Abstract
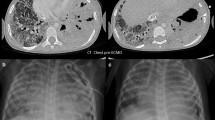
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis is a rare disease defined by the triad of iron deficiency anemia, hemoptysis, and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates on chest radiograph. Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis is known to cause dyspnea and, in some cases, acute onset of massive pulmonary hemorrhage which is traditionally treated with conventional mechanical ventilation or high-frequency oscillation in conjunction with immunosuppressive therapy. In this case report, we describe a 5-week-old infant presenting with hemoptysis, massive pulmonary hemorrhage, and significant hypercapnic respiratory failure. The patient failed conventional ventilation but responded well to extracorporeal life support that was initiated early in his course. Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis was suspected in light of his response to high-dose steroids and was confirmed by subsequent lung biopsies. Conclusion: Patients with severe pulmonary hemorrhage secondary to idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis can be safely supported with extracorporeal life support when conventional therapies have been exhausted.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson JC, Parakininkas D, Rice TB (2011) Pneumonitis and intersitial disease. In: Fuhrman BP, Zimmerman JJ (eds) Pediatric critical care, 4th edn. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 609–631
Chryssanthopoulos C, Cassimos C, Panagiotidou C (1983) Prognostic criteria in idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis in children. Eur J Pediatr 140(2):123–125
Collard HR, Schwarz MI (2004) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Clin Chest Med 25(3):583–592. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2004.04.007, vii
Dearborn DG, Smith PG, Dahms BB, Allan TM, Sorenson WG, Montana E, Etzel RA (2002) Clinical profile of 30 infants with acute pulmonary hemorrhage in Cleveland. Pediatrics 110(3):627–637
Ioachimescu OC, Sieber S, Kotch A (2004) Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis revisited. Eur Respir J 24(1):162–170
Joseph M, Charles AG (2011) Early extracorporeal life support as rescue for Wegener granulomatosis with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a case report and literature review. Pediatr Emerg Care 27(12):1163–1166. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e31823b01a2
Kolovos NS, Schuerer DJ, Moler FW, Bratton SL, Swaniker F, Bartlett RH, Custer JR, Annich G (2002) Extracorporal life support for pulmonary hemorrhage in children: a case series. Crit Care Med 30(3):577–580
Le Clainche L, Le Bourgeois M, Fauroux B, Forenza N, Dommergues JP, Desbois JC, Bellon G, Derelle J, Dutau G, Marguet C, Pin I, Tillie-Leblond I, Scheinmann P, De Blic J (2000) Long-term outcome of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis in children. Medicine 79(5):318–326
Mongero LB, Brodie D, Cunningham J, Ventetuolo C, Kim H, Sylvan E, Bacchetta MD (2010) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and severe hypoxemic respiratory failure from silicone embolism. Perfusion 25(4):249–252. doi:10.1177/0267659110375327, discussion 253–244
Saeed MM, Woo MS, MacLaughlin EF, Margetis MF, Keens TG (1999) Prognosis in pediatric idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis. Chest 116(3):721–725
Conflict of interest
The authors did not receive any financial support for the study and declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was performed at Children's National Medical Center in Washington, DC, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutierrez, S., Shaw, S., Huseni, S. et al. Extracorporeal life support for a 5-week-old infant with idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis. Eur J Pediatr 173, 1573–1576 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2130-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2130-4