Abstract
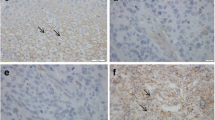
Occludin is a tight-junction-associated transmembrane protein, and previous observations suggested that occludin might play a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of organized tubular structures. Based on these observations, we explored the possible role of occludin immunostaining in the diagnosis of lung carcinomas. A total of 68 lung carcinomas and surrounding normal lung tissues were studied. A formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded section from each tumor was stained with a new anti-occludin monoclonal antibody raised in our laboratory. In normal lung tissues, the anti-occludin antibody strongly stained the apicoluminal borders of the bronchial/bronchiolar epithelia and bronchial glands as a dot or short line. The antibody also stained the intercellular borders of alveolar epithelia. In cancer cells that faced lumina of all adenocarcinomas, regardless of grade, including bronchioloalveolar carcinomas, occludin showed an expression pattern identical to that of the normal bronchial and alveolar epithelia. Occludin reactivity was not noted in any cases of squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma, or large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. The results of the present study suggest that occludin can serve as an immunohistochemical indicator of the “true” glandular differentiation that forms tubulo-papillary structures in human lung carcinoma tissues.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JM, Balda MS, Fanning AS (1993) The structure and regulation of tight junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:772–778
Arai T, Kino I (1994) Histochemical and ultrastructural analyses of glandular differentiation in typical carcinoid tumor of the hindgut. Pathol Int 44:49–56
Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, Gonzalez S, Cereijido M, Matter K (1996) Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol 134:1031–1049
Bartels H (1979) The air–blood barrier in the human lung. A freeze-fracture study. Cell Tissue Res 198:269–285
Busch C, Hanssen TA, Wagener C, OBrink B (2002) Down-regulation of CEACAM1 in human prostate cancer: correlation with loss of cell polarity, increased proliferation rate, and Gleason grade 3 to 4 transition. Hum Pathol 33:290–298
Citi S, Amorosi A, Franconi F, Giotti A, Zampi G (1991) Cingulin, a specific protein component of tight junctions, is expressed in normal and neoplastic human epithelial tissues. Am J Pathol 138:781–789
Cott GR, Sugahara K, Mason RJ (1986) Stimulation of net active ion transport across alveolar type II cell monolayers. Am J Physiol 250:222–227
Diamond JM (1977) The epithelial junction: bridge, gate, and fence. Physiologist 20:10–18
Eaton S, Simons K (1995) Apical, basal, and lateral cues for epithelial polarization. Cell 82:5–8
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
Gumbiner B, Louvard D (1985) Localized barriers in the plasma membrane: a common way to form domains. Trends Biochem Sci 10:435–438
Hirase T, Staddon JM, Saitou M, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Itoh M, Furuse M, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S, Rubin LL (1997) Occludin as a possible determinant of tight junction permeability in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 110:1603–1613
Hoover KB, Liao SY, Bryant PJ (1998) Loss of the tight junction MAGUK ZO-1 in breast cancer: relationship to glandular differentiation and loss of heterozygosity. Am J Pathol 153:1767–1773
Kimura Y, Shiozaki H, Hirao M, Maeno Y, Doki Y, Inoue M, Monden T, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Monden M (1997) Expression of occludin, tight-junction-associated protein, in human digestive tract. Am J Pathol 151:45–54
King RJ (1982) Pulmonary surfactant. J Appl Physiol 53:1–8
Morita K, Furuse M, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1999) Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:511–516
Nadel JA, Davis B, Phipps RJ (1979) Control of mucus secretion and ion transport in airways. Annu Rev Physiol 41:369–381
Polak-Charcon S, Shoham J, Ben-Shaul Y (1980) Tight junctions in epithelial cells of human fetal hindgut, normal colon, and colon adenocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 65:53–62
Saitou M, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Itoh M, Furuse M, Inazawa J, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1997) Mammalian occludin in epithelial cells: its expression and subcellular distribution. Eur J Cell Biol 73:222–231
Schneeberger EE, Karnovsky MJ (1976) Substructure of intercellular junctions in freeze-fractured alveolar-capillary membranes of mouse lung. Circ Res 38:404–411
Schneeberger EE, McCormack JM (1984) Intercellular junctions in upper airway submucosal glands of the rat: a tracer and freeze fracture study. Anat Rec 210:421–433
Simons K, Fuller SD (1985) Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Ann Rev Cell Biol 1:289–315
Soler AP, Miller RD, Laughlin KV, Carp NZ, Klurfeld DM, Mullin JM (1999) Increased tight junctional permeability is associated with the development of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 20:1425–1431
Tobioka H, Isomura H, Kokai Y, Sawada N (2002) Polarized distribution of carcinoembryonic antigen is associated with a tight junction molecule in human colorectal adenocarcinoma. J Pathol 198:207–212
Tobioka H, Isomura H, Kokai Y, Tokunaga Y, Yamaguchi J, Sawada N (2004) Occludin expression decreases with the progression of human endometrial carcinoma. Hum Pathol 35:159–164
Tokunaga Y, Tobioka H, Isomura H, Kokai Y, Sawada N (2004) Expression of occludin in human rectal carcinoid tumours as a possible marker of glandular differentiation. Histopathology 44:247–250
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants-in-aids from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan, and from the Smoking Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tobioka, H., Tokunaga, Y., Isomura, H. et al. Expression of occludin, a tight-junction-associated protein, in human lung carcinomas. Virchows Arch 445, 472–476 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-1054-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-1054-9