Abstract
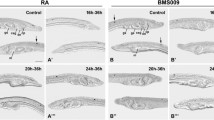
In vertebrate embryos, ectopic application of all-trans retinoic acid (RA) alters the expression of Otx genes in the developing midbrain. In conjunction with RA-induced misexpression of other regulatory genes this leads to a loss of anterior CNS. In the ascidian Herdmania curvata, RA primarily inhibits the development of the juvenile pharynx. An ascidian Otx gene, Hec-Otx, is expressed largely in this tissue, associated stomodeal structures and the anterior endostyle of the juvenile. Treatment with 10–6 M RA reduces Hec-Otx mRNA levels in the juvenile to about 12% of normal and is correlated closely with the loss of pharyngeal structures. During embryogenesis the expression of Hec-Otx becomes restricted to cell lineages fated to give rise to the anterior-most nervous system and the stomodeal component of the primordial pharynx. In hatched larvae Hec-Otx transcripts are detected only in the sensory (brain) vesicle. RA reduces Hec-Otx expression in the tailbud stomodeal pharynx primordium/anterior nervous system cell line but not in the larval sensory vesicle, suggesting that RA regulation of Hec-Otx expression is restricted to pharyngeal tissues throughout embryonic and postlarval development. RA does not affect expression of Hec-Pax2/5/8, which is normally expressed within the developing nervous system immediately posterior to Hec-Otx at the tailbud stage, lending support to the proposition that RA does not impact CNS axial patterning. These data combined with those from other chordates suggest that RA regulation of Otx expression in the anterior nerve cord and pharynx is a primitive chordate feature which has been maintained predominantly in pharyngeal tissues in the ascidian.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 August 1999 / Accepted: 22 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinman, V., Degnan, B. Retinoic acid perturbs Otx gene expression in the ascidian pharynx. Dev Gene Evol 210, 129–139 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270050019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270050019