
Purcell MK, Kurath G, Garver KA, Herwig RP, Winton JR (2004) Quantitative expression profiling of immune response genes in rainbow trout following infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) infection or vaccination. Fish Shellfish Immunol 17:447–462
Rose JD, Marrs GS, Lewis C, Schisler G (2000) Whirling disease behaviour and its relation to pathology of brain stem and spinal cord in rainbow trout. J Aquat Anim Health 12:107–118
Ruscetti FW, Palladino MA (1991) Transforming growth factor-beta and the immune system. Prog Growth Factor Res 3:159–175
Ryce EKN, Zale AV, MacConnell E, Nelson M (2005) Effects of fish age versus size on the development of Whirling disease of rainbow trout. Dis Aquat Org 63:69–76
Saeij JPJ, Stet RJM, Groeneveld A, Verburg-Van Kemenade LBM, Van Muiswinkel WB, Wiegertjes GF (2000) Molecular and functional characterization of a fish inducible-type nitric oxide synthase. Immunogenetics 51:339–346
Schäperclaus W (1931) Die Drehkrankheit in der Forellenzucht und ihre Bekämpfung. Zeitschrift für Fischerei 29:521–567
Sigh J, Lindenstrom T, Buchmann K (2004a) The parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis induces expression of immune relevant genes in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 27(7):409–417
Sigh J, Lindenstrom T, Buchmann K (2004b) Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during an infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 17:75–86
Tafalla C, Coll J, Secombes CJ (2005) Expression of genes related to the early immune response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) infection. Dev Comp Immunol 29(7):615–626
Titus RG, Sherry B, Cerami A (1991) The involvement of TNF, IL-1, and IL-6 in the immune response to protozoan parasites. Immunol Today 12:13–16
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalisation of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:34
Vincent ER (1996) Whirling disease and wild trout: the Montana experience. Fisheries (Bethesda) 21(6):32–34
Wolf K, Markiw ME (1984) Biology contravenes taxonomy in the Myxozoa: new discoveries show alternation of invertebrate and vertebrate hosts. Science 225:1449–1452
Zou J, Neumann NF, Holland JW, Belosevic M, Cunningham C, Secombes CJ, Rowley AF (1999) Fish macrophages express a cyclo-oxygenase-2 homologue after activation. Biochem J 340:153–159
Zou J, Holland J, Pleguezuelos O, Cunningham C, Secombes C (2000) Factors influencing the expression of interleukin-1β in cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) leukocytes. Dev Comp Immunol 24(6–7):575–582
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Whirling Disease Foundation and the US Fish and Wildlife Service and by the German Research Foundation (DFG, EI 174/3–1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Severin, V.I.C., El-Matbouli, M. Relative quantification of immune-regulatory genes in two rainbow trout strains, Oncorhynchus mykiss, after exposure to Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease. Parasitol Res 101, 1019–1027 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0582-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0582-z