Abstract
Introduction
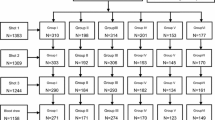
This randomised, observer-blind clinical trial conducted in Turkey evaluated the immunogenicity, safety and interchangeability of three paediatric inactivated hepatitis A vaccines in 424 seronegative children between 1 and 15 years of age.
Methods
Potential subjects were screened for anti-hepatitis A virus (HAV) antibodies prior to receiving a first dose of Avaxim 80, Havrix 720 or Vaqta 25, followed by a second dose of either the same vaccine or Avaxim 6 months later. Anti-HAV antibody concentrations were measured 2 weeks after the first injection, at 24 weeks (before the second dose) and at 28 weeks for the evaluation of the immune response.
Results
Nearly 80% of the children between 1 and 5 years of age and half of those between the ages of 6 and 10 in the population from which the subjects were recruited were seronegative for HAV antibodies. Two weeks after the first dose, 98.2% of all subjects had anti-HAV antibody concentrations equal to or higher than 20 mIU/mL, believed to be seroprotective, and all subjects were seroprotected before and after the second dose. Anti-HAV geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) 2 weeks after the first dose and before the second were similar in children who received Avaxim and Vaqta (P = 0.2), but both were higher than Havrix (P < 0.01). There were no significant differences in the anti-HAV GMCs between the study groups that received two doses of the same vaccine compared with two doses of different vaccines. There were no significant differences in the frequency of any local or systemic adverse events among the study groups following either of the two doses.
Conclusion
All three vaccines are safe and highly immunogenic in healthy children aged 1 to 15 years. Avaxim 80 may also be given as the second dose when Havrix 720 or Vaqta 25 are given as the first dose. The pattern of seroprevalence seen here is similar to that reported in a number of recent evaluations in Turkey, and are supportive of the routine hepatitis A vaccination of young children.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarca K, Ibanez I, Perret C, Vial P, Zinsou J-A (2004) Immunogenicity and safety of Avaxim 80U-Pediatric and Havrix 720 in Chilean children from 1 to 15 years of age. Int J Infect Dis 8(Suppl 1):S18
Ambrosch F, Wiedermann G, Jonas S, Althaus B, Finkel B, Gluck R, Herzog C (1997) Immunogenicity and protectivity of a new liposomal hepatitis A vaccine. Vaccine 15(11):1209–1213
Atabek ME, Fyndyk D, Gulyuz A, Erkul I (2004) Prevalence of anti-HAV and anti-HEV antibodies in Konya, Turkey. Health Policy 67(3):265–269
Bell BP (2002) Hepatitis A vaccine. Sem Pediatr Infect Dis 13(3):165–173
Bell BP, Feinstone SM (2004) Hepatitis A vaccine. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA (eds) Vaccine, 4th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, pp 269–297
Bryan JP, Henry CH, Hoffman AG, South-Paul JE, Smith JA, Cruess D, Spieker JM, de Medina M (2000) Randomized, cross-over, controlled comparison of two inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. Vaccine 19(7–8):743–750
Castillo de Febres O, Chacon de Petrola M, Casanova de Escalona L, Naveda O, Naveda M, Estopinan M, Bordones G, Zambrano B, Garcia A, Dumas R (1999) Safety, immunogenicity and antibody persistence of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in 4 to 15 year old children. Vaccine 18(7–8):656–664
Dagan R, Greenberg D, Goldenbertg-Gehtman P, Vidor E, Briantais P, Pinsk V, Athias O, Dumas R (1999) Safety and immunogenicity of a new formulation of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. Vaccine 17(15–16):1919–1925
Dagan R, Greenberg D, Weber F (2005) Immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A pediatric vaccine: three-year post-booster follow-up. Vaccine 23(44):5144–5148
Dagan R, Leventhal A, Anis E, Slater P, Ashur Y, Shouval D (2005) Incidence of hepatitis A in Israel following universal immunization of toddlers. JAMA 294(2):202–210
Dominguez A, Bruguera M, Plans P, Costa J, Salleras L (2004) Prevalence of hepatitis A antibodies in schoolchildren in Catalonia (Spain) after the introduction of universal hepatitis A immunization. J Med Virol 73(2):172–176
Erdogan MS, Otkun M, Tatman-Otkun M, Akata F, Ture M (2004) The epidemiology of hepatitis A virus infection in children, in Edirne, Turkey. Eur J Epidemiol 19(3):267–273
Franco E, Giambi C, Ialacci R, Maurici M (2003) Prevention of hepatitis A by vaccination. Expert Opin Biol Ther 3(6):965–974
Hollinger FB, Ticehurst JR (1996) Hepatitis A virus. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds) Fields virology, 3rd edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, pp 735–782
Hoppenbrouwers K, Kanra G, Roelants M, Ceyhan M, Vandermeulen C, Yurdakök K, Silier T, Dupuy M, Pehlivan T, Özmert E, Desmyter J (1999) Priming effect, immunogenicity and safety of an Haemophilus influenzae type b-tetanus toxoid conjugate (PRP-T) and diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis (DTaP) combination vaccine administered to infants in Belgium and Turkey. Vaccine 17(7–8):875–886
Kanra G, Tezkan S, Badur S; Turkish National Study Team (2002) Hepatitis A seroprevalence in a random sample of the Turkish population by simultaneous EPI cluster and comparison with surveys in Turkey. Turk J Pediatr 44(3):204–210
Koff RS (1992) Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hepatitis A virus infection. Vaccine 10(Suppl 1):S15–S17
Koff RS (1998) Hepatitis A. Lancet 351(9116):1643–1649
Lemon SM (1985) Type A viral hepatitis. New developments in an old disease. N Engl J Med 313(17):1059–1067
Lemon SM, Murphy PC, Provost PJ, Chalikonda I, Davide JP, Schofield TL, Nalin DR, Lewis JA (1997) Immunoprecipitation and virus neutralization assays demonstrate qualitative differences between protective antibody responses to inactivated hepatitis A vaccine and passive immunization with immune globulin. J Infect Dis 176(1):9–19
Lolekha S, Pratuangtham S, Punpanich W, Bowonkiratikachorn P, Chimabutra K, Weber F (2003) Immunogenicity and safety of two doses of a paediatric hepatitis A vaccine in Thai children: comparison of three vaccination schedules. J Trop Pediatr 49(6):333–339
Lopez EL, Del Carmen Xifro M, Tarrado LE, De Rosa MF, Gomez R, Dumas R, Wood SC, Contrini MM (2001) Safety and immunogenicity of a pediatric formulation of inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in Argentinean children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 20(1):48–52
MacIntyre CR, Burgess MA, Hull B, McIntyre PB (2003) Hepatitis A vaccination options for Australia. J Paediatr Child Health 39(2):83–87
Ministro de Salud y Ambiente (2005) Comenzó la vacunción gratuita contra la hepatitis A en todo el pais. Available online at http://www.msal.gov.ar/htm/site/Noticias_plantilla.asp?Id=569
Scheifele DW (2005) Hepatitis A vaccines: the growing case for universal immunisation of children. Expert Opin Pharmacother 6(2):157–164
Sidal M, Ünüvar E, Oguz F, Cihan C, Önel D, Badur S (2001) Age-specific seroepidemiology of hepatitis A, B, and E infections among children in Istanbul, Turkey. Eur J Epidemiol 17(2):141–144
Tosun S, Ertan P, Kasirga E, Atman Ü (2004) Changes in seroprevalence of hepatitis A in children and adolescents in Manisa, Turkey. Pediatr Int 46(6):669–672
Ungan M, Yaman H, Taheri N (2002) The prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis A among preschool children in an urban setting in Turkey. J Trop Pediatr 48(3):180–182
Van Herck K, Van Damme P (2005) Prevention of hepatitis A by Havrix: a review. Expert Rev Vaccines 4(4):459–471
Vidor E, Dumas R, Porteret V, Bailleux F, Veitch K (2004) Aventis Pasteur vaccines containing inactivated hepatitis A virus: a compilation of immunogenicity data. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23(4):300–309
Vidor E, Xueref C, Blondeau C, Bajard A, Françon A, Goudeau A, Peyron F, Brasseur P, Zuckerman A (1996) Analysis of the antibody response in humans with a new inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. Biologicals 24(3):235–242
WHO (2000) WHO position paper on hepatitis A vaccines. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 75:37–44
Wiedmann M, Boehm S, Schumacher W, Swysen C, Zauke M (2003) Evaluation of three commercial assays for the detection of hepatitis A virus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22(2):129–130
Yapicioglu H, Alhan E, Yildizdas D, Yaman A, Bozdemir N (2002) Prevalence of hepatitis A in children and adolescents in Adana, Turkey. Indian Pediatr 39(10):936–941
Zuckerman JN, Kirkpatrick CT, Huang M (1998) Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of Avaxim (160 AU) as compared with Havrix (1440 EL.U) as a booster following primary immunization with Havrix (1440 EL.U) against Hepatitis A. J Travel Med 5(1):18–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soysal, A., Gokçe, I., Pehlivan, T. et al. Interchangeability of a hepatitis A vaccine second dose: Avaxim 80 following a first dose of Vaqta 25 or Havrix 720 in children in Turkey. Eur J Pediatr 166, 533–539 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-007-0432-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-007-0432-0