Abstract
Purpose
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are regulatory molecules capable of positively or negatively regulating signaling pathways, and are involved in tumorigenesis as well as various aspects of cancer. The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression levels of miR-133a, miR-637, and miR-944 in serum and tumor tissues as well as their relationship with the expression level of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase-B (AKT) genes and proteins along with their clinical significance in breast cancer.
Methods
The expressions of miR-133a, miR-637, miR-944, PI3K, and AKT genes were examined in the tumor and tumor margin tissues of 40 patients with breast cancer, as well as the serum levels of miR-133a, miR-637, and miR-944 in these patients and 40 healthy groups by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). PI3K and AKT proteins expression in tumor and tumor margin tissues were detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Results
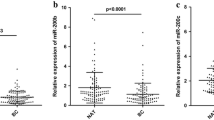
The expression levels of miR-133a and miR-637 in the tumor tissue and serum of patients were lower than those in the tumor margin tissue and serum of the healthy group, respectively. In addition, the expression level of miR-944 in the tumor tissue was lower than that in the tumor margin tissue, but its expression increased in the serum of cancer patients compared to that in the healthy group. The expression of miR-637 was correlated with tumor location and Her2 receptors, and the expression of miR-944 was correlated with tumor location and family history. PI3K and AKT mRNA and protein levels were higher in the tumor tissues than in the tumor margin tissues (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
The results of our study revealed that miR-637 has a better diagnostic value in breast cancer than miR-133a and miR-944.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abolghasemi M, Tehrani SS, Yousefi T, Karimian A, Mahmoodpoor A, Ghamari A, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Yousefi M, Kafil HS, Bastami M (2020) MicroRNAs in breast cancer: roles, functions, and mechanism of actions. J Cell Physiol 235:5008–5029. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29396
Bhattacharyya PN, Das E, Bucha S, Das S, Choudhury A (2016) Regulation of cell cycle associated genes by microRNA and transcription factor. Microrna 5:180–200
Cui W, Zhang S, Shan C, Zhou L, Zhou Z (2013) Micro-RNA-133a regulates the cell cycle and proliferation of breast cancer cells by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor through the EGFR/A kt signaling pathway. FEBS J 280:3962–3974. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12398
Du Y, Wang Y (2019) MiR-637 inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatoma cells by targeted degradation of AKT1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:567–575
Flores-Pérez A, Marchat LA, Rodríguez-Cuevas S, Bautista VP, Fuentes-Mera L, Romero-Zamora D, Maciel-Dominguez A, de la Cruz OH, Fonseca-Sánchez M, Ruíz-García E (2016) Suppression of cell migration is promoted by miR-944 through targeting of SIAH1 and PTP4A1 in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 16:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2470-3
Godfrey AC, Xu Z, Weinberg CR, Getts RC, Wade PA, Deroo LA, Sandler DP, Taylor JA (2013) Serum microRNA expression as an early marker for breast cancer risk in prospectively collected samples from the Sister Study cohort. Breast Cancer Res 15:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3428
He H, Tian W, Chen H, Jiang K (2016) MiR-944 functions as a novel oncogene and regulates the chemoresistance in breast cancer. Tumor Biol 37:1599–1607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3844-x
Hesari A, Azizian M, Darabi H, Nesaei A, Hosseini SA, Salarinia R, Motaghi AA, Ghasemi F (2019) Expression of circulating miR-17, miR-25, and miR-133 in breast cancer patients. J Cell Biochem 120:7109–7114. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27984
Hu Z-H, Wang G-J, Li R-X, Zhu T-Y, Wang Z-Y, Ding H-X, Hu X-M (2020) Upregulation of miR-133a-3p enhances Bufothionine-induced gastric cancer cell death by modulating IGF1R/PI3K/Akt signal pathway mediated ER stress. Life Sci 259:118180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118180
Huang G-L, Zhang X-H, Guo G-L, Huang K-T, Yang K-Y, Shen X, You J, Hu X-Q (2009) Clinical significance of miR-21 expression in breast cancer: SYBR-Green I-based real-time RT-PCR study of invasive ductal carcinoma. Oncol Rep 21:673–679. https://doi.org/10.3892/or_00000270
Itani MM, Nassar FJ, Tfayli AH, Talhouk RS, Chamandi GK, Itani ARS, Makoukji J, Boustany R-MN, Hou L, Zgheib NK (2021) A signature of four circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosing early-stage breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci 22:6121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22116121
Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X, Peng J (2020) Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep 47:4587–4629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05435-1
Kołodziej P, Nicoś M, Krawczyk PA, Bogucki J, Karczmarczyk A, Zalewski D, Kubrak T, Kołodziej E, Makuch-Kocka A, Madej-Czerwonka B (2021) The correlation of mutations and expressions of genes within the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in breast cancer—a preliminary study. Int J Mol Sci 22:2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22042061
Leivonen S-K, Sahlberg KK, Mäkelä R, Due EU, Kallioniemi O, Børresen-Dale A-L, Perälä M (2014) High-throughput screens identify microRNAs essential for HER2 positive breast cancer cell growth. Mol Oncol 8:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2013.10.001
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen X, Qi Y, Jiang Y, Zou C, Zhang X, Liu S, Wang X (2011) Analysis of MiR-195 and MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast Cancer MiR-195 and MiR-497 in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17:1722–1730. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1800
Lv L, Wang X, Ma T (2019) Microrna-944 inhibits the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by directly targeting IGF-1R and deactivating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cancer Manag Res 11:2531. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S199818
Macfarlane L-A, Murphy PR (2010) MicroRNA: biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Current Genom 11:537–561. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920210793175895
Marusyk A, Janiszewska M, Polyak K (2020) Intratumor heterogeneity: the rosetta stone of therapy resistance. Cancer Cell 37:471–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.007
Miricescu D, Totan A, Stanescu-Spinu I-I, Badoiu SC, Stefani C, Greabu M (2020) PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer: from molecular landscape to clinical aspects. Int J Mol Sci 22:173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010173
Owusu-Brackett N, Shariati M, Meric-Bernstam F (2019) Role of pi3k/akt/mtor in cancer signaling. In: Badve S (ed) Predictive biomarkers in oncology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95228-4_20
Pei Q, Liu G, Li H, Zhang Y, Xu X, Gao H, Zhang W, Li T (2019) Long noncoding RNA SNHG14 accelerates cell proliferation, migration, invasion and suppresses apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by targeting miR-944/KRAS axis through PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:9871–9881
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucl Acids Res 29:e45–e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Pishbin F, Ziamajidi N, Abbasalipourkabir R, Najafi R, Farhadian M (2021) Correlation of miR-600 with WT1 expression and its potential clinical significance in breast cancer. Pers Med 18:31–42. https://doi.org/10.2217/pme-2020-0010
Que T, Song Y, Liu Z, Zheng S, Long H, Li Z, Liu Y, Wang G, Zhou J, Zhang X (2015) Decreased miRNA-637 is an unfavorable prognosis marker and promotes glioma cell growth, migration and invasion via direct targeting Akt1. Oncogene 34:4952–4963. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.419
Rahmani F, Ferns GA, Talebian S, Nourbakhsh M, Avan A, Shahidsales S (2020) Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Gene 737:144459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144459
Rascio F, Spadaccino F, Rocchetti MT, Castellano G, Stallone G, Netti GS, Ranieri E (2021) The pathogenic role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer onset and drug resistance: an updated review. Cancers 13:3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13163949
Saikia M, Paul S, Chakraborty S (2020) Role of microRNA in forming breast carcinoma. Life Sci 259:118256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118256
Sideris N, Dama P, Bayraktar S, Stiff T, Castellano L (2022) LncRNAs in breast cancer: a link to future approaches. Cancer Gene Ther. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-022-00487-w
Tang Y, Pan J, Huang S, Peng X, Zou X, Luo Y, Ren D, Zhang X, Li R, He P (2018) Downregulation of miR-133a-3p promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0813-4
Tarhriz V, Bandehpour M, Dastmalchi S, Ouladsahebmadarek E, Zarredar H, Eyvazi S (2019) Overview of CD24 as a new molecular marker in ovarian cancer. J Cell Physiol 234:2134–2142. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27581
Wu Z-S, Wang C-Q, Xiang R, Liu X, Ye S, Yang X-Q, Zhang G-H, Xu X-C, Zhu T, Wu Q (2012) Loss of miR-133a expression associated with poor survival of breast cancer and restoration of miR-133a expression inhibited breast cancer cell growth and invasion. BMC Cancer 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-51
Xu R-L, He W, Tang J, Guo W, Zhuang P, Wang C-Q, Fu W-M, Zhang J-F (2018) Primate-specific miRNA-637 inhibited tumorigenesis in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells by suppressing Akt1 expression. Exp Cell Res 363:310–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.01.026
Yan L-X, Liu Y-H, Xiang J-W, Wu Q-N, Xu L-B, Luo X-L, Zhu X-L, Liu C, Xu F-P, Luo D-L (2016) PIK3R1 targeting by miR-21 suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion by reducing PI3K/AKT signaling and reversing EMT, and predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Int J Oncol 48:471–484. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.3287
Yu JS, Cui W (2016) Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development 143:3050–3060. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.137075
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Liu Z (2016) MicroRNA-147 suppresses proliferation, invasion and migration through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer. Oncol Lett 11:405–410. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3842
Ziasarabi P, Sorayayi S, Hesari A, Ghasemi F (2019) Circulating microRNA-133, microRNA-17 and microRNA-25 in serum and its potential diagnostic value in gastric cancer. J Cell Biochem 120:12376–12381. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28503
Zou X, Xia T, Li M, Wang T, Liu P, Zhou X, Huang Z, Zhu W (2021) MicroRNA profiling in serum: potential signatures for breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Biomark 30:41–53. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-201547
Acknowledgements
The current research is derived from the PhD thesis (project 140002281458) which was approved and financed by Hamedan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan.
Funding
This project was supported by the Deputy of Research and Technology of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (No 140002281458).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZB did all experiments and wrote the manuscript, NM, confirming patients and giving samples, RA analyzed and interpreted the data, SAM-N revised the manuscript and NZ generated and developed the study hypothesis, design and completed the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barartabar, Z., Moini, N., Abbasalipourkabir, R. et al. Investigation of miR-133a, miR-637 and miR-944 genes expression and their relationship with PI3K/AKT signaling in women with breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 6115–6129 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04583-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04583-8