Abstract
Purpose
The tumor suppressor gene PTEN negatively regulates Akt, a downstream mediator phosphoinositol 3-kinase. Several studies have reported the role of PTEN gene in Akt downregulation and apoptosis induction in different cancers and cell lines. However, the role of loss of PTEN expression in Akt activation and spontaneous apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma clinical specimens is not well established.
Methods
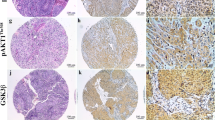
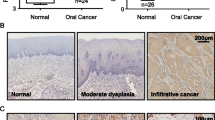
We investigated the expression of PTEN and phospho-Akt in 146 formalin-fixed (archived) paraffin-embedded oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue sections through immunohistochemical analysis. Programmed cell death (apoptosis) was determined by Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Biotin-dUTP Nick End Labeling assay.
Results
Sixty-one percent loss of PTEN expression and 68.5% Akt activation was observed in oral squamous cell carcinoma. A significant correlation was found between loss of PTEN expression and Akt activation. Loss of PTEN expression and Akt activation were further correlated with different clinical parameters and found to be significantly correlated with tumor stage. Apoptotic index was estimated and correlated with PTEN expression and Akt activation. The percentage of apoptotic cells varied from 0.2 to 14.1%. Low apoptotic index was observed in 105 (72%) of samples, and it was found to be significantly related with loss of PTEN expression and phospho-Akt
Conclusion
The present study confirms the contribution of loss of PTEN expression in Akt phosphorylation and spontaneous apoptosis suppression in the specimens of oral cancer. Both PTEN and phospho-Akt are likely to be concerned with oral cancer progression and reduced incidence of spontaneous apoptosis

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali IU, Schriml LM, Dean M (1999) Mutational spectra of PTEN/MMAC1: a tumor suppressor with lipid phosphatase activity. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1922–1932
Altomare DA, Wang HQ, Skele KL, Rienzo AD, Szanto AJ, Godwin A, Testa JR (2004) AKT and mTOR phosphorylation is frequently detected in ovarian cancer and can be targeted to disrupt ovarian tumor cell growth. Oncogene 23:5853–5857
Amornphimoltham P, Sriuranpong V, Patel V, Benavides F, Conti CJ, Sauk J, Sausville EA, Molinolo AA, Gutkind JS (2004) Persistent activation of the Akt pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a potential target for UCN-01. Clin Cancer Res 10:4029–4037
Bankfalvi A, Piffko J (2000) Prognostic and predictive factors in oral cancer: the role of the invasive tumour front. J Oral Pathol Med 29(7):291–298
Bettendorf O, Piffko J, Bankfalvi A (2004) Prognostic and predictive factors in oral squamous cell cancer: important tools for planning individual therapy. Oral Oncol 40(2):110–119
Bowen KA, Doan HQ, Zhou BP, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Rychahou PG, Evers BM (2009) PTEN loss induces epithelial—mesenchymal transition in human colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res 29(11):4439–4449
Cappuzzo F, Magrini E, Ceresoli GL, Bartolini S, Rossi E, Ludovini V, Gregorc V, Ligorio C, Cancellieri A, Damiani S, Spreafico A, Paties CT, Lombardo L, Calandri C, Bellezza G, Tonato M, Crinò L (2004) Akt phosphorylation and gefitinib efficacy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1133–1141
Chen Q, Samaranayake LP, Zhou H, Xiao L (2000) Homozygous deletion of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene is not a feature in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 36:95–99
Dürr E-M, Rollbrocker B, Hayashi Y, Peters N, Meyer-Puttlitz B, Louis DN, Schramm J, Wiestler OD, Parsons R, Eng C, von Deimling A (1998) PTEN mutations in gliomas and glioneuronal tumors. Oncogene 16:2259–2264
Gan YH, Zhang S (2009) PTEN/AKT pathway involved in histone deacetylases inhibitor induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oral Oncol 45(10):150–154
Henderson YC, Wang G, Clayman GL (1998) Genotypic analysis of tumor suppressor genes PTEN/MMAC1 and p53 in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Laryngoscope 108:1553–1556
Jang KS, Song YS, Jang SH, Min KW, Na W, Jang SM, Jun YJ, Lee KH, Choi D, Paik SS (2010) Clinicopathological significance of nuclear PTEN expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Histopathology 56:229–239
Kirkegaard T, Witton CJ, McGlynn LM, Tovey SM, Dunne B, Lyon A, Bartlett JM (2005) AKT activation predicts outcome in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. J Pathol 207:139–146
Kreisberg JI, Malik SN, Prihoda TJ, Bedolla RG, Troyer DA, Kreisberg S, Ghosh PM (2004) Phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473) is an excellent predictor of poor clinical outcome in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 64:5232–5236
Kurasawa Y, Shiba M, Nakamura M, Fushimi K, Ishigami T, Bukawa H, Yokoe H, Uzawa K, Tanzawa H (2008) PTEN expression and methylation status in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 19:1429–1434
Lee JI, Soria JC, Hassan KA, El-Naggar AK, Tang X, Liu DD, Hong WK, Mao L (2002) Loss of PTEN expression as a prognostic marker for tongue cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127:1441–1445
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, Bigner SH, Giovanella BC, Ittmann M, Tycko B, Hibshoosh H, Wigler MH, Parsons R (1997) PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science 275:1943–1947
Lim J, Kim JH, Paeng JY, Kim MJ, Hong SD, Lee JI, Hong SP (2005) Prognostic value of activated Akt expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 58:1199–1205
Lu Y, Lin YZ, Lapushin R, Cuevas B, Fang X, Yu SX, Davies MA, Khan H, Furui T, Mao M, Zinner R, Hung MC, Steck P, Siminovitch K, Mills GB (1999) The PTEN/MMAC1/TEP tumor suppressor gene decreases cell growth and induces apoptosis and inoikis in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 18:7034–7045
Massarelli E, Liu DD, Lee JJ, El-Naggar AK, Lo Muzio L, Staibano S, De Placido S, Myers JN, Papadimitrakopoulou VA (2005) Akt activation correlates with adverse outcome in tongue cancer. Cancer 104:2430–2436
Mavros A, Hahn M, Wieland I, Koy S, Koufaki ON, Strelocke K, Koch R, Haroske G, Schackert HK, Eckelt U (2002) Infrequent genetic alterations of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN/MMAC1 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. J Oral Pathol Med 31:270–276
Mutter GL, Lin M-C, Fitzgerald JT, Kum JB, Baak JP, Lees JA, Weng LP, Eng C (2000) Altered PTEN expression as a diagnostic marker for the earliest endometrial precancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:924–930
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Preacher KJ (2001) Calculation for the Chi-Square test: an interactive tool for Chi-Square tests of goodness of fit and independence (computer software). Available from http://www.quantpsy.org
Rizvi MA, Shabbir MA, Ali A, Mehdi SJ, Batra S, Mandal AK (2011) Aberrant promoter methylation and inactivation of PTEN gene in cervical carcinoma from Indian population. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(8):1255–1262
Rodrigues VC, Moss SM, Tuomainen H (1998) Oral cancer in the UK: to screen or not to screen. Oral Oncol 34:454–465
Sano D, Myers JN (2007) Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26(3–4):645–662
Saranath D, Bhoite LT, Deo MG (1993) Molecular lesion in human oral cancer: the Indian scene. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 29:107–112
Schmitz KJ, Wohlschlaeger J, Lang H, Sotiropoulos GC, Malago M, Steveling K, Reis H, Cicinnati VR, Schmid KW, Baba HA (2008) Activation of the ERK and AKT signalling pathway predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and ERK activation in cancer tissue is associated with hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol 48(1):83–90
Shao X, Tandon R, Samara G, Kanki H, Yano H, Close LG, Parsons R, Sato T (1998) Mutational analysis of the PTEN gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 77:684–688
Shin Lee J, Seok Kim H, Bok Kim Y, Cheol Lee M, Soo Park C (2003) Expression of PTEN in renal cell carcinoma and its relation to tumor behavior and growth. J Surg Oncol 84:166–172
Snaddon J, Parkinson EK, Craft JA, Bartholomew C, Fulton R (2001) Detection of functional PTEN lipid phosphatase protein and enzyme activity in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck, despite loss of heterozygosity at this locus. Br J Cancer 84:1630–1634
Squarize CH, Castilho RM, Pinto DS (2002) Immunohistochemical evidence of PTEN in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its correlation with the histological malignancy grading system. J Oral Pathol Med 31:379–384
Tang JM, He QY, Guo RX, Chang XJ (2005) Phosphorylated Akt overexpression and loss of PTEN expression in non-small cell lung cancer confers poor prognosis. Lung Cancer 51(2):181–191
Tsao HS, Zhang X, Benoit E, Haluska FG (1998) Identification of PTEN/MMAC1 alterations in uncultured melanomas and melanoma cell lines. Oncogene 16:3397–3402
Weng LP, Brown JL, Eng C (2001) PTEN induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt-dependent and -independent pathways. Hum Mol Genet 10:237–242
Yang XF, Xin Y, Mao LL (2008) Clinicopathological significance of PTEN and caspase-3 expressions in breast cancer. Chin Med Sci J 23(2):95–102
Yu Z, Weinberger PM, Sasaki C, Egleston BL, Speier WF IV, Haffty B, Kowalski D, Camp R, Rimm D, Vairaktaris E, Burtness B, Psyrri A (2007) Phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473) predicts poor clinical outcome in oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16(3):553–558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alyasiri, N.S., Mehdi, S.J., Alam, M.S. et al. PTEN-mediated AKT activation contributes to the reduced apoptosis among Indian oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 103–109 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-011-1077-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-011-1077-y