Abstract
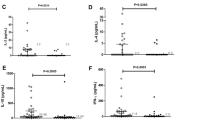
Neurocysticercosis, a clinically and radiologically pleomorphic parasitic disease, is still endemic to most non-developed countries of Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Anti-helminthic drugs (AHD) are generally effective and rapidly destroy parenchymal cysticerci. In contrast, several cycles of AHD are frequently necessary to damage extraparenchymally located parasites. The present study was designed to evaluate whether differences in the immunological profile of the patients is involved in the diversity of the response to AHD. To this end, a global gene expression microarray and a cytokine analysis were made. Responder patients were those showing a radiological reduction greater than 50 % in the parasite burden following AHD treatment. Microarray pre- and post-treatment comparisons showed that a total of eighteen immune-related genes were up-regulated in the five responder patients with respect the expression profile seen in the four non-responder subjects. The function of up-regulated genes exerted pro-inflammatory (RORγC, Sema4A, SLAMF3, SLAMF6), anti-inflammatory (TGFβ, TNFRSF25, TNFRS18, SLAMF1, ILF2), or immunomodulatory effects (CXCL2, RUNX3, SLAMF9, TGFBR3). To further explore the causes of the heterogeneity in the response to treatment, a wide ELISA cytokine analysis was performed in serum, PBMC supernatants, and CSF samples from 39 responder and 26 non-responder patients. Responder patients showed higher CSF IL-17A levels (P = 0.04) and higher supernatant IL-6 levels (P = 0.03) 60 days after treatment. These results suggest a possible influence of pro-inflammatory cytokines on the response to AHD as observed by radiological methods, and thus the possible participation of the host immunity in the effectiveness of AHD treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sciutto E, Fragoso G, Fleury A, Laclette JP, Sotelo J, Aluja A, Vargas L, Larralde C (2000) Taenia solium disease in humans and pigs: an ancient parasitosis disease rooted in developing countries and emerging as a major health problem of global dimensions. Microbes Infect 2:1875–1890
Fleury A, Carrillo-Mezo R, Flisser A, Sciutto E, Corona T (2011) Subarachnoid basal neurocysticercosis: a focus on the most severe form of the disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 9:123–133
Suastegui Roman RA, Soto-Hernandez JL, Sotelo J (1996) Effects of prednisone on ventriculoperitoneal shunt function in hydrocephalus secondary to cysticercosis: a preliminary study. J Neurosurg 84:629–633
Fleury A, Dessein A, Preux PM, Dumas M, Tapia G, Larralde C, Sciutto E (2004) Symptomatic human neurocysticercosis: age, sex and exposure factors relating with disease heterogeneity. J Neurol 251:830–837
Chavarria A, Fleury A, Garcia E, Márquez C, Fragoso C, Sciutto E (2005) Relationship between the clinical heterogeneity of neurocysticercosis and the immune-inflammatory profiles. Clin Immunol 116:271–278
Bustos JA, Pretell EJ, Llanos-Zavalaga F, Gilman RH, Del Brutto OH, Garcia HH, Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru (2006) Efficacy of a 3-day course of albendazole treatment in patients with single neurocysticercosis cyst. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108:193–194
Cárdenas G, Carrillo-Mezo R, Jung H, Sciutto E, Hernández JL, Fleury A (2010) Subarachnoidal neurocysticercosis non-responsive to cysticidal drug: a case series. BMC Neurol 10:16. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-10-16
Diazgranados-Sánchez JA, Barrios-Arrázola G, Costa JL, Burbano-Pabon J, Pinzón-Bedoya J (2008) Ivermectin as a therapeutic alternative in neurocysticercosis that is resistant to conventional pharmacological treatment. Rev Neurol 46:671–674
Guilpain P, Le Jeunne C (2012) Anti-inflammatory and immunosupressive properties of corticosteroids. Presse Med 41:378–383
Chavarria A, Roger B, Fragoso G, Tapia G, Fleury A, Dumas M, Dessein A, Larralde C, Sciutto E (2003) Th2 profile in asymptomatic Taenia solium human neurocysticercosis. Microbes Infect 5:1109–1115
Chavarria A, Fleury A, Bobes RJ, Morales J, Fragoso G, Sciutto E (2006) A depressed peripheral cellular immune response is related to symptomatic neurocysticercosis. Microbes Infect 8:1082–1089
Adalid-Peralta L, Fleury A, García-Ibarra TM, Hernández M, Parkhouse M, Crispin JC, Voltaire Proaño J, Cardenas G, Fragoso G, Sciutto E (2012) Human neurocysticercosis: in vivo expansion of peripheral regulatory T cells and their recruitment in the central nervous system. J Parasitol 98:142–148
Del Brutto OH, Rajshekhar V, White AC Jr, Tsang VC, Nash TE, Takayanagui OM, Schantz PM, Evans CA, Flisser A, Correa D, Botero D, Allan JC, Sarti E, Gonzalez AE, Gilman RH, Garcia HH (2001) Proposed diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis. Neurology 57:177–183
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JY, Zhang J (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5:R80
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad DM, Irizarry RA (2004) Affy: analysis of Affymetrix Gene Chip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20:307–315
Dessau RB, Pipper CB (2008) “R”—project for statistical computing. UgeskrLaeger 170:328–330
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP (2003) A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on bias and variance. Bioinformatics 19:185–193
Wu Z, Irizarry RA, Gentleman R, Martinez-Murillo F, Spencer F (2004) A model-based background adjustment for oligonucleotide expression arrays. J Am Stat Assoc 99:909–917
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Sáenz B, Fleury A, Chavarria A, Hernandez M, Crispin JC, Vargas-Rojas MI, Fragoso G, Sciutto E (2012) Neurocysticercosis: local and systemic immune-inflammatory features related to severity. Med Microbiol Immunol 201:73–80
Sciutto E, Cárdenas G, Adalid-Peralta L, Fragoso G, Larralde C, Fleury A (2013) Human neurocysticercosis: immunological features involved in the host’s susceptibility to become infected and to develop disease. Microbes Infect 15:524–530. doi:10.1016/j.miuncinf.2013.03.007
Trakhtenberg EF, Goldberg JL (2011) Immunology. Neuroimmune communication. Science 334:47–48
de Wit J, Souwer Y, van Beelen AJ, de Groot R, Muller FJ, Klaasse Bos H, Jorritsma T, Kapsenberg ML, de Jong EC, van Ham SM (2011) CD5 costimulation induces stable Th17 development by promoting IL-23R expression and sustained STAT3 activation. Blood 118:6107–6114. doi:10.1182/blood-2011/05-352682
Linsley PS, Bradshaw J, Urnes M, Grosmaire L, Ledbetter JA (1993) CD28 engagement by B7/BB-1 induces transient down-regulation of CD28 synthesis and prolonged unresponsiveness to CD28 signaling. J Immunol 150:3161–3169
Hu SM, Luo YL, Lai WY, Chen PF (2009) Effects of dexamethasone on intracellular expression of Th17 cytokine interleukin 17 in asthmatic mice. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da XueBao 29:1185–1188
Prado C, Gomez J, Lopez P, de Paz B, Gutierrez C, Suarez A (2011) Dexamethasone up regulates FOXP3 expression without increasing regulatory activity. Immunobiology 216:386–392
Medina-Escutia E, Morales-Lopez Z, Proaño JV, Vazquez J, Bermudez V, Navarrete VO, Madrid-Marina V, Laclette JP, Correa D (2001) Cellular immune response and Th1/Th2 cytokines in human neurocysticercosis: lack of immune suppression. J Parasitol 87:587–590
Restrepo BI, Alvarez JI, Castaño JA, Arias LF, Restrepo M, Trujillo J, Colegial CH, Teale JM (2001) Brain granulomas in neurocysticercosis patients are associated with a Th1 and Th2 profile. Infect Immun 69:4554–4560
Cua DJ, Kastelein RA (2006) TGF-beta, a “double agent” in the immune pathology war. Nat Immunol 7:557–559
McGeacgy MJ, Bak-Jensen KS, Chen Y, Tato CM, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, Cua DJ (2007) TGF-beta and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain T(H)-17 cell mediated pathology. Nat Immunol 8:1390–1397
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B (2006) TGFbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17 producing T cells. Immunity 24:179–189
Lee Y, Awasthi A, Yosef N, Quintana FJ, Xiao S, Peters A, Wu C, Kleinewietfeld M, Kunder S, Hafler DA, Sobel RA, Regev A, Kuchroo VK (2012) Induction and molecular signature of pathogenic Th17 cells. Nat Immunol 13:991–999
Mezioug D, Touil-Boukoffa C (2012) Interleukin-17A correlates with interleukin-6 production in human cystic echinococcosis: a possible involvement of IL-17A in immunoprotection against Echinococcusgranulosus infection. Eur Cytokine Netw 23:112–119
Miyazaki Y, Hamano S, Wang S, Shimanoe Y, Iwakura Y, Yoshida H (2010) IL-17 is necessary for host protection against acute-phase Trypanosomacruzi infection. J Immunol 185:1150–1157
Passos ST, Silver JS, O’Hara AC, Shy D, Stumhofer JS, Hunter CA (2010) IL-6 promotes NK cell production of IL-17 during toxoplasmosis. J Immunol 184:1776–1783
Wen X, He L, Chi Y, Zhou S, Hoellwarth J, Zhang C, Zhu J, Wu C, Dhesi S, Wang X, Liu F, Su C (2011) Dynamics of Th17 cells and their role in Schistosoma japonicum infection in C57BL/6 mice. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5:e1399. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd0001399
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Oscar Bottasso and Professor José Luis Soto-Hernández for their critical revision of this manuscript, and the Programa de Doctorado en Ciencias Biomédicas of the UNAM. This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología Grant #86527. The English version of this manuscript was proofread by Juan Francisco Rodríguez.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standard
This study fulfilled all research regulations for human beings required by Mexican laws and international regulations. The Ethical Committee of the INNN approved this protocol. The patients were instructed about the aim of the study and signed informed consent letters.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cárdenas, G., Fragoso, G., Rosetti, M. et al. Neurocysticercosis: the effectiveness of the cysticidal treatment could be influenced by the host immunity. Med Microbiol Immunol 203, 373–381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0345-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0345-2