Abstract
Purpose
Prostate cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer death for male. In the present study, we applied an integrated bioinformatics approach to provide a novel perspective and identified some hub genes of prostate cancer.
Method
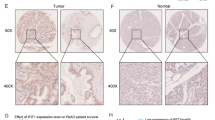
Microarray data of fifty-nine prostate cancer were downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus. Gene Ontology and pathway analysis were applied for differentially expressed genes between high and low grade prostate cancer. Weighted gene coexpression network analysis was applied to construct gene network and classify genes into different modules. The most related module to high grade prostate cancer was identified and hub genes in the module were revealed. Ingenuity pathway analysis was applied to check the chosen module’s relationship to high grade prostate cancer. Hub gene’s expression profile was verified with clinical samples and a dataset from The Cancer Genome Atlas project.
Result
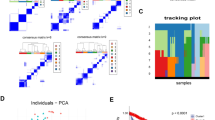
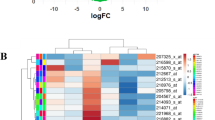
3193 differentially expressed genes were filtered and gene ontology and pathway analysis revealed some cancer- and sex hormone-related results. Weighted gene coexpression network was constructed and genes were classified into six modules. The red module was selected and ingenuity pathway analysis confirmed its relationship with high grade prostate cancer. Hub genes were identified and their expression profile was also confirmed.
Conclusion
The present study applied integrate bioinformatics approaches to generate a holistic view of high grade prostate cancer and identified hub genes could serve as prognosis markers and potential treatment targets.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25:25–29. doi:10.1038/75556
Assinder SJ, Dong Q, Kovacevic Z, Richardson DR (2009) The TGF-β, PI3K/Akt and PTEN pathways: established and proposed biochemical integration in prostate cancer. Biochem J 417:411–421. doi:10.1042/BJ20081610
Barabasi A-L (2009) Scale-free networks: a decade and beyond. Science (80-) 325:412–413. doi:10.1126/science.1173299
Bi D, Ning H, Liu S et al (2015) Gene expression patterns combined with network analysis identify hub genes associated with bladder cancer. Comput Biol Chem 56:71–83. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2015.04.001
Bibikova M, Chudin E, Arsanjani A et al (2007) Expression signatures that correlated with Gleason score and relapse in prostate cancer. Genomics 89:666–672. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.02.005
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H et al (2009) ClueGO: a cytoscape plug-into decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 25:1091–1093. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp101
Blake JA, Christie KR, Dolan ME et al (2015) Gene ontology consortium: going forward. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D1049–D1056. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1179
Castilla C, Flores ML, Medina R et al (2014) Prostate cancer cell response to paclitaxel is affected by abnormally expressed securin PTTG1. Mol Cancer Ther 13(10):2372–2383. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0405
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U et al (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2:401–404. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
Chen Z, Zhang C, Wu D et al (2011) Phospho-MED1-enhanced UBE2C locus looping drives castration-resistant prostate cancer growth. EMBO J 30:2405–2419. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.154
Chiang YT, Wang K, Fazli L et al (2014) GATA2 as a potential metastasis-driving gene in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 5:451–461
Choi J-W, Kim Y, Lee J-H, Kim Y-S (2013) High expression of spindle assembly checkpoint proteins CDC20 and MAD2 is associated with poor prognosis in urothelial bladder cancer. Virchows Arch 463:681–687. doi:10.1007/s00428-013-1473-6
Cui W, Qian Y, Zhou X et al (2015) Discovery and characterization of long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNA) module biomarkers in prostate cancer: an integrative analysis of RNA-Seq data. BMC Genomics 16:S3. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-16-S7-S3
Cuzick J, Swanson GP, Fisher G et al (2011) Prognostic value of an RNA expression signature derived from cell cycle proliferation genes in patients with prostate cancer: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol 12:245–255. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70295-3
de Resende MF, Vieira S, Chinen LT et al (2013) Prognostication of prostate cancer based on TOP2A protein and gene assessment: TOP2A in prostate cancer. J Transl Med 11:36
Erho N, Crisan A, Vergara IA et al (2013) Discovery and validation of a prostate cancer genomic classifier that predicts early metastasis following radical prostatectomy. PLoS One 8:e66855. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066855
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U et al (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 6:pl1. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2004088
Ghazalpour A, Doss S, Zhang B et al (2006) Integrating genetic and network analysis to characterize genes related to mouse weight. PLoS Genet 2:1182–1192. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020130
Gleason DF (1966) Classification of prostatic carcinomas. Cancer Chemother Rep 50:125–128
Gleason DF, Mellinger GT (1974) Prediction of prognosis for prostatic adenocarcinoma by combined histological grading and clinical staging. J Urol 111:58–64
Huang DW, Lempicki RA, Sherman BT (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Huang S, Liao Q, Li L, Xin D (2014) PTTG1 inhibits SMAD3 in prostate cancer cells to promote their proliferation. Tumour Biol 35:6265–6270
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M et al (2017) KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D353–D361. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1092
Khatri P, Sirota M, Butte AJ (2012) Ten years of pathway analysis: current approaches and outstanding challenges. PLoS Comput Biol. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002375
Khongkow P, Gomes AR, Gong C et al (2016) Paclitaxel targets FOXM1 to regulate KIF20A in mitotic catastrophe and breast cancer paclitaxel resistance. Oncogene 35:990–1002. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.152
Kidokoro T, Tanikawa C, Furukawa Y et al (2008) CDC20, a potential cancer therapeutic target, is negatively regulated by p53. Oncogene 27:1562–1571. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210799
Kim Y, Choi J-W, Lee J-H, Kim Y-S (2014) MAD2 and CDC20 are upregulated in high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and squamous cell carcinomas of the uterine cervix. Int J Gynecol Pathol 33:517–523. doi:10.1097/PGP.0000000000000082
Kirk JS, Schaarschuch K, Dalimov Z et al (2015) Top2a identifies and provides epigenetic rationale for novel combination therapeutic strategies for aggressive prostate cancer. Oncotarget 6:3136–3146
Kuner R, Fälth M, Pressinotti NC et al (2013) The maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) is upregulated in high-grade prostate cancer. J Mol Med 91:237–248. doi:10.1007/s00109-012-0949-1
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform 9:559. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Langfelder P, Zhang B, Horvath S (2008) Defining clusters from a hierarchical cluster tree: the dynamic tree cut package for R. Bioinformatics 24:719–720. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm563
Lee B, Mazar J, Aftab MN et al (2014) Long noncoding RNAs as putative biomarkers for prostate cancer detection. J Mol Diagn 16:615–626. doi:10.1016/j.jmoldx.2014.06.009
Li K, Mao Y, Lu L et al (2016) Silencing of CDC20 suppresses metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer growth and enhances chemosensitivity to docetaxel. Int J Oncol 49:1679–1685. doi:10.3892/ijo.2016.3671
Loeb S, Bruinsma SM, Nicholson J et al (2015) Active surveillance for prostate cancer: a systematic review of clinicopathologic variables and biomarkers for risk stratification. Eur Urol 67:619–626. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.10.010
Ma R, Kang X, Zhang G et al (2016) High expression of UBE2C is associated with the aggressive progression and poor outcome of malignant glioma. Oncol Lett 11:2300–2304. doi:10.3892/ol.2016.4171
MacLennan NK, Dong J, Aten JE et al (2009) Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identifies biomarkers in glycerol kinase deficient mice. Mol Genet Metab 98:203–214. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.05.004
Malki K, Tosto MG, Jumabhoy I et al (2013) Integrative mouse and human mRNA studies using WGCNA nominates novel candidate genes involved in the pathogenesis of major depressive disorder research article. Pharmacogenomics 14:1979–1990. doi:10.2217/pgs.13.154
Mao Y, Li K, Lu L et al (2016) Overexpression of Cdc20 in clinically localized prostate cancer: relation to high Gleason score and biochemical recurrence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Cancer Biomark 16:351–358
Mason MJ, Fan G, Plath K et al (2009) Signed weighted gene co-expression network analysis of transcriptional regulation in murine embryonic stem cells. BMC Genom 10:327. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-327
Moura IMB, Delgado ML, Silva PMA et al (2014) High CDC20 expression is associated with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 43:225–231. doi:10.1111/jop.12115
Murphy AJ, Hughes CA, Barrett C et al (2007) Low-level TOP2A amplification in prostate cancer is associated with HER2 duplication, androgen resistance, and decreased survival. Cancer Res 67:2893–2898
Psyrri A, Kalogeras KT, Kronenwett R et al (2012) Prognostic significance of UBE2C mRNA expression in high-risk early breast cancer. A Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) Study. Ann Oncol 23:1422–1427. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr527
Puniya BL, Kulshreshtha D, Verma SP et al (2013) Integrated gene co-expression network analysis in the growth phase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals new potential drug targets. Mol BioSyst 9:2798–2815. doi:10.1039/c3mb70278b
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. doi:10.1101/gr.1239303
Shen Z, Jiang X, Zeng C et al (2013) High expression of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 2C (UBE2C) correlates with nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression. BMC Cancer 13:192. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-192
Shuliang S, Lei C, Guangwu J, Changjie L (2013) Involvement of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C in proliferation and invasion of prostate carcinoma cells. Oncol Res 21:121–127. doi:10.3727/096504013X13832473329953
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21332
Stangel D, Erkan M, Buchholz M et al (2015) Kif20a inhibition reduces migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Res 197:91–100. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2015.03.070
Stark JR, Perner S, Stampfer MJ et al (2009) Gleason score and lethal prostate cancer: does 3 + 4 = 4 + 3? J Clin Oncol 27:3459–3464. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.4669
Taniuchi K, Furihata M, Saibara T (2014) KIF20A-mediated RNA granule transport system promotes the invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. Neoplasia 16:1082–1093. doi:10.1016/j.neo.2014.10.007
Wan X, Huang W, Yang S et al (2016) Identification of androgen-responsive lncRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic markers for prostate cancer. Oncotarget 7:60503–60518. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11391
Wang Q, Li W, Zhang Y et al (2009) Androgen receptor regulates a distinct transcription program in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cell 138:245–256. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.056
Wang H, Zhang C, Rorick A et al (2011) CCI-779 inhibits cell-cycle G2-M progression and invasion of castration-resistant prostate cancer via attenuation of UBE2C transcription and mRNA stability. Cancer Res 71:4866–4876. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4576
Wang L, Gong Y, Chippada-Venkata U et al (2015) A robust blood gene expression-based prognostic model for castration-resistant prostate cancer. BMC Med 13:201
Yan G-R, Zou F-Y, Dang B-L et al (2012) Genistein-induced mitotic arrest of gastric cancer cells by downregulating KIF20A, a proteomics study. Proteomics 12:2391–2399. doi:10.1002/pmic.201100652
Zhang S, Cao J (2009) A close examination of double filtering with fold change and T test in microarray analysis. BMC Bioinform 10:402. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-10-402
Zhang B, Genetics H, Zhang B, Horvath S (2005) A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. doi:10.2202/1544-6115.1128
Zhang W, He W, Shi Y et al (2016) High expression of KIF20A is associated with poor overall survival and tumor progression in early-stage cervical squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One 11:e0167449. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0167449
Zhao S, Geybels MS, Leonardson A et al (2016) Epigenome-wide tumor DNA methylation profiling identifies novel prognostic biomarkers of metastatic-lethal progression in men with clinically localized prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0549
Zhu X, Mao Z, Na Y et al (2006) Significance of pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 (PTTG1) in prostate cancer. Anticancer Res 26:1253–1259
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81172191; 81602238); the General Program of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (No. 201440511); The Key Basic Research Foundation of Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology of China (No. 14JC1491200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the ethics committee of Shanghai Changzheng Hospital and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Funding
No funding was received.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was exempted because of the retrospective study design.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Zhang, Q., Ye, C. et al. Identification of prognostic markers of high grade prostate cancer through an integrated bioinformatics approach. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 2571–2579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2497-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2497-0