Abstract
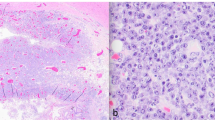
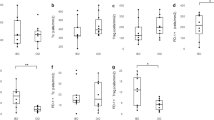
Abnormalities in humoral immunity are implicated in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. However, the detailed mechanisms of B-cell activation in the locale remain unaccounted for. We analyzed ulcerative colitis from the standpoint of lymphocytic expansion in the loco. Intestinal specimens obtained at surgery from 30 patients with ulcerative colitis treated with corticosteroids and 15 with Crohn’s disease were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry. Ulcerative colitis was characterized by a diffuse distribution of Ki-67+ small round cells particularly in the ulcer base (that were CD19+ and CD20–), with a significant number of them also CD138+. Immunoelectron microscopy for CD19 revealed an abundance of rough endoplasmic reticulum in the cytoplasm. These indicated that they are of immature plasma lineage cells. By contrast, plasma cells in Crohn’s disease were negative for CD19, and the labeling for Ki-67 was infrequent, showing mature phenotype. Flow cytometry revealed an occurrence of CD19+ and CD20– cells in ulcerative colitis but not in Crohn’s disease. The labeling index of Ki-67 among CD19+ plasma cells was positively correlated with the clinical activity of ulcerative colitis. High labeling of Ki-67 in CD19+ plasma cells is specific for active ulcerative colitis that was resistant to medical treatment by corticosteroids.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldassano RN, Schreiber S, Johnston RB Jr, Fu RD, Muraki T, MacDermott RP (1993) Crohn’s disease monocytes are primed for accentuated release of toxic oxygen metabolites. Gastroenterology 105:60–66
Berland R, Wortis HH (2002) Origins and functions of B-1 cells with notes on the role of CD5. Annu Rev Immunol 20:253–300
Bull DM, Bookman MA (1977) Isolation and functional characterization of human intestinal mucosal lymphoid cells. J Clin Invest 59: 966–974
Cario E (2005) Bacterial interactions with cells of the intestinal mucosa: toll-like receptors and NOD2. Gut 54:1182–1193
Das KM, Dubin R, Nagai T (1978) Isolation and characterization of colonic tissue-bound antibodies from patients with idiopathic ulcerative colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:4523–4532
Fell JME, Walker-Smith JA, Spencer J, Macdonald TT (1996) The distribution of dividing T cells throughout the intestinal wall in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol 104:280–285
Fiocchi C (1985) Lymphoid cells of the gastrointestinal tract. Isolation procedures. Acta Chir Scand Suppl 525: 11–23
Gerdes J, Li L, Schlueter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C, Gerlach C, Stahmer I, Kloth S, Brandt E, Flad HD (1991) Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Am J Pathol 138:867–873
Halstensen TS, Das KM, Brandtzaeg P (1993) Epithelial deposits of immunoglobulin G1 and activated complement colocalise with 40kD putative autoantigen in ulcerative colitis. Gut 34:650–657
Iatropoulos MJ, Williams GM (1996) Proliferation markers. Exp Toxicol Pathol 48:175–181
Kawachiya T, Oshitani N, Jinno Y, Watanabe K, Nakamura S, Fujiwara Y, Higuchi K, Maeda K, Nishiguchi Y, Hirakawa K, Matsumoto T, Arakawa T (2005) Significance of increased proliferation of immature plasma cells in the appendix of patients with ulcerative colitis. Int J Mol Med 15:417–423
Kullmann F, Fadale M, Gross V, Knuchel R, Bocker T, Steinbach P, Scholmerich J, Ruschoff J (1996) Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and Ki-67 in dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:371–379
Leonard JP, Schattner EJ, Coleman M (2001) Biology and management of mantle cell lymphoma. Curr Opin Oncol 13:342–347
MacLennan I, Vinuesa C (2002) Dendritic cells, BAFF, and APRIL: innate players in adaptive antibody responses. Immunity 17:235–238
Meinzer U, Hugot JP (2005) NOD2 and Crohn’s disease: many connected highways. Lancet 365:1752–1754
Monteleone I, Vavassori P, Biancone L, Monteleone G, Pallone F (2002) Immunoregulation in the gut: success and failures in human disease. Gut 50(Suppl 3):III60–64
Nagler-Anderson C (2001) Man the barrier! Strategic defenses in the intestinal mucosa. Nat Rev Immunol 1:59–67
Saiki Y, Ohtani H, Naito Y, Miyazawa M, Nagura H (1996) Immunophenotypic characterization of Epstein–Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma: massive infiltration by proliferating CD8+ T-lymphocytes. Lab Invest 75:67–76
Seo M, Okada M, Yao T, Ueki M, Arima S, Okumura M (1992) An index of disease activity in patients with ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 87:971–976
Tibble JA, Sigthorsson G, Foster R, Forgacs I, Bjarnason I (2002) Use of surrogate markers of inflammation and Rome criteria to distinguish organic from nonorganic intestinal disease. Gastroenterology 123:450–460
Truelove SC, Witts LJ (1959) Cortisone and corticotrophin in ulcerative colitis. Br Med J 14:387–394
Tsujikawa T, Satoh J, Uda K, Ihara T, Okamoto T, Araki Y, Sasaki M, Fujiyama Y, Bamba T (2000) Clinical importance of n-3 fatty acid-rich diet and nutritional education for the maintenance of remission in Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol 35:99–104
Wijdenes J, Dore JM, Clement C, Vermot-Desroches C (2002) CD138. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 16:152–155
Yacyshyn BR (1993) Activated CD19+ B cell lamina propria lymphocytes in ulcerative colitis. Immunol Cell Biol 71:265–274
Youngman KR, Simon PL, West GA, Cominelli F, Rachmilewitz D, Klein JS, Fiocchi C (1993) Localization of intestinal interleukin 1 activity and gene expression to lamina propria cells. Gastroenterology 104:749–758
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Atsuo Kitano, Dr. Yukio Nishiguchi, Yoshitaka Kinouchi, and Iwao Sasaki for helpful discussions. This work was supported in part by grants-in-aid for cancer research and a grant for intractable inflammatory bowel disease from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jinno, Y., Ohtani, H., Nakamura, S. et al. Infiltration of CD19+ plasma cells with frequent labeling of Ki-67 in corticosteroid-resistant active ulcerative colitis. Virchows Arch 448, 412–421 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0136-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0136-7