Abstract
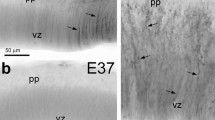
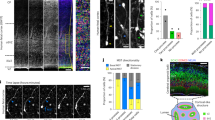
We have investigated the pattern of glia associated with central complex lineages in the embryonic brain of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Using the glia-specific marker Repo, we identified glia associated externally with such lineages, termed lineage-extrinsic glia, and glia located internally within the lineages, termed lineage-intrinsic glia. Populations of both glial types increase up to 60 % of embryogenesis, and thereafter decrease. Extrinsic glia change their locations over time, while intrinsic ones are consistently found in the more apical part of a lineage. Apoptosis is not observed for either glial type, suggesting migration is a likely mechanism accounting for changes in glial number. Proliferative glia are present both within and without individual lineages and two glial clusters associated with the lineages, one apically and the other basally, may represent sources of glia.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams JM, White K, Fessler LI, Steller H (1993) Programmed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development 117:29–43
Adams RR, Maiato H, Earnshaw WC, Carmena M (2001) Essential Roles of Drosophila Inner Centromere Protein (INCENP) and Aurora B in histone H3 phosphorylation, metaphase chromosome alignment, kinetochore disjunction, and chromosome segregation. J Cell Bio 153(4):865–879
Akiyama Y, Hosoya T, Poole AM, Hotta Y (1996) The gcm-motif: a novel DNA-binding motif conserved in Drosophila and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14912–14916
Awasaki T, Lai S-L, Ito K, Lee T (2008) Organization and postembryonic development of glial cells in the adult central brain of Drosophila. J Neurosci 28:13742–13753
Bentley D, Keshishian H, Shankland M, Torian-Raymond A (1979) Quantitative staging of embryonic development of the grasshopper, Schistocerca nitens. J Embryol Exp Morphol 54:47–74
Boyan G, Williams L (2011) Embryonic development of the insect central complex: insights from lineages in the grasshopper and Drosophila. Arthr Struct Dev 40(4):334–348
Boyan GS, Reichert H (2011) Mechanisms for complexity in the brain: generating the insect central complex. Trends Neurosci 34(5):247–257
Boyan G, Williams L, Meier T (1993) Organization of the commissural fibers in the adult brain of the locust. J Comp Neurol 332:358–377
Boyan GS, Therianos S, Williams JLD, Reichert H (1995) Axogenesis in the embryonic brain of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria: an identified cell analysis of early brain development. Development 121:75–86
Boyan G, Richert H, Hirth F (2003) Commissure formation in the embryonic insect brain. Arthr Struct Dev 32:61–77
Boyan G, Herbert Z, Williams L (2010a) Cell death shapes embryonic lineages of the central complex in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. J Morphol 271:949–959
Boyan GS, Williams L, Legl A, Herbert Z (2010b) Proliferative cell types in embryonic lineages of the central complex of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Cell Tissue Res 341:259–277
Boyan G, Loser M, Williams L, Liu Y (2011) Astrocyte-like glia associated with the embryonic development of the central complex in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Dev Genes Evol 221:141–155
Boyan G, Liu Y, Loser M (2012) A cellular network of dye-coupled glia associated with the embryonic central complex in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Dev Genes Evol 222:125–138
Bravo R, Celis JE (1980) A search for differential polypeptide synthesis throughout the cell cycle of Hela cells. J Cell Biol 84:795–802
Bravo R, Macdonald-Bravo H (1987) Existence of two populations of Cyclin/Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol 105:1549–1554
Cayre M, Strambi C, Charpin P, Augier R, Meyer MR, Edwards JS, Strambi A (1996) Neurogenesis in adult insect mushroom bodies. J Comp Neurol 371:300–310
Celis JE, Celis A (1985) Cell cycle-dependent variatioins in the distribution of the nuclear protein cyclin proliferating cell nuclear antigen in cultured cells: subdivision of S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3262–3266
Celis JE, Madsen P, Celis A, Nielsen HV, Gesser B (1987) Cyclin (PCNA, auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase delta) is a central component of the pathway(s) leading to DNA replication and cell division. FEBS Lett 220(1):1–7
Doe CQ, Goodman CS (1985a) Early events in insect neurogenesis: I. Development and segmental differences in the pattern of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol 111:193–205
Doe CQ, Goodman CS (1985b) Early events in insect neurogenesis: II. The role of cell interactions and cell lineage in the determination of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol 111:206–219
Edwards TN, Meinertzhagen IA (2010) The functional organisation of glia in the adult brain of Drosophila and other insects. Prog Neurobiol 90:471–497
Egger B, Leemans R, Loop T, Kammermeier L, Fan Y, Radimerski T, Strahm MC, Certa U, Reichert H (2002) Gliogenesis in Drosophila: genome-wide analysis of downstream genes of glial cells missing in the embryonic nervous system. Development 129:3295–3309
el Jundi B, Heinze S, Lenschow C, Kurylas A, Rohlfing T, Homberg U (2010) The locust standard brain: a 3D standard of the central complex as a platform for neural network analysis. Front Syst Neurosci 3:21
Fairman MP (1990) DNA polymerase delta/PCNA: actions and interactions. J Cell Sci 95:1–4
Gocht D, Wagner S, Heinrich R (2009) Recognition, presence, and survival of locust central nervous glia in situ and in vitro. Microsc Res Tech 72(5):385–397
Haase A, Stern M, Wachtler K, Bicker G (2001) A tissue-specific marker of Ecdysozoa. Dev Genes Evol 211:428–433
Hähnlein I, Bicker G (1997) Glial patterning during postemebryonic development of central neuropiles in the brain of the honeybee. Dev Genes Evol 207:29–41
Hall PA, Levison DA, Woods AL, Yu CC-W, Kellock DB, Watkins JA, Barnes DM, Gillett CE, Camplejohn R, Dover R, Waseem NH, Lane DP (1990) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolocalization in paraffin sections: an index of cell proliferation with evidence of deregulated expression in some neoplasms. J Pathol 162:285–294
Halter DA, Urban J, Rickert C, Ner SS, Ito K, Travers AA, Technau GM (1995) The homeobox gene repo is required for the differentiation and maintenance of glial function in the embryonic nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. Development 121:317–322
Hartenstein V (2011) Morphological diversity and development of glia in Drosophila. Glia 59:1237–1252
Hartenstein V, Nassif C, Lekven A (1998) Embryonic development of the Drosophila brain: II. Pattern of glia cells. J Comp Neurol 402:32–47
Heinze S, Homberg U (2007) Maplike representation of celestial e-vector orientations in the brain of an insect. Science 315:995–997
Hendzel MJ, Wei Y, Mancini MA, Hooser AV, Ranalli T, Brinkley BR, Bazett-Jones DP, Allis CD (1997) Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of histone H3 initiates primarily within pericentromeric heterochromatin during G2 and spreads in an ordered fashion coincident with mitotic chromosome condensation. Chromosoma 106:348–360
Ito K, Awasaki T (2008) Clonal unit architecture of the adult fly brain. In: Technau GM (ed) Brain development in Drosophila melanogaster. Springer, New York, pp 137–158
Izergina N, Balmer J, Bello B, Reichert H (2009) Postembryonic development of transit amplifying neuroblast lineages in the Drosophila brain. Neural Dev 4:44
Jan LY, Jan YN (1982) Antibodies to horseradish peroxidase as specific neuronal markers in Drosophila and in grasshopper embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:2700–2704
Jiang C, Baehrecke EH, Thummel CS (1987) Steroid regulated programmed cell death during Drosophila metamorphosis. Development 124:4673–4683
Liu G, Seiler H, Wen A, Zars T, Ito K, Wolf M, Heisenberg M, Liu L (2006) Distinct memory traces for two visual features in the Drosophila brain. Nature 439:551–556
Naimski P, Bierzyimageski A, Fikus M (1980) Quantitative fluorescent analysis of different conformational forms of DNA bound to the dye 4′,6-diamidine-2-phenylindole, and separated by gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 106:471–475
Neuser K, Triphan T, Mronz M, Poeck B, Strauss R (2008) Analysis of a spatial orientation memory in Drosophila. Nature 453:1244–1247
Ng L, Prelich G, Anderson CW, Stillman B, Fisher PA (1990) Drosophila proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem 266(20):11948–11954
Nordlander RH, Edwards JS (1969) Postembryonic brain development in the monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus plexippus, L.: I. Cellular events during brain morphogenesis. Wilh Roux´Archiv 162:197–217
Oland LA, Tolbert LP (1989) Patterns of glial proliferation during formation of olfactory glomeruli in an insect. Glia 2(1):10–24
Paschinger K, Rendic D, Wilson IBH (2009) Revealing the anti-HRP epitope in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis. Glycoconj J 26:385–395
Pereanu W, Shy D, Hartenstein V (2005) Morphogenesis and proliferation of the larval brain glia in Drosophila. Dev Biol 283:191–203
Seaver EC, Carpenter EM, Bastiani MJ (1993) Glial cells in the development of the nervous system: developmental expression and molecular characterization of REGA-1 in grasshoppers. Neurosci Abstr 19:266
Shreeram S, Blow JJ (2003) The role of the replication licensing system in cell proliferation and cancer. Prog Cell cycle Res 5:287–293
Spreij THE (1971) Cell death during the development of the imaginal disks of Calliphora erythrocephala. Netherland J Zool 21(3):221–264
Stacey SM, Muraro NI, Peco E, Labbe A, Thomas GB, Baines RA, van Meyel DJ (2010) Drosophila glial glutamate transporter Eaat1 is regulated by fringe-mediated Notch signaling and is essential for larval locomotion. J Neuro 30(43):14446–14457
Stork T, Bernardos R, Freeman MR (2012) Analysis of glial cell development and function in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. doi:10.1101/pdb.top067587
Strausfeld NJ (2009) Brain organization and the origin of insects: an assessment. Proc Biol Sci 276(1664):1929–1937
Strauss R (2002) The central complex and the genetic dissection of locomotor behaviour. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:633–638
Sumara I, Vorlaufer E, Gieffers C, Peters BH, Peters J-M (2000) Characterization of vertebrate cohesin complexes and their regulation in prophase. J Cell Biol 151(4):749–761
Takizawa T, Meshorer E (2008) Chromatin and nuclear architecture in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci 31(7):343–352
Vanhems E (1985) An in vitro autoradiographic study of gliogenesis in the embryonic locust brain. Dev Brain Res 23:269–275
Viktorin G, Riebli N, Popkova A, Giangrande A, Reichert H (2011) Multipotent neural stem cells generate glial cells of the central complex through transit amplifying intermediate progenitors in Drosophila brain development. Dev Biol 356:553–565
Williams JLD, Guentner M, Boyan GS (2005) Building the central complex of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria: temporal topology organizes the neuroarchitecture of the w, x, y, z tracts. Arthr Struct Dev 34:97–110
Xiong W, Okano H, Patel N, Blendy J, Montell C (1994) Repo endodes a glial-specific homeo domain protein required in the Drosophila nervous system. Genes Dev 8:981–994
Yamaguchi M, Date T, Matsukage A (1991) Distribution of PCNA in Drosophila embryo during nuclear division cycles. J Cell Sci 100:729–733
Yamaguchi M, Nishimoto Y, Hirose F, Matsukage A (1995) Distribution of PCNA during postblastoderm cell division cycles in the Drosophila melanogaster embryo: effect of a string- mutation. Cell Struc Funct 20:47–57
Zacharias D, Williams JLD, Meier T, Reichert H (1993) Neurogenesis in the insect brain: cellular identification and molecular characterization of brain neuro- blasts in the grasshopper embryo. Development 118:941–955
Zudaire E, Simpson SJ, Illa I, Montuenga LM (2004) Dietary influences over proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in the locust midgut. J Exp Biol 207:2255–2265
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. G. Technau (Repo) and M. Wullimann (PCNA) for their gifts of antibodies, Michael Loser for critical comments, and Karin Fischer for excellent technical assistance. Grant sponsor: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (BO 1434/3-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Siegfried Roth
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Boyan, G. Glia associated with central complex lineages in the embryonic brain of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria . Dev Genes Evol 223, 213–223 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-013-0439-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-013-0439-7