Abstract
Background and aims
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression by targeting mRNAs. Our previous study found that miR-29b strongly regulates the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Here, we aimed to identify the mRNAs targeted by miR-29b.
Methods
We used microarray experiments in conjunction with computational methods to identify the mRNAs that were most susceptible to miR-29b-mediated repression. We further confirmed the activities of three target genes, C1QTNF6, SPARC, and COL4A2, by luciferase reporter analyses and invasion assays.
Results
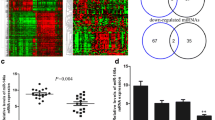
We evaluated the impact of miR-29b on global mRNA expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells through microarray analysis and further analyzed four genes that were at least twofold down-regulated and predicted as miR-29b targets by at least two of the four widely used miRNA target prediction algorithms. We also analyzed one mRNA that was down-regulated by 1.8-fold but was predicted to have significant interactions with miR-29b in pathway analysis and was predicted as a miR-29b target by all four algorithms. Luciferase reporter and invasion assays revealed that C1QTNF6, SPARC, and COL4A2 were targeted by miR-29b and that the degradation of any one of these mRNAs could promote invasion in MCF-7 cells.
Conclusions
C1QTNF6, SPARC, and COL4A2 are targeted by miR-29b, and the down-regulation of these three mRNAs can contribute to the invasion ability of MCF-7 cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Dumont N, Tlsty TD (2009) Reflections on miR-ing effects in metastasis. Cancer Cell 16(1):3–4
Eyholzer M, Schmid S, Wilkens L, Mueller BU, Pabst T (2010) The tumour-suppressive miR-29a/b1 cluster is regulated by CEBPA and blocked in human AML. Br J Cancer 103:275–284
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9:102–114
Gunduz M, Beder LB, Gunduz E, Nagatsuka H, Fukushima K, Pehlivan D, Cetin E, Yamanaka N, Nishizaki K, Shimizu K, Nagai N (2008) Downregulation of ING3 mRNA expression predicts poor prognosis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Sci 99(3):531–538
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Welch DR (2009) Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is spreading. Cancer Res 69(19):7495–7498
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG et al (2005) MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:7065–7070
Koblinski JE, Kaplan-Singer BR, VanOsdol SJ, Wu M, Engbring JA, Wang S, Goldsmith CM, Piper JT, Vostal JG, Harms JF, Welch DR, Kleinman HK (2005) Endogenous osteonectin/SPARC/BM-40 expression inhibits MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell metastasis. Cancer Res 65(16):7370–7377
Kwiecinski M, Noetel A, Elfimova N, Trebicka J, Schievenbusch S, Strack I, Molnar L, von Brandenstein M, Töx U, Nischt R, Coutelle O, Dienes HP, Odenthal M (2011) Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibits collagen I and IV synthesis in hepatic stellate cells by miRNA-29 induction. PLoS One 6(9):e24568
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115(7):787–798
Luna C, Li G, Qiu J, Epstein DL, Gonzalez P (2009) Role of miR-29b on the regulation of the extracellular matrix in human trabecular meshwork cells under chronic oxidative stress. Mol Vis 15:2488–2497
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J et al (2006) Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer biopsies. Mol Cancer 5:24
Mizukami S, Ichimura R, Kemmochi S, Taniai E, Shimamoto K, Ohishi T, Takahashi M, Mitsumori K, Shibutani M (2010) Induction of GST-P-positive proliferative lesions facilitating lipid peroxidation with possible involvement of transferring receptor up-regulation and ceruloplasmin down-regulation from the early stage of liver tumor promotion in rats. Arch Toxicol 84:319–331
Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (2007) mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene 26:6133–6140
Ogawa T, Iizuka M, Sekiya Y, Yoshizato K, Ikeda K, Kawada N (2010) Suppression of type I collagen production by microRNA-29b in cultured human stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:316–321
Pedro C-R, Teresa R, Marina M-S, Wu SV, Salazar EP (2008) Src kinase regulates metalloproteinase-9 secretion induced by type IV collagen in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Matrix Biol 27:220–231
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, Vucur M, Zimmermann H, Schmidt S, Janssen J, Koppe C, Knolle P, Castoldi M, Tacke F, Trautwein C, Luedde T (2011) Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 53(1):4–6
Sahab ZJ, Hall MD (2011) Tumor suppressor RARRES1 interacts with cytoplasmic carboxypeptidase AGBL2 to regulate the α-tubulin tyrosination cycle. Cancer Res 71(4):1219–1228
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH, Newton MA, Stanhope SA, Cheng YJ, Chen CJ, Hildesheim A, Sugden B, Ahlquist P (2008) MicroRNA 29c is down-regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinomas, up-regulating mRNAs encoding extracellular matrix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5874–5878
Sethupathy P, Mcgraw M, Hatzigeorgion AG (2006) A guide through present computational approaches for the identification of mammalian microRNA targets[J]. Nat Methods 3:881–886
Sood P, Krek A, Zavolan M, Macino G, Rajewsky N (2006) Cell-type-specific signatures of microRNAs on target mRNA expression. PNAS 103(8):2746–2751
Steele R, Mott JL, Ray RB (2010) MBP-1 up-regulates miR-29b, which represses Mcl-1, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 in prostate cancer cells. Genes Cancer 1(4):381–387
Stefani G, Slack FJ (2008) Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:219–230
Takeuchi T, Adachi Y, Nagayama T (2011) Expression of a secretory protein C1qTNF6, a C1qTNF family member, in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 34(3):113–121
Wang C, Bian Z, Wei D, Zhang JG (2011) MiR-29b regulates migration of human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 352(1–2):197–207
Wu L, Fan J, Belasco JG (2006) MicroRNAs direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4034–4039
Zhdanov VP (2009) Conditions of appreciable influence of microRNA on a large number of target mRNAs. Mol BioSyst 5(6):638–643
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81170541) and the Natural Basic Research Program of China (973 program 2010CB945103).
Conflict of interest
There are no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Gao, C., Zhuang, JL. et al. A combined approach identifies three mRNAs that are down-regulated by microRNA-29b and promote invasion ability in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 2127–2136 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1288-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1288-x