Abstract
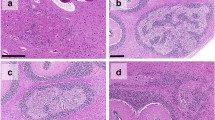
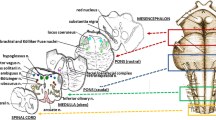
Recent anatomo-pathological studies have revealed a frequent associated hypoplasia of both arcuate nucleus and lungs in stillbirths. The purpose of this study is to analyze the lung and brainstem development in sudden unexplained perinatal death and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). A total of 51 cases were investigated. A complete autopsy was performed in each case. Anatomo-pathologic examination of the central autonomic nervous system included an in-depth study on histological serial sections of the brains where the main structures participating in control of the vital functions are located. The stage of lung development was evaluated by macroscopic and microscopic criteria. In 52.9% of cases, a pulmonary hypoplasia was detected. The pulmonary hypoplasia was significantly more frequent in the SIDS group compared to the sudden perinatal unexplained death groups (p < 0.05). In 72.5% of cases, histological examination of the brainstem on serial sections showed hypodevelopment of the brainstem nuclei, particularly hypoplasia, of the arcuate nucleus (60.8%). In 47.1% of cases, pulmonary hypoplasia was associated with brainstem hypodevelopment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lavezzi AM, Ottaviani G, Ballabio G et al (2004) Preliminary study on the cytoarchitecture of the human parabrachial/Kölliker-fuse complex, with reference to sudden infant death syndrome and sudden intrauterine unexplained death. Pediatr Dev Pathol 7:171–179
Lavezzi AM, Ottaviani G, Rossi L et al (2004) Hypoplasia of the parabrachial/Kölliker-Fuse complex in perinatal death. Biol Neonate 86:92–97
Lavezzi AM, Matturri L (2008) Functional neuroanatomy of the human pre-Bötzinger complex with particular reference to sudden unexplained perinatal and infant death. Neuropathology 28:10–16
Matturri L, Lavezzi AM, Minoli I et al (2003) Association between pulmonary hypoplasia and hypoplasia of arcuate nucleus in stillbirth. J Perinatol 23:328–332
Matturri L, Ottaviani G, Minoli I et al (2007) Neonatal pulmonary hypoplasia frequently associated with brainstem hypodevelopment. 8th World Congress of Perinatal Medicine. September 9–13th, Florence, Italy. J Perinat Med Suppl 35:209
Frøen JF, Arnestad M, Frey K et al (2001) Risk factors for sudden intrauterine unexplained death: epidemiologic characteristics of singleton cases in Oslo, Norway, 1986–1995. Am J Obstet Gynecol 184:694–702
Ottaviani G, Matturri L (2008) Histopathology of the Cardiac Conduction System in Sudden Intrauterine Unexplained Death (SIUD). Cardiovasc Pathol 17:146–155
Lavezzi AM, Ottaviani G, Mauri M et al (2006) Alterations of biological features of the cerebellum in sudden perinatal and infant death. Curr Mol Med 6:429–435
Lavezzi AM, Ottaviani G, Matturri L (2007) Ontogenesis of human cerebellar cortex and biopathological characterization in sudden unexplained fetal and infant death. Virchows Arch 450:31–40
Willinger M, James LS, Catz C (1991) Defining the sudden infant syndrome (SIDS): deliberations of an expert panel convened by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Pediatr Pathol 11:677–684
Matturri L, Ottaviani G, Alfonsi G et al (2004) Study of the brainstem, particularly the arcuate nucleus, in sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and sudden intrauterine unexplained death (SIUD). Am J Forensic Med Pathol 25:44–48
Matturri L, Ottaviani G, Lavezzi AM (2005) Techniques and criteria in pathologic and forensic-medical diagnostics in sudden unexpected infant and perinatal death. Am J Clin Pathol 124:259–268
Matturri L, Ottaviani G, Lavezzi AM (2008) Guidelines for neuropathologic diagnostics of perinatal unexpected loss and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) - A technical protocol. Virchows Arch 452:19–25
Emery JL, Mithal A (1960) The number of alveoli in the terminal respiratory unit of man during late intrauterine life and childhood. Arch Dis Child 35:544–547
Emery JL, Mithal A (1969) The weight of the lungs. In: Emery J (ed) The Anatomy of the Developing Lung. Heinemann Medical, London, pp 203–205
Weller U, Jorch G (1993) Current percentile curves for body weight, body length and head circumference of newborn infants after the 25th week of pregnancy. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 141:665–669
Boddy K, Dawes GS (1975) Fetal breathing. Br Med Bull 31:3–7
Harding R, Bocking AD, Sigger JN (1986) Influence of upper respiratory tract on liquid flow to and from fetal lungs. J Physiol 61:68–71
Barness EG (1997) Respiratory system. In: Barness EG (ed) Potter’s pathology of the fetus and infant. Mosby, St.Louis, MI, pp 712–773
Teitel DF (1996) Fetal chemoreception: a developing story. Reprod Fertil Dev 8:471–482
Blanco CE, Hanson MA, Kumar P (1995) Breathing and sleep states in the fetus and at birth. In: Loughlin GM, Carrol JL, Marcus CL (eds) Sleep and Breathing in Children. A Developmental Approach. Marcel Dekker. Inc. New York, pp, pp 161–179
Ottaviani G (2007) Crib death: sudden unexplained death of infants—the pathologist’s viewpoint. Springer, Heidelberg
Nakamura Y (1993) Pulmonary disorders in infants. Acta Pathol Jpn 43:347–359
Lan LM, Yamashita Y, Tang Y et al (2000) Normal fetal brain development: MR Imaging with a half-Fourier rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement sequence. Radiology 215:205–210
Inder TE, Huppi PS (2000) In vivo studies of brain development by magnetic resonance techniques. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 6:59–67
Kuwashima S, Nishimura G, Timura F et al (2001) Low-intensity fetal lungs on MRI may suggest the diagnosis of pulmonary hypoplasia. Pediatr Radiol 31:669–672
Duncan KR, Gowland PA, Moore RJ et al (1999) Assessment of fetal lung growth in utero with echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 210:197–200
Acknowledgements
Dr. Giulia Ottaviani, MD, PhD, is supported by PUR personal funding, University of Milano, project “Cardiovascular pathology of sudden infant and perinatal death with clinico-pathological correlations”.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that have no conflict of interest. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests statement
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. In particular, there are no competing interests related to this article. All authors have no conflict to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ottaviani, G., Mingrone, R., Lavezzi, A.M. et al. Infant and perinatal pulmonary hypoplasia frequently associated with brainstem hypodevelopment. Virchows Arch 454, 451–456 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-009-0754-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-009-0754-6